Ancient. Raw. Primitive. Within the realms of dietary choices, these words may not seem enticing at first glance. However, dig a little deeper, and you may discover a captivating realm of scientific appeal when it comes to the Paleolithic nutrition. This era-based eating pattern, commonly referred to as the Caveman Diet, taps into our ancestral roots, delving into the depths of our prehistoric past to unravel the mysteries behind what our bodies truly crave.
In a modern world driven by convenience and processed fare, the attraction of the Paleo Diet lies in its primal simplicity. Stripped of complex additives and artificial embellishments, this dietary approach hones in on wholesome, unprocessed ingredients that echo the tastes and sensations familiar to our early human predecessors. By emulating their diet, enthusiasts believe they can unlock a wealth of health benefits and optimize their overall well-being.
By acknowledging the hunter-gatherer lifestyle of our Paleolithic ancestors, the Paleo Diet emphasizes consumption of lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds – a combination that is rich in natural enzymes, vitamins, and minerals. Proponents of this lifestyle argue that our bodies evolved to thrive on such nourishment, endorsing the idea that returning to these primal eating habits may alleviate modern afflictions such as inflammation, allergies, and even chronic diseases.
- Reviving the Caveman Diet: The Scientific Appeal of the Paleo Diet
- Understanding the Basics
- Exploring the Origins of the Paleolithic Diet
- Key Principles and Concepts of the Paleo Diet
- Examining the Evolutionary Argument
- The Health Benefits
- Weight Loss and Improved Metabolism
- Lower Risk of Chronic Diseases
- Questions and answers
Reviving the Caveman Diet: The Scientific Appeal of the Paleo Diet
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in an age-old way of eating, known as the Paleo diet. This dietary approach takes inspiration from the eating habits of our ancient ancestors, who lived during the Paleolithic era. The scientific appeal of the Paleo diet lies in its alignment with the natural human physiology and its potential to improve overall health and well-being.
One of the main principles of the Paleo diet is the exclusion of processed foods and the focus on consuming whole, nutrient-dense foods. This approach is supported by scientific evidence that suggests our bodies are more adapted to handle the types of foods available to our ancestors, such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. By following the Paleo diet, individuals can harness the nutritional benefits of these natural foods and avoid the negative health effects associated with modern processed foods.
Another aspect of the Paleo diet that appeals to scientific reasoning is its emphasis on consuming foods with a low glycemic load. This means that the diet primarily consists of foods that do not cause a sharp increase in blood sugar levels. Scientific studies have shown that excessive consumption of high glycemic foods can lead to insulin resistance, weight gain, and various chronic diseases. By avoiding these foods and opting for low glycemic alternatives, individuals following the Paleo diet can better manage their blood sugar levels and potentially reduce the risk of developing such conditions.
The Paleo diet also places importance on the quality of fats consumed, opting for sources such as avocados, olive oil, and nuts, which are rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats. These fats have been scientifically proven to have numerous health benefits, including reducing inflammation, improving heart health, and supporting brain function. By incorporating these healthy fats into their diet, individuals can reap the rewards of these scientifically supported benefits.
| The Scientific Appeal of the Paleo Diet: |
|---|
| Alignment with natural human physiology |
| Exclusion of processed foods and focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods |
| Emphasis on low glycemic load foods for blood sugar management |
| Inclusion of healthy fats with proven health benefits |
Understanding the Basics
In this section, we will delve into the fundamental principles underlying the Paleo Diet, shedding light on its essence and core concepts. By grasping the underlying principles, we can gain a deeper understanding of the rationale behind this dietary approach.
First and foremost, the Paleo Diet advocates for a return to our ancestral eating patterns, mirroring the dietary habits of our Paleolithic ancestors. The fundamental idea is to align our modern eating habits with the nutritional needs of our evolutionary predecessors. By doing so, proponents argue that we can optimize our health and well-being.
Central to the Paleo Diet is the idea that our bodies are genetically adapted to thrive on the foods available during the Paleolithic era. This means consuming whole, unprocessed foods, primarily consisting of lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. The emphasis is on nutrient-dense foods that are high in natural fats, proteins, and essential vitamins and minerals.
Exploring the Origins of the Paleolithic Diet
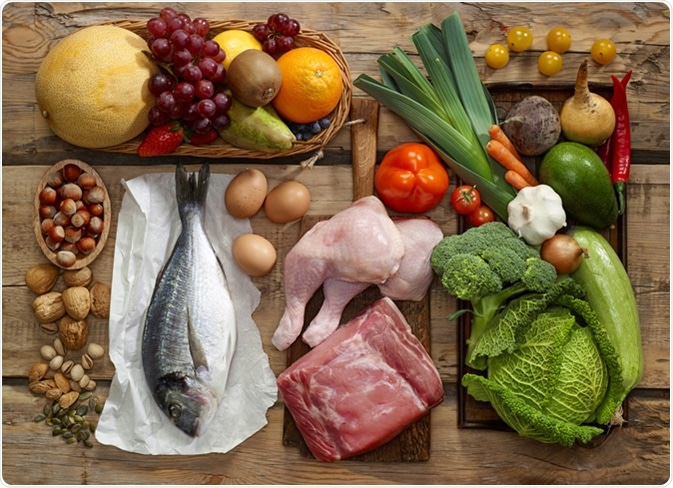

Delving into the foundation of the Paleolithic eating pattern allows us to gain a deeper understanding of its origins and the reasoning behind its widespread popularity. By retracing the roots of this dietary approach, we can explore its historical context and the principles that guide its followers today.
Embedded within the Paleolithic diet is a reverence for the eating habits of our ancient ancestors. This dietary philosophy draws inspiration from the prehistoric era, when human beings relied on their natural surroundings for sustenance. By emulating the eating patterns and food sources of our early predecessors, some believe that we can optimize our health and well-being.
Central to the Paleolithic diet is the emphasis on consuming whole, unprocessed foods. This echoes the natural state in which food was consumed during the Paleolithic era, before the advent of modern agricultural practices. By focusing on nutrient-dense vegetables, fruits, nuts, seeds, and lean meats, this diet aims to restore our connection with nature and the foods it offers.
Furthermore, the ancestral wisdom ingrained in the Paleolithic diet encourages the avoidance of refined sugars, processed grains, and overly processed foods. Instead, the diet advocates for a return to simpler, more natural alternatives that are less likely to cause inflammation and other negative health effects.
While the Paleolithic diet has gained popularity in recent years, it is important to acknowledge that its scientific basis remains a subject of ongoing discussion. Critics argue that our understanding of ancient human diets is far from comprehensive, and that modern interpretations of the Paleolithic era may not accurately reflect the true eating habits of our ancestors. Nonetheless, proponents of the Paleolithic diet find inspiration in the simplicity and harmony they believe it brings to their lives.
Key Principles and Concepts of the Paleo Diet

Exploring the underlying principles and concepts of the popular Paleo diet unveils a fascinating approach rooted in the ancestral past. This dietary philosophy draws on the evolutionary patterns of our hunter-gatherer ancestors, bringing forward a collection of principles and concepts that resonate with our modern understanding of human health and nutrition.
One of the fundamental principles of the Paleo diet is the focus on whole, unprocessed foods. Emphasizing the consumption of natural and nutrient-dense sources of sustenance, this approach encourages individuals to choose fresh fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Additionally, the diet advocates for the avoidance of refined sugars, processed grains, dairy products, and industrial oils.
Another key principle of the Paleo diet is the exclusion of modern agricultural products like grains and legumes. By eliminating these food groups, the diet aims to reduce potential sources of inflammation and anti-nutrients, which some argue can have adverse effects on the human body. Instead, the Paleo diet recommends relying on alternative sources of carbohydrates such as sweet potatoes and root vegetables.
Furthermore, the Paleo diet promotes an increased intake of quality animal protein. Proponents of this dietary philosophy argue that consuming grass-fed meat, wild-caught fish, and pastured poultry not only provides essential amino acids but also valuable nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin B12. This emphasis on animal protein aligns with the idea of our evolutionary past, where acquiring adequate protein from animal sources was crucial for survival.
Lastly, a principle woven into the Paleo diet is the inclusion of regular physical activity. Recognizing the physically demanding lifestyle of our hunter-gatherer ancestors, this approach emphasizes the importance of incorporating exercise into daily routines. Whether it be through walking, running, strength training, or other forms of movement, the Paleo diet aims to promote an active lifestyle for overall health and wellbeing.
In summary, the key principles and concepts of the Paleo diet revolve around the consumption of whole, unprocessed foods, the exclusion of modern agricultural products, an increased intake of quality animal protein, and the inclusion of regular physical activity. By adopting these principles, individuals may seek to align their modern lifestyles with a more ancestral approach to nutrition, potentially reaping the benefits attributed to this dietary philosophy.
Examining the Evolutionary Argument

The Evolutionary Argument is an essential aspect worth considering when evaluating the principles underlying the modern Paleo diet. This argument focuses on the belief that the human body has evolved over millions of years to consume certain types of foods and thrive under specific dietary conditions. By examining this argument, we can gain valuable insights into the rationale behind the Paleo diet.
One key aspect of the Evolutionary Argument is the notion that early humans were hunter-gatherers, relying on natural resources for sustenance. They consumed diets that consisted primarily of animal protein, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, as these were the foods readily available to them in their environment. Advocates of the Paleo diet argue that our genetic makeup has not significantly changed since those early times, making us better suited to consume similar foods.
Proponents of the Paleo diet suggest that the introduction of modern processed foods, such as refined grains, dairy products, and sugars, is relatively recent in the evolutionary history of Homo sapiens. According to this argument, since our bodies have not had sufficient time to adapt to these new dietary components, consuming them may lead to adverse health effects. Therefore, adhering to a diet that resembles that of our ancestors is believed to promote overall well-being and improve various aspects of health.
While the Evolutionary Argument provides a compelling perspective, it is important to note that scientific evidence supporting the Paleo diet’s claims is still limited. Critics argue that the human diet has significantly evolved since the Paleolithic era, and our bodies have adapted to a wider range of foods. They propose that a more balanced, evidence-based approach, which includes a variety of foods and focuses on individual needs, might be more beneficial for overall health and well-being.
- The Evolutionary Argument emphasizes the idea that humans have evolved to consume certain types of foods.
- Early humans relied on animal protein, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds as their primary sources of nutrition.
- Advocates suggest that our genetic makeup has not significantly changed, making us better adapted to a Paleo-like diet.
- Processed foods introduced in modern times may have negative health effects due to the lack of adaptation.
- Scientific evidence supporting the Paleo diet’s claims is limited, and alternative approaches may be more beneficial.
The Health Benefits

When it comes to the Paleolithic diet, it’s not just about an ancient way of eating but also about the potential health benefits it offers. With a focus on natural, unprocessed foods, this dietary approach emphasizes the consumption of fresh fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and nuts. By adopting this ancestral eating pattern, individuals may experience a range of health advantages.
Improved Weight Management: The Paleo diet’s emphasis on nutrient-dense foods and the avoidance of processed and sugar-laden products can contribute to better weight management. By reducing the intake of empty calories and high glycemic index foods, it may help individuals maintain a healthy body weight or even promote weight loss.
Enhanced Nutrient Intake: One of the key tenets of the Paleolithic diet is consuming a variety of whole foods that are rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. This can result in a higher intake of essential nutrients which are vital for optimal health and wellbeing.
Reduced Inflammation: Chronic inflammation has been linked to numerous health conditions, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. The Paleo diet places a strong emphasis on anti-inflammatory foods such as fatty fish, olive oil, and a wide range of fruits and vegetables, which may help reduce inflammation in the body.
Better Blood Sugar Control: By limiting the consumption of refined carbohydrates and sugar-rich foods, the Paleo diet may assist in stabilizing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. This dietary approach promotes whole, unprocessed foods that have a lower glycemic load, allowing for better blood sugar control.
Increased Energy Levels: By providing the body with a steady supply of nutrient-dense foods, the Paleo diet can help improve energy levels and overall vitality. Unlike heavily processed and sugary foods that can cause energy crashes, this dietary approach focuses on foods that provide a sustained release of energy, supporting optimal physical and mental performance.
Support for Gut Health: The Paleo diet encourages the consumption of high-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, and nuts, which can promote a healthy gut microbiome. A thriving gut microbiome is vital for good digestion, nutrient absorption, and immune system function.
While individual results may vary, adopting a Paleo lifestyle and incorporating its principles into your diet may offer a wide range of potential health benefits. From weight management to improved energy levels, this ancestral way of eating has garnered attention for its positive impact on overall health and wellbeing.
Weight Loss and Improved Metabolism
Exploring the relationship between the Paleo lifestyle and its potential effects on weight loss and metabolism reveals fascinating insights into this popular dietary approach. By adopting a dietary pattern inspired by our ancestors, individuals may experience positive changes in body weight and metabolic functioning.
Lower Risk of Chronic Diseases
The Paleo diet has been touted as a way to reduce the likelihood of developing chronic diseases. By embracing a way of eating that mimics the diet of our ancestors, proponents of the Paleo diet believe that individuals can lower their risk of various health conditions.
One of the key factors in the Paleo diet that is thought to contribute to a lower risk of chronic diseases is its focus on whole, unprocessed foods. Unlike modern diets that are filled with refined grains, sugars, and processed oils, the Paleo diet emphasizes the consumption of lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
Eliminating processed foods that are often high in harmful additives, preservatives, and artificial ingredients helps to reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes. By choosing natural, nutrient-dense foods, individuals following the Paleo diet are providing their bodies with the necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants to promote overall health and well-being.
- Increased consumption of lean proteins, such as grass-fed meats and wild-caught fish, provides essential amino acids for muscle growth and repair, while reducing the intake of saturated fats commonly found in processed meats.
- Abundant intake of fruits and vegetables offers a rich source of dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals, which can aid in digestion and support a healthy immune system.
- The inclusion of healthy fats from sources such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil can help reduce inflammation in the body and support brain health.
Furthermore, the Paleo diet encourages individuals to avoid or limit refined sugars, which can contribute to weight gain, insulin resistance, and ultimately, an increased risk of chronic diseases. By replacing sugary snacks and beverages with natural alternatives, such as fresh fruits and water, followers of the Paleo diet can help regulate blood sugar levels and maintain a healthier weight.
In conclusion, the emphasis on whole, unprocessed foods and the elimination of refined grains, sugars, and processed oils found in the Paleo diet can potentially lead to a lower risk of chronic diseases. By making conscious efforts to consume nutrient-dense foods and avoid harmful additives, individuals may enhance their overall health and well-being.
Questions and answers
What is the Caveman Diet?
The Caveman Diet, also known as the Paleo Diet, is a dietary plan that replicates the eating habits of our ancestors in the Paleolithic era. It primarily includes whole foods such as lean meats, fish, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, while avoiding processed foods, grains, dairy, and refined sugars.
What is the scientific appeal of the Paleo Diet?
The scientific appeal of the Paleo Diet lies in the belief that it is more in line with the evolutionary adaptations of our bodies. Proponents argue that our genes have not changed significantly since the Paleolithic era, so a return to the diet of our ancestors may lead to better health outcomes.
Does the Paleo Diet have any health benefits?
The Paleo Diet has been associated with several health benefits. Studies suggest that it may improve blood sugar control, aid in weight loss, and reduce the risk of heart disease and certain chronic conditions. However, more research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects and potential drawbacks of this diet.
Is the Paleo Diet suitable for everyone?
The Paleo Diet may not be suitable for everyone. It restricts several food groups, which can make it challenging for individuals with specific dietary needs or medical conditions. Additionally, it requires careful planning to ensure adequate nutrient intake. Consulting a healthcare professional or registered dietitian is recommended before starting any new diet.
Does the scientific evidence support the claims of the Paleo Diet?
The scientific evidence supporting the claims of the Paleo Diet is mixed. While some studies show positive effects on certain health markers, others have found conflicting results. It is important to consider the overall body of scientific literature and not rely solely on individual studies to make informed dietary choices.
What is the Caveman Diet?
The Caveman Diet, also known as the Paleo Diet, is a dietary plan that aims to mimic the eating habits of our ancestors from the Paleolithic period. It involves consuming foods that were available to humans during that time, such as lean meats, fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, while excluding processed foods, grains, legumes, and dairy products.
What is the scientific appeal of the Paleo Diet?
The scientific appeal of the Paleo Diet stems from the belief that our bodies have not evolved enough to handle the modern processed foods that have been introduced in recent centuries. Proponents of the diet argue that by eating the same foods our ancestors did, we can optimize our health by avoiding the potentially harmful effects of certain modern food groups.
Is there any scientific evidence to support the claims of the Paleo Diet?
While some studies have shown potential benefits of the Paleo Diet, such as weight loss and improved metabolic markers, the overall scientific evidence is limited and inconclusive. Most of the research conducted so far has been small-scale and short-term, making it difficult to draw definitive conclusions about the long-term effects of following this diet.
Are there any potential drawbacks or risks associated with the Paleo Diet?
One potential drawback of the Paleo Diet is its restrictiveness, as it excludes entire food groups such as grains and legumes. This can make it challenging to meet certain nutrient needs, particularly for those following a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle. Additionally, the elimination of dairy products may result in inadequate calcium intake, leading to an increased risk of osteoporosis.
What are some alternatives to the Paleo Diet?
If you are interested in adopting a healthier eating plan but not convinced by the Paleo Diet, there are many other options to consider. These include the Mediterranean Diet, which emphasizes whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats; the DASH Diet, which focuses on reducing high blood pressure through a balanced eating plan; and the flexitarian diet, which allows for the occasional inclusion of animal products while primarily emphasizing plant-based foods.

I’m Jake Morgan, a 23-year-old Keto diet and fitness expert from sunny California. Passionate about helping you achieve your dream body with the right nutrition and workout. Connect or consult via Telegram.