Efficient operation of the mind and body is an evocative subject that has long captured the attention of researchers and health enthusiasts alike. The intricate link between cortisol imbalance and mental health has emerged as a topic of significant interest within the medical community. This exploration delves into the profound repercussions associated with the fluctuating levels of cortisol. By examining the effects of this crucial hormone and its interplay with psychological well-being, we aim to shed light on the intricate mechanisms that govern our mental and emotional states.
Delving into the realm of neuroendocrinology, where the intricate interplay between the nervous and endocrine systems takes place, we become cognizant of the pivotal role cortisol plays in regulating our physiological responses. This hormone, secreted by the adrenal glands, exhibits a multifaceted influence on various bodily systems, including metabolism, immune function, and stress response. However, erratic cortisol levels have shown a compelling association with an array of mental health conditions, ranging from anxiety disorders to depression.
Understandably, the implications of cortisol imbalance extend far beyond the scope of physical health. As a potent modulator of stress response, cortisol is intricately entwined with our emotional and cognitive well-being. Studies have suggested that individuals with elevated cortisol levels often exhibit heightened vulnerability to mood disorders and cognitive impairments. Moreover, the delicate equilibrium between cortisol secretion and mental health has drawn attention due to its potential role in the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Unveiling the intricate web of interactions between cortisol and mental health necessitates a comprehensive examination of the underlying mechanisms. From dysregulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis to alterations in glucocorticoid receptor sensitivity, diverse factors contribute to the nuanced impact of cortisol on our psychological states. By better understanding these complex dynamics, researchers and clinicians strive to develop targeted interventions that may mitigate the adverse consequences of cortisol imbalance and improve mental well-being.
- The Impact of Cortisol Imbalance on Mental Health
- Understanding the Relationship
- Exploring Cortisol’s Role in Mental Health Disorders
- The Link between Chronic Stress and Cortisol
- Effects of Cortisol Imbalance on Mental Well-being
- Influence on Mood Disorders
- Consequences for Cognitive Function
- Impact on Anxiety and Depression
- Questions and answers
The Impact of Cortisol Imbalance on Mental Health
The influence of irregular hormone levels on psychological well-being has gained significant attention in recent years. Exploring the consequences of an imbalance in cortisol, commonly referred to as the body’s primary stress hormone, provides valuable insights into its effect on mental health. This section aims to delve into the intricate relationship between cortisol levels and various aspects of psychological functioning, shedding light on the potential implications for individuals experiencing cortisol dysregulation.
Understanding the Relationship
Exploring the intricate correlation between cortisol levels and mental well-being is vital to comprehending the underlying mechanisms at play. By delving into the intricate interplay between these hormonal factors and psychological states, researchers aim to shed light on the complex relationship that exists, ultimately seeking to unravel the delicate balance between cortisol regulation and mental health.
- Uncovering the intricate web of connections between cortisol imbalance and mental health is an ongoing area of research, motivated by the recognition that the state of one’s mental well-being can significantly impact their overall quality of life.
- Examining the intersection between cortisol levels and psychological states presents a unique opportunity to gain insights into the physiological factors that contribute to mental health conditions.
- By understanding the intricate relationship between cortisol and mental health, researchers strive to identify potential targets for interventions and develop innovative approaches to managing and treating mental health disorders.
- Exploring the impacts of cortisol imbalance on mental health encompasses investigating the effects of chronic stress, adrenal dysfunction, and other factors that contribute to disruptions in cortisol levels, ultimately shedding light on how these imbalances can potentially lead to the development or exacerbation of mental health conditions.
- Understanding the intricate relationship between cortisol and mental health not only contributes to theoretical knowledge but also holds significant implications for clinical practices, enabling healthcare professionals to develop more targeted and individualized treatment approaches.
In summary, comprehending the relationship between cortisol imbalance and mental health necessitates an exploration of the multifaceted connections that exist within the physiological and psychological realms. By unraveling the complex interplay between these factors, researchers aim to improve our understanding of mental health conditions and pave the way for more effective interventions and treatments.
Exploring Cortisol’s Role in Mental Health Disorders
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cortisol-371314fd2ef34947969e615ee1e75691.jpg)
Delving into the intricate relationship between cortisol and various mental health disorders unveils fascinating insights into the profound influence this hormone exerts on psychological well-being. Understanding the mechanisms through which cortisol impacts the development, progression, and manifestation of these disorders offers crucial insights for intervention and support.
Cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress, plays a significant role in regulating a wide array of physiological processes. It affects the immune system, metabolism, and even cognitive function. However, when cortisol levels become imbalanced, either elevated or diminished, a cascade of effects on mental health can ensue.
In the realm of mental health disorders, dysregulation of cortisol levels has been linked to a range of conditions, including anxiety disorders, depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and even schizophrenia. Cortisol’s intricate interplay with neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, as well as its impact on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, contributes to the manifestation and severity of these disorders.
For individuals with anxiety disorders, cortisol imbalances are often associated with heightened levels of anxiety and exaggerated stress responses. In depression, cortisol dysregulation can contribute to the persistence of depressive symptoms and impaired functioning. PTSD, characterized by intrusive memories and hyperarousal, frequently involves alterations in cortisol secretion, further compounding the disorder’s impact on mental well-being.
Researchers have also observed correlations between cortisol abnormalities and schizophrenia, a complex psychiatric disorder characterized by hallucinations, delusions, and impaired cognitive function. The intricate relationship between cortisol and dopamine, a neurotransmitter implicated in schizophrenia, highlights the potential significance of cortisol dysregulation in the disorder’s etiology and progression.
By elucidating the mechanisms linking cortisol imbalances to mental health disorders, researchers and clinicians can develop targeted interventions and therapeutic strategies. This in-depth understanding paves the way for exploring cortisol-regulating interventions, such as pharmacological agents or psychosocial interventions, to improve outcomes for individuals grappling with mental health disorders.
In summary, exploring the role of cortisol in mental health disorders reveals the intricate connections between this hormone and various aspects of psychological well-being. Understanding these connections enhances our understanding of the etiology, progression, and potential interventions for mental health disorders that involve cortisol dysregulation.
The Link between Chronic Stress and Cortisol
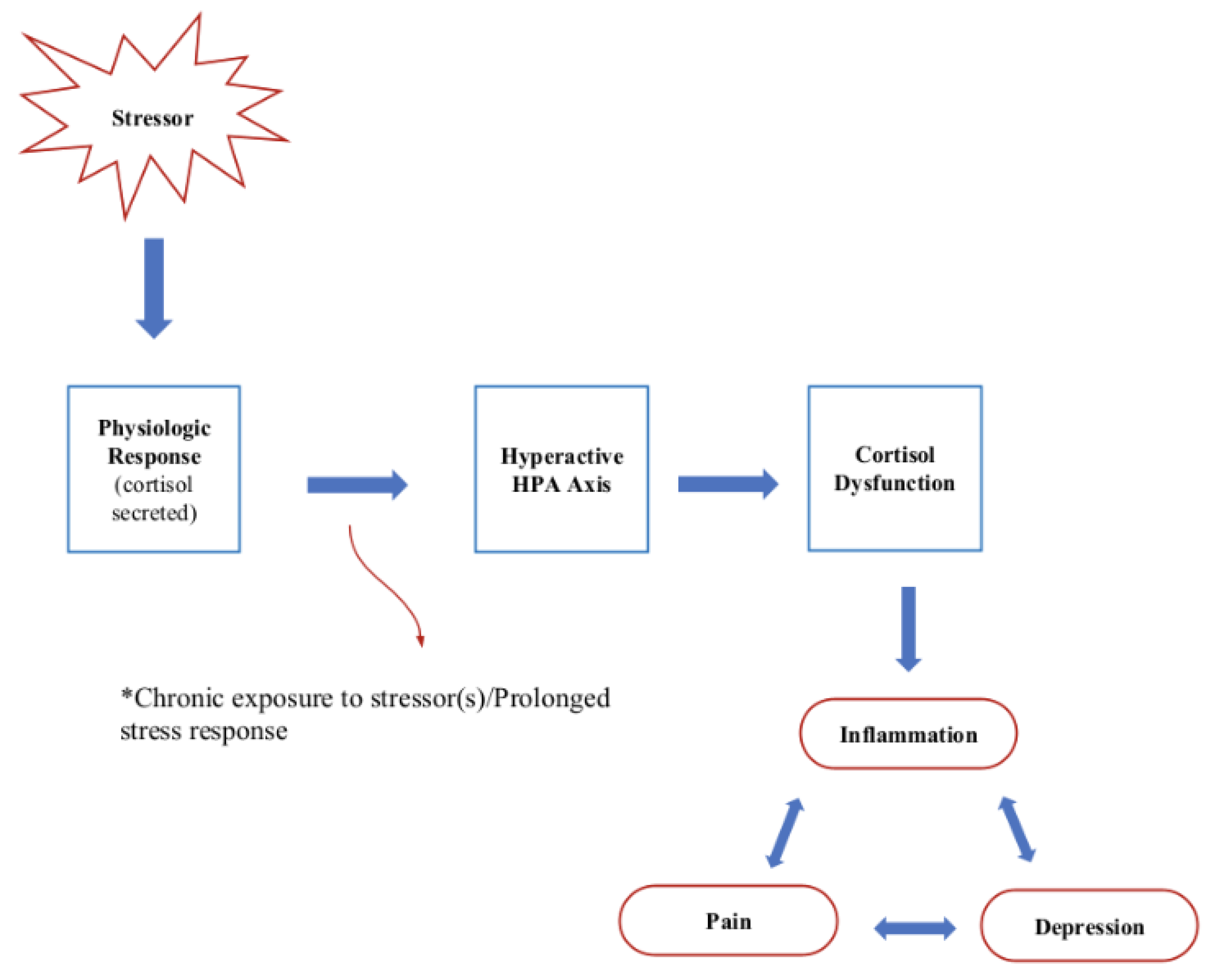
Chronic stress and cortisol have an intricate interconnection, with unbalanced cortisol levels often being a consequence of prolonged high-stress situations. This section explores the association between chronic stress and cortisol, shedding light on how chronic stress impacts the regulation of cortisol in our bodies.
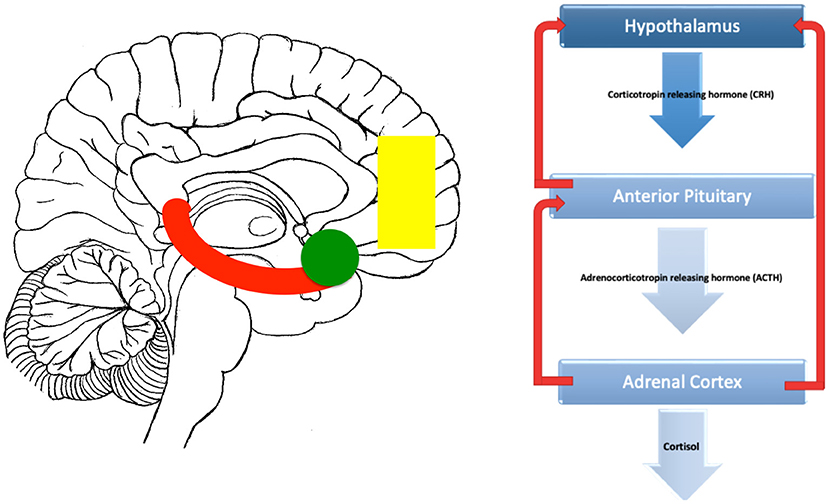
When faced with chronic stress, our bodies experience prolonged activation of the stress response system. This system involves the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands. The hypothalamus releases corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which signals the pituitary gland to produce adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). In turn, ACTH stimulates the adrenal glands to release cortisol.
Elevated cortisol levels, resulting from chronic stress, can disrupt the delicate homeostasis of our body’s stress response system. This disruption leads to a dysregulation of cortisol production and function. Excessive cortisol production can negatively impact various physiological and psychological processes, contributing to mental health issues.
- Increased cortisol levels have been associated with symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Chronic stress and elevated cortisol may impair cognitive function, including memory and attention.
- Insomnia and sleep disturbances can arise from the dysregulation of cortisol, further exacerbating stress and affecting mental well-being.
- Studies have suggested that chronic stress and cortisol imbalance might influence the development of mood disorders, such as bipolar disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder.
Understanding the link between chronic stress and cortisol is crucial for comprehending the impact of prolonged stress on mental health. By recognizing this connection, healthcare professionals can develop targeted interventions to address cortisol dysregulation and promote better mental well-being.
Effects of Cortisol Imbalance on Mental Well-being
In this section, we will delve into the impact of an imbalance in cortisol levels on a person’s overall mental well-being. The intricate relationship between cortisol and mental health highlights the significance of maintaining a balanced cortisol level for optimal psychological functioning.
- Alterations in cortisol levels can have profound effects on emotional stability and mood regulation. Excessive cortisol levels, known as hypercortisolism or Cushing’s syndrome, can lead to increased anxiety, irritability, and depression. On the other hand, insufficient cortisol levels, known as hypocortisolism or Addison’s disease, can result in lethargy, apathy, and prolonged periods of sadness.
- The cognitive functions, including memory and concentration, are also significantly influenced by cortisol imbalances. Excessive cortisol can impair memory consolidation and retrieval, leading to difficulties in learning and retaining information. Conversely, insufficient cortisol can contribute to poor focus, attention deficits, and decreased mental clarity.
- Sleep disturbances are often observed in individuals with cortisol imbalances, affecting their mental well-being. High cortisol levels can disrupt the normal sleep-wake cycle, causing insomnia and restlessness. Conversely, low cortisol levels can result in excessive sleepiness, fatigue, and a feeling of constant drowsiness.
- An imbalance in cortisol levels can contribute to alterations in appetite and weight regulation, ultimately impacting mental well-being. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to increased appetite, emotional eating, and weight gain, potentially exacerbating feelings of dissatisfaction and low self-esteem. In contrast, decreased cortisol levels can cause a loss of appetite, leading to weight loss and reduced energy levels.
- The effects of cortisol imbalance on overall stress levels and resilience cannot be overlooked. Chronic exposure to high cortisol levels can lead to an overactive stress response, increasing vulnerability to anxiety disorders and other mental health conditions. Conversely, low cortisol levels can impair the body’s ability to respond to stress, making individuals more susceptible to feeling overwhelmed and experiencing prolonged periods of distress.
In conclusion, the effects of cortisol imbalance on mental well-being are far-reaching, influencing various aspects of emotional, cognitive, and physical functioning. Understanding the intricate relationship between cortisol and mental health can provide valuable insights in developing effective interventions and treatments for individuals experiencing cortisol imbalances.
Influence on Mood Disorders
The impact of cortisol levels on mood disorders has been widely studied and documented. This section explores the profound influence that cortisol imbalance can have on various mood disorders.
One of the key factors in understanding the influence of cortisol on mood disorders is recognizing its role in regulating emotions and stress response. Cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands, is closely associated with the body’s fight-or-flight response. When cortisol levels become imbalanced, it can disrupt the delicate equilibrium in the brain that regulates mood.
Mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety, are often characterized by significant changes in mood, emotions, energy levels, and overall well-being. Research has shown that individuals with mood disorders frequently exhibit abnormal cortisol levels; some may have elevated cortisol levels, while others may have reduced levels.
Elevated cortisol levels, often associated with chronic stress, can lead to sustained activation of the body’s stress response system. This can result in negative effects on mental health, as increased cortisol levels have been linked to symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, and a higher risk of developing depression.
On the other hand, individuals with reduced cortisol levels may experience symptoms such as low mood, lack of motivation, and fatigue. It is crucial to note that cortisol imbalance is not the sole cause of mood disorders, but rather a contributing factor that interacts with other biological, psychological, and environmental elements.
Understanding the influence of cortisol imbalance on mood disorders is critical for developing effective treatment strategies. By targeting cortisol regulation through various interventions, such as stress management techniques, cognitive-behavioral therapy, and medication, it may be possible to alleviate symptoms and improve overall mental well-being.
Further research into the complex relationship between cortisol and mood disorders will help enhance our understanding of these conditions and pave the way for more personalized and comprehensive approaches to treatment.
Consequences for Cognitive Function
The impact of cortisol imbalances on the functioning of our brain and its cognitive abilities is an area of significant concern and study. This section aims to explore the repercussions that arise from such imbalances, focusing on their effects on cognitive function.
Overall, cognitive function refers to the mental processes and abilities involved in acquiring, processing, storing, and using information. It encompasses various aspects, including attention, memory, learning, problem-solving, decision-making, and perception.
In the presence of cortisol imbalances, cognitive function can be significantly affected. Excessive cortisol levels, often associated with chronic stress, can have detrimental effects on attention span and concentration. Individuals may struggle to stay focused and may experience difficulties in processing and retaining information. This can lead to decreased productivity and impaired academic or work performance.
Moreover, cortisol imbalances may also impact memory processes. High cortisol levels can interfere with memory consolidation, making it challenging to form and retrieve memories. This can manifest as forgetfulness, difficulty recalling information, and confusion.
Furthermore, cognitive flexibility, which refers to the ability to adapt and change thinking strategies, can be compromised due to cortisol imbalances. Stress-related cortisol fluctuations may lead to rigid thinking patterns and difficulties in shifting attention or adapting to new situations. Individuals may find it harder to switch between tasks or generate innovative solutions to problems.
In addition to these effects, cortisol imbalances can influence decision-making processes. Excessive cortisol can promote risk aversion and impede rational thinking, potentially leading to suboptimal choices. This can have implications across various domains, including finance, relationships, and overall life satisfaction.
Overall, understanding the consequences of cortisol imbalance on cognitive function allows us to comprehend the intricate relationship between mental health and the stress hormone. By recognizing the potential impacts, appropriate interventions and strategies can be developed to help individuals maintain optimal cognitive performance and overall well-being.
Impact on Anxiety and Depression
The influence of cortisol imbalance on anxiety and depression has been extensively studied and well-documented. This section will delve into the effects of this hormonal dysregulation on these mental health conditions, exploring the intricate relationship between cortisol and the experience of anxiety and depression.
| Anxiety | Depression |
|---|---|
| Anxiety is a psychological state characterized by feelings of unease, nervousness, and worry. When cortisol levels are imbalanced, individuals may exhibit heightened anxiety symptoms such as persistent fear, restlessness, and irritability. This hormone plays a crucial role in the body’s stress response, and its dysregulation can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters involved in anxiety regulation. | Depression, a common mood disorder, involves a persistent feeling of sadness, loss of interest or pleasure, and a variety of physical and emotional symptoms. Cortisol imbalance has been linked to increased susceptibility to depression, as elevated levels of this hormone can disrupt the production and functioning of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are important in regulating mood. |
| Moreover, excessive cortisol levels can impair the functioning of the hippocampus, a brain region responsible for emotional regulation. This can further contribute to the development or exacerbation of anxiety and depressive symptoms. | Additionally, research has shown that chronic stress and prolonged exposure to elevated cortisol levels can lead to structural changes in the brain, particularly in areas associated with emotion processing and mood regulation. These alterations may contribute to the persistence of depression. |
| Understanding the impact of cortisol imbalance on anxiety and depression is crucial in developing effective treatment strategies. By targeting cortisol dysregulation, interventions can aim to reduce anxiety and depressive symptoms, ultimately improving individuals’ overall mental well-being. | While further research is needed to fully comprehend the complex interaction between cortisol and mental health, current evidence highlights the importance of recognizing cortisol imbalance as a significant factor in the development and maintenance of anxiety and depression. |
In conclusion, cortisol imbalance exerts a substantial influence on anxiety and depression, affecting various aspects of these mental health conditions. Recognizing the impact of cortisol dysregulation enables healthcare professionals to develop tailored interventions, fostering a comprehensive approach towards managing and treating anxiety and depression.
Questions and answers
What is cortisol imbalance and how does it affect mental health?
Cortisol imbalance refers to an excessive or insufficient production of cortisol, which is commonly known as the stress hormone. This imbalance can have significant effects on mental health. Excess cortisol can lead to increased anxiety, irritability, and depression, while insufficient cortisol can result in fatigue, apathy, and low mood.
What are the factors that can contribute to cortisol imbalance?
There are several factors that can contribute to cortisol imbalance. Chronic stress, lack of sleep, poor diet, and certain medical conditions can all play a role in disrupting cortisol levels. Additionally, genetics and hormonal imbalances can also contribute to cortisol imbalance.
Can cortisol imbalance be treated and if so, how?
Yes, cortisol imbalance can be treated. The specific treatment approach may vary depending on whether cortisol levels are too high or too low. For high cortisol levels, stress management techniques such as mindfulness, exercise, and relaxation exercises can be helpful. For low cortisol levels, medications or supplements may be prescribed to regulate cortisol production.
What are the long-term effects of cortisol imbalance on mental health?
The long-term effects of cortisol imbalance on mental health can be significant. Chronic high cortisol levels can increase the risk of developing anxiety disorders, depression, and other mental health conditions. On the other hand, chronically low cortisol levels can contribute to chronic fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and feelings of worthlessness.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help regulate cortisol levels and improve mental health?
Yes, there are several lifestyle changes that can help regulate cortisol levels and improve mental health. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing stress management techniques like meditation or yoga, getting enough sleep, maintaining a balanced diet, and minimizing exposure to chronic stressors can all contribute to a healthier cortisol balance and improved mental well-being.
What is cortisol imbalance and how does it affect mental health?
Cortisol imbalance refers to an abnormal level of cortisol, which is a hormone released in response to stress. When cortisol levels are too high or too low, it can have negative effects on mental health. High cortisol levels can contribute to anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders, while low cortisol levels can lead to fatigue, lack of motivation, and difficulty coping with stress.
What are some common symptoms of cortisol imbalance?
Common symptoms of cortisol imbalance include persistent fatigue, weight gain or loss, difficulty sleeping, irritability, difficulty concentrating, and changes in appetite. Additionally, individuals with cortisol imbalance may experience mood swings, feelings of sadness or worthlessness, and heightened anxiety.
What factors can contribute to cortisol imbalance?
Several factors can contribute to cortisol imbalance, including chronic stress, prolonged use of medications like corticosteroids, physical or emotional trauma, certain medical conditions such as Cushing’s syndrome or Addison’s disease, and inadequate sleep or rest. Additionally, lifestyle choices such as poor diet, lack of exercise, and substance abuse can also impact cortisol levels.
Can cortisol imbalance be treated?
Yes, cortisol imbalance can be treated. The specific treatment approach depends on the underlying cause and severity of the imbalance. Lifestyle changes such as stress management techniques, regular exercise, and a well-balanced diet can help regulate cortisol levels. In some cases, medical intervention may be necessary, including the use of medication or hormone therapy. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
How can cortisol imbalance be prevented?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent cortisol imbalance, there are steps that can be taken to minimize the risk. These include practicing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness meditation or yoga, maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise and a balanced diet, ensuring adequate sleep and rest, and seeking support from friends, family, or a therapist to cope with stress. Additionally, it is important to avoid excessive use of medications like corticosteroids unless medically necessary.