In our fast-paced and stress-filled lives, finding ways to manage and reduce stress is crucial for overall well-being. While there are various methods to tackle stress, one often overlooked aspect is the impact of our diet on cortisol levels. Cortisol, often called the stress hormone, plays a significant role in our body’s response to stress. Understanding how our food choices can affect cortisol levels is vital in finding balance and reducing the negative effects of stress.
When it comes to cortisol, certain dietary factors can either promote its production or help regulate its levels. Paying attention to the types of foods we eat, the nutrients they contain, and how they interact with our body can make a noticeable difference in managing stress. The foods we consume can either exacerbate stress levels or offer relief by helping to maintain a healthy balance of cortisol in our system. This delicate equilibrium can be achieved through mindful dietary choices and an understanding of the relationship between food and cortisol.
By incorporating a diet rich in stress-reducing nutrients, you can support your body’s natural ability to regulate cortisol levels. Key nutrients such as magnesium, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins B and C have been shown to have a calming effect on the body and aid in cortisol regulation. Including foods like leafy greens, fatty fish, nuts, and citrus fruits in your daily meals can help promote a sense of calmness, reduce inflammation, and support your body’s response to stress.
- The Impact of Diet on Cortisol Levels: Exclusive Insights
- Understanding Cortisol: The Stress Hormone
- The Role of Cortisol in the Body
- The Link Between Cortisol and Stress
- Dietary Factors That Influence Cortisol Levels
- The Power of a Balanced Diet
- The Effects of Sugar Consumption on Cortisol
- The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Lowering Cortisol
- Optimal Food Choices for Reducing Cortisol
- The Importance of Whole Grains and Complex Carbohydrates
- Questions and answers
The Impact of Diet on Cortisol Levels: Exclusive Insights
In this exclusive exploration, we delve into the profound influence that dietary choices have on the levels of cortisol, the body’s stress hormone. By examining the intricate connection between what we consume and our cortisol production, we uncover fascinating insights that shed light on the importance of mindful eating for stress management.
1. Dietary Patterns:
- Optimal Eating Habits
- Food Selection Factors
- Role of Nutrients
2. Stress-Reducing Foods:
- Natural Stress-Fighting Ingredients
- Aromatherapy through Diet
- The Power of Herbal Teas
3. Gut-Brain Axis:
- Microbiota’s Influence on Cortisol
- Probiotics and Stress Regulation
- High-Fiber Foods and Hormonal Balance
4. Hormonally Beneficial Diets:
- Mediterranean Diet and Cortisol
- Effects of Low-carb and High-carb Diets
- The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
5. Food Sensitivities and Cortisol:
- Identifying Trigger Foods
- Allergies, Inflammation, and Stress
- Elimination Diets for Stress Relief
By comprehending the intricate interplay between diet and cortisol levels, we can make informed choices and adopt dietary strategies that promote hormonal balance and stress reduction. This exclusive insight empowers us to harness the potential of nutrition for cultivating a healthier and more resilient mind and body.
Understanding Cortisol: The Stress Hormone

In this section, we will delve into the concept of cortisol, which is commonly known as the stress hormone. We will explore its role in the body and how it affects our overall well-being. By gaining a thorough understanding of cortisol, we can better comprehend its relationship with diet and the potential impact of food choices on our stress hormone levels.
Cortisol, also referred to as the stress hormone, is a vital hormone produced by the adrenal glands. It plays a crucial role in our body’s response to stress, influencing various physiological processes. Cortisol helps regulate blood sugar levels, metabolism, inflammation, and our immune response. It is a natural and necessary hormone for our survival, enabling us to adapt and cope with challenging situations.
When we encounter stress, whether it be physical, emotional, or psychological, the body releases cortisol as part of the fight-or-flight response. This response prepares us to deal with the stressor by increasing our energy levels, improving focus and alertness, and suppressing non-essential functions such as digestion and reproductive processes.
While cortisol is essential for short-term stress management, prolonged elevation of cortisol levels due to chronic stress can have negative effects on our health. High levels of cortisol have been associated with increased inflammation, immune system dysfunction, weight gain, impaired cognitive function, and a higher risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease and diabetes.
The relationship between cortisol and diet is multifaceted. Research suggests that certain foods and dietary patterns can influence cortisol levels. For example, a diet high in refined carbohydrates and sugar has been shown to increase cortisol secretion. On the other hand, consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients and antioxidants may help regulate cortisol levels and mitigate the negative impact of chronic stress.
By understanding the role of cortisol as the stress hormone, we can make informed choices about our diet to support optimal cortisol regulation. In the following sections, we will explore specific food choices and dietary strategies that can help lower cortisol levels and promote overall well-being.
| Previous | Next |
|---|---|
| << Previous Article | Next Article >> |
The Role of Cortisol in the Body
Cortisol plays a vital role in various physiological processes within the human body. This hormone, commonly known as the stress hormone, is produced by the adrenal glands in response to both physical and psychological stressors. It acts as a chemical messenger, influencing and regulating numerous bodily functions necessary for survival.
Regulation of Metabolism: Cortisol plays an essential role in the regulation of metabolism by aiding in the breakdown of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It helps to increase blood sugar levels by triggering the release of glucose from storage sites, such as the liver, into the bloodstream. Additionally, cortisol promotes the breakdown of fats for energy, especially during periods of prolonged stress.
Inflammatory Response: Cortisol also plays a significant role in regulating the body’s inflammatory response. It acts as an anti-inflammatory agent, helping to suppress and control excessive inflammation. By reducing the production of inflammatory substances, cortisol helps prevent tissue damage and promotes quicker healing.
Stress Response: As the primary stress hormone, cortisol is responsible for initiating the body’s stress response. It helps prepare the body for the fight or flight response by increasing heart rate, constricting blood vessels, and mobilizing energy stores. These physiological changes enable the body to respond effectively to stressful situations.
Immune System Regulation: Cortisol plays a crucial role in regulating immune system function. It helps suppress the immune response to prevent overactivity, which can lead to autoimmune disorders. Moreover, cortisol acts as an immunosuppressant, reducing inflammation and the activity of immune cells.
Emotional Regulation: Cortisol also influences emotional regulation and mood. It interacts with brain regions involved in mood regulation, stress response, and emotional processing. Abnormal cortisol levels have been associated with mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Overall, cortisol plays an integral role in various physiological processes, ensuring the body’s ability to respond to stress effectively and maintaining homeostasis. Understanding the role of cortisol can help individuals make informed choices regarding their diet and lifestyle to maintain optimal cortisol levels and overall well-being.
The Link Between Cortisol and Stress
In this section, we explore the profound connection between cortisol and stress, examining how these two factors intertwine and influence each other. Understanding this link is crucial for individuals seeking to manage their stress levels effectively and optimize their overall well-being.
Cortisol is a vital hormone intricately involved in the body’s stress response. Often referred to as the stress hormone, cortisol plays a significant role in regulating various physiological processes related to stress, including metabolism, blood pressure, and the immune system.
Stress, on the other hand, is the body’s response to any environmental or psychological demand. It is a natural reaction designed to help us cope with challenging situations. However, chronic stress can have detrimental effects on both our mental and physical health, leading to conditions such as anxiety, depression, and cardiovascular disease.
The link between cortisol and stress arises from the body’s intricate feedback system. When faced with a stressor, the hypothalamus in the brain signals the pituitary gland to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which then stimulates the adrenal glands to produce cortisol.
Elevated cortisol levels are commonly observed during periods of chronic stress. This can occur due to ongoing stressors such as work pressure, relationship problems, or financial difficulties. When cortisol levels remain high for prolonged periods, it can disrupt the body’s natural equilibrium and potentially lead to various health issues, both physical and mental.
Conversely, strategies to reduce stress such as practicing mindfulness, engaging in regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy diet can help regulate cortisol levels. Making conscious food choices is particularly beneficial as specific nutrients and substances can influence cortisol production in the body.
Understanding the intricate link between cortisol and stress empowers individuals to take proactive measures to manage their stress levels effectively. By adopting healthy lifestyle choices and incorporating stress-reducing techniques, it becomes possible to maintain optimal cortisol levels and promote overall well-being.
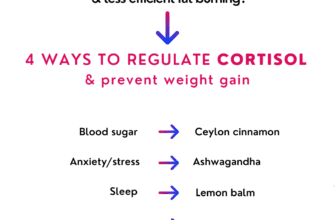
Dietary Factors That Influence Cortisol Levels
When it comes to regulating cortisol levels, our diet plays a crucial role. Certain dietary factors can impact the production and release of cortisol in our bodies, either increasing or decreasing its levels. Understanding these factors can help us maintain a healthy balance of this stress hormone and promote overall well-being.
One key dietary factor that can influence cortisol levels is the consumption of sugar. Studies have shown that consuming a diet high in refined sugars can lead to an increase in cortisol production. On the other hand, opting for complex carbohydrates that are rich in fiber, such as whole grains, can help stabilize cortisol levels and prevent sudden spikes.
In addition, the amount and type of fat we consume can also affect cortisol levels. Diets high in saturated and trans fats have been linked to higher cortisol levels, while diets rich in healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids, have shown to reduce cortisol production. Including sources of healthy fats like fatty fish, nuts, and avocados in our diet can help manage cortisol levels.
Furthermore, the inclusion of protein in our meals can impact cortisol levels. Consuming adequate amounts of protein can help regulate cortisol release, as protein is involved in the synthesis of hormones, including cortisol. Incorporating lean sources of protein, such as poultry, fish, and legumes, can contribute to maintaining cortisol balance.
Lastly, certain nutrients and vitamins have also been found to have an impact on cortisol levels. For example, studies suggest that consuming foods rich in vitamin C can help lower cortisol levels, while a deficiency in this vitamin may lead to higher cortisol production. Similarly, consuming magnesium-rich foods, such as leafy greens and nuts, may also help regulate cortisol levels.
Overall, our dietary choices have a significant influence on cortisol levels. A diet that includes complex carbohydrates, healthy fats, adequate protein, and essential nutrients can help maintain a healthy balance of cortisol, promoting overall well-being and reducing stress.
The Power of a Balanced Diet
Discover the remarkable benefits of maintaining a well-rounded eating plan. A balanced diet provides a multitude of advantages that positively impact various aspects of your overall well-being. Embracing a diverse range of nutritious food choices is crucial to promote optimal health, boost energy levels, support cognitive function, and even manage stress.
|
1. Nourishing your body: When you prioritize a balanced diet, you ensure that your body receives essential nutrients, vitamins, and minerals it needs to function at its best. By consuming a wide variety of foods, you can maintain a healthy weight, build muscle mass, strengthen your immune system, and improve your overall physical health. |
2. Enhancing mental well-being: A diverse and balanced diet not only benefits your body but also plays a significant role in maintaining good mental health. Certain foods, such as those rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, have been linked to improved brain function, enhanced mood stability, and reduced risk of mental health disorders. |
|
3. Managing stress levels: Stress is a natural response to various factors in our lives, but it can become chronic and detrimental to our well-being if not managed properly. Consuming a balanced diet can help regulate cortisol levels, the primary stress hormone, keeping it within a healthy range. This can lead to decreased feelings of stress and anxiety, promoting a more focused and balanced state of mind. |
4. Sustaining energy levels: Feeding your body with a balanced diet ensures a steady supply of energy throughout the day. Incorporating complex carbohydrates, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your meals can prevent energy crashes and provide the fuel needed to perform daily activities effectively. Additionally, maintaining stable energy levels can positively impact your mood, productivity, and ability to cope with stress. |
In conclusion, adopting a well-balanced diet is an essential component of maintaining a healthy lifestyle. The choices you make regarding the food you consume can greatly impact your physical health, mental well-being, stress levels, and energy levels. By prioritizing a diverse and nutrient-rich eating plan, you can unlock the tremendous power of a balanced diet and experience improved overall wellness.
The Effects of Sugar Consumption on Cortisol
Sugar consumption has been found to have a significant impact on the levels of cortisol, a stress hormone, in the body. Research suggests that high sugar intake can lead to an increase in cortisol production, resulting in elevated stress levels and potential long-term negative health effects.
When individuals consume foods high in sugar, such as sweets, sugary beverages, or processed snacks, it can trigger the release of cortisol. This hormone is responsible for regulating the body’s response to stress by mobilizing energy and increasing blood sugar levels. While cortisol is essential in short bursts, chronic high levels can have detrimental consequences.
Excessive sugar consumption can disrupt the body’s natural cortisol balance. This can lead to prolonged periods of elevated cortisol levels, which may negatively impact various aspects of health, including immune function, metabolism, and mental well-being. Additionally, the increased stress response associated with high cortisol levels can contribute to weight gain and an increased risk of developing chronic conditions such as diabetes and heart disease.
Reducing sugar intake can help regulate cortisol levels and mitigate the negative effects of chronic stress. Making conscious food choices that prioritize whole, unprocessed foods and limiting the consumption of foods with added sugars can have a positive impact on cortisol regulation. Incorporating a balanced diet that includes nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help maintain cortisol levels within a healthy range.
In conclusion, sugar consumption can have significant effects on cortisol levels in the body. Understanding the relationship between sugar and cortisol is crucial for maintaining overall well-being and managing stress. By reducing sugar intake and adopting a balanced diet, individuals can support optimal cortisol regulation and promote better physical and mental health.
The Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Lowering Cortisol
Introduction: This section explores the significance of Omega-3 fatty acids in reducing cortisol production. Omega-3 fatty acids have been found to play a crucial role in regulating stress hormone levels in the body. Understanding the impact of these essential fatty acids on cortisol can provide insights into managing stress and promoting overall well-being.
Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, commonly found in fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, are known for their numerous health benefits. These polyunsaturated fats not only contribute to heart health but also possess anti-inflammatory properties. Studies have shown that omega-3 fatty acids can potentially attenuate cortisol levels, resulting in lower stress levels and improved resilience to stressors.
Effects on Cortisol Regulation: The mechanism through which omega-3 fatty acids influence cortisol levels is not fully understood, but research suggests several possible ways. Omega-3 fatty acids may modulate the release of corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which are involved in cortisol synthesis and secretion. Additionally, these fatty acids may enhance the availability of precursors needed for cortisol production, ultimately leading to more balanced cortisol levels.
Beneficial Food Sources: Incorporating omega-3 fatty acids into your diet can be achieved through consumption of not only fish but also plant-based sources such as flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. These sources are rich in alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), which can be converted to the active forms of omega-3 fatty acids in the body. By including a variety of these foods in your meals, you can optimize your omega-3 intake and potentially promote cortisol regulation.
Considerations and Further Research: While omega-3 fatty acids show promise in cortisol modulation, it is important to note that individual responses may vary. Factors such as genetics, overall dietary patterns, and lifestyle choices can influence the effectiveness of these fatty acids in reducing cortisol levels. Further research is warranted to elucidate the specific mechanisms and potential synergistic effects of omega-3 fatty acids with other dietary components in cortisol regulation.
In conclusion, the incorporation of omega-3 fatty acids in your diet may offer potential benefits in lowering cortisol levels. By including fatty fish and plant-based sources of omega-3s in your meals, you can support your overall stress management strategies and promote a healthier balance of stress hormone levels in your body.
Optimal Food Choices for Reducing Cortisol
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Health-Ways-to-Lower-Cortisol_Horiz-3b2f5e9ccace4c20b1416d36c0f93914.jpg)
In this section, we will delve into the various food choices that you can incorporate into your diet to help lower your cortisol levels, the stress hormone. By making thoughtful and strategic decisions about what you eat, you can promote a healthier and more balanced hormonal response in your body, leading to reduced stress and improved well-being.
| Food Group | Key Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Fruits and Vegetables | Rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients that support overall health and reduce inflammation, promoting cortisol regulation. | Blueberries, spinach, oranges, bell peppers |
| Whole Grains | Provide a steady release of energy, preventing blood sugar spikes and crashes that can contribute to increased cortisol levels. | Brown rice, quinoa, oats, whole wheat bread |
| Lean Proteins | Contain amino acids that contribute to the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood and reduce stress. | Chicken breast, turkey, tofu, lentils |
| Healthy Fats | Play a role in maintaining hormone production and balance, helping to prevent excessive cortisol release. | Avocado, olive oil, nuts, seeds |
| Herbs and Spices | Offer natural compounds that possess anti-inflammatory and stress-reducing properties, assisting in cortisol regulation. | Turmeric, ginger, cinnamon, garlic |
It’s important to note that while these food choices can support cortisol regulation, they should be part of a balanced and varied diet. Additionally, it’s always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice and guidance.
By selecting optimal foods that nourish both your body and mind, you can take proactive steps towards reducing cortisol levels and improving your overall well-being.
The Importance of Whole Grains and Complex Carbohydrates
Discovering the significance of incorporating whole grains and complex carbohydrates into your diet can bring about numerous benefits for both your physical health and mental well-being. The consumption of these nutritionally dense food options not only contributes to a balanced diet but also plays a vital role in regulating cortisol levels, effectively managing stress, and enhancing overall health.
Incorporating whole grains in your diet can contribute to maintaining steady cortisol levels due to their complex carbohydrate content. Unlike refined carbohydrates, whole grains are packed with fiber, vitamins, and minerals that ensure a slow and sustained release of glucose into the bloodstream, preventing sharp spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. This steady supply of energy helps to stabilize cortisol levels, reducing the likelihood of experiencing stress-induced symptoms.
Furthermore, whole grains possess essential nutrients that aid in reducing inflammation and promoting a healthy gut microbiome. The antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties present in whole grains can mitigate the body’s stress response and minimize excessive cortisol production. By supporting a healthy gut environment, whole grains contribute to enhanced overall well-being and provide a stronger defense against stress-related ailments.
Complex carbohydrates, found in foods such as legumes, quinoa, and sweet potatoes, are another crucial component in regulating cortisol levels. These carbohydrates release energy slowly, promoting a balanced blood sugar level and preventing the sudden insulin spikes observed with simple carbohydrates. As a result, the body can maintain stable cortisol levels, preventing excessive stress hormone release and its adverse effects on both mental and physical health.
In conclusion, the inclusion of whole grains and complex carbohydrates in your diet can play a vital role in maintaining optimal cortisol levels, managing stress, and improving overall health. By opting for these nutrient-dense food choices, you can enjoy the benefits of sustained energy, reduced inflammation, and a strengthened defense against the negative effects of stress.
Questions and answers
How does our diet affect cortisol levels?
Our diet plays a significant role in regulating cortisol levels in our body. Certain foods can increase cortisol production, while others can help lower its levels. It is essential to pay attention to our food choices to maintain healthy cortisol levels.
Which foods should I avoid to lower cortisol levels?
To lower cortisol levels, it is best to avoid foods high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated fats. These foods can increase cortisol production and contribute to higher stress hormone levels in the body.
What are some foods that can help lower cortisol?
There are several foods that can help lower cortisol levels. Some examples include dark chocolate, berries, omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon, green leafy vegetables, and foods rich in vitamin C, such as oranges and strawberries. These foods have beneficial properties that can help regulate cortisol levels in the body.
Is there a direct link between stress and cortisol levels?
Yes, there is a direct link between stress and cortisol levels. When our body perceives stress, it releases cortisol as part of the stress response. Chronic stress can lead to consistently high cortisol levels, which can have negative effects on our health. Managing stress is crucial for maintaining healthy cortisol levels.
How long does it take for dietary changes to affect cortisol levels?
The time it takes for dietary changes to affect cortisol levels can vary from person to person. Generally, noticeable changes in cortisol levels can be observed within a few weeks of making dietary adjustments. However, it is essential to maintain a healthy diet consistently for long-term cortisol regulation.
Can changing your diet help lower cortisol levels?
Yes, changing your diet can indeed help lower cortisol levels. Certain foods can either increase or decrease cortisol production in the body. By making mindful food choices, you can regulate your cortisol levels and reduce overall stress.
What are some foods that can lower cortisol levels?
There are several foods that have been shown to lower cortisol levels. These include dark chocolate, berries, nuts, fatty fish such as salmon, foods rich in probiotics like yogurt, and green leafy vegetables. These foods contain antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and other nutrients that can help regulate cortisol production.
Are there any specific diets that are known to reduce cortisol levels?
While there isn’t one specific diet that guarantees a reduction in cortisol levels, certain dietary approaches have been linked to lower stress hormone levels. The Mediterranean diet, for example, which is characterized by high consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, has been associated with lower levels of cortisol. Additionally, the DASH diet, which focuses on low sodium and high potassium intake, has shown similar effects on cortisol levels.
Can caffeine increase cortisol levels?
Yes, caffeine can increase cortisol levels. When you consume caffeine, it stimulates the release of cortisol by the adrenal glands. This can be particularly problematic if you already have high cortisol levels or if you’re sensitive to caffeine. It’s recommended to consume caffeine in moderation to avoid excessive cortisol production.
Is there a relationship between sugar intake and cortisol levels?
Yes, there is a relationship between sugar intake and cortisol levels. Consuming high amounts of sugar can lead to increased cortisol production. When you consume sugar, it causes a spike in blood sugar levels, triggering the release of insulin. As a response, cortisol is released in order to counteract the effects of insulin. This constant fluctuation in cortisol levels can contribute to chronic stress.