When it comes to our dietary choices, the consequences they have on our overall well-being cannot be underestimated. One particular aspect that has sparked much debate and curiosity among nutritionists and health enthusiasts alike is the influence of a hearty, lipid-laden evening meal on our health. By delving into the intricacies of this topic, we can gain valuable insights into the potential advantages and disadvantages associated with consuming a high-fat dinner.
Amidst this multifaceted discourse, the exploration of the repercussions a substantial, lipid-rich supper can have on our daily lives has taken center stage. Delving deeper into the intricacies of this phenomenon, researchers have sought to dissect the possible risks and rewards that align with indulging in a culinary experience infused with copious amounts of dietary fat. With this in mind, the intricate web of biochemical processes that unfold within our bodies can shed light on the qualitative nature of the effects brought about by such a meal.
As we embark on this enlightening journey exploring the intricacies of a fat-laden feast, it becomes increasingly evident that there is a delicate balance to be struck between the potential benefits and drawbacks. The dynamic interplay between factors such as metabolic rate, cardiovascular health, and nutritional balance intertwines to shape the final outcome. By uncovering the nuances that lie beneath the surface, we can better equip ourselves with the knowledge needed to make informed dietary choices for a healthier tomorrow.
- Understanding the Link Between High-Fat Dinners and Health
- The Role of Fat Consumption in Overall Well-being
- The Effect of High-Fat Dinners on Body Weight and Obesity
- Potential Health Risks Associated with High-Fat Dinners
- Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases
- Impacts on Cholesterol Levels and Blood Pressure
- Potential Health Benefits of High-Fat Dinners
- The Role of Healthy Fats in Nutrient Absorption
- Possible Benefits for Brain Health and Cognitive Function
- Questions and answers
Understanding the Link Between High-Fat Dinners and Health
Exploring the Relationship between Dinners Rich in Fat and Overall Well-being
Examining the Association between Meals Containing High Levels of Fat and Individual Health Conditions
Investigating the Interplay between High-Fat Dinners and Physical and Mental Well-being
|
Unraveling the Connection between High-Fat Dinner Choices and Health Outcomes Analyzing the Impact of Consuming Fat-Heavy Dinners on Human Health |
Probing into the Relationship between Dinners High in Fat Content and Their Implications on Health Examining the Effects of High-Fat Dinners on Overall Wellness and Potential Consequences |
Efforts to comprehend the association between high-fat dinners and health have gained increasing attention in recent years. Researchers strive to unravel the complex link between dietary choices and various aspects of well-being. This section aims to explore the potential implications of consuming meals rich in fat, investigating the effects it may have on physical and mental health. By examining existing scientific studies and considering view points from medical professionals, individuals can enhance their understanding of the potential risks and benefits associated with high-fat dinners.
The Role of Fat Consumption in Overall Well-being
Exploring the significance of fat consumption in relation to a person’s overall well-being stems from the need to understand the intricate complexities of dietary choices and their potential effects on one’s health and quality of life. By delving into the role of fat consumption, we can gain insight into the various aspects that it encompasses and evaluate its implications on multifaceted dimensions of well-being.
Examining the intricate relationship between fat consumption and overall well-being involves considering its impact on various physiological, psychological, and emotional aspects. Understanding the potential benefits and risks associated with the consumption of fats requires a comprehensive exploration of the influence these dietary choices have on important factors such as physical health, mental well-being, and overall satisfaction with one’s lifestyle.
- Physical Health: Fat consumption can impact bodily functions, including energy production, hormone regulation, and nutrient absorption. It is crucial to assess the potential effects of dietary fats on factors such as cardiovascular health, weight management, and the prevention of chronic diseases.
- Mental Well-being: Exploring the relationship between fat consumption and mental health becomes essential when considering the potential impact on mood, cognitive function, and overall mental well-being. Analyzing the influence of dietary fats on mental health parameters can provide valuable insights into maintaining optimal cognitive performance and emotional stability.
- Lifestyle Satisfaction: The link between fat consumption and overall satisfaction with one’s lifestyle extends beyond physical and mental health. Evaluating the potential impact of dietary choices, including fat consumption, on factors such as dietary satisfaction, food enjoyment, and adherence to dietary patterns can contribute to an individual’s overall sense of well-being and long-term dietary compliance.
Given the complexity of the topic, exploring the multifaceted relationship between fat consumption and overall well-being necessitates a comprehensive analysis of various scientific studies, dietary guidelines, and expert opinions. By gaining a deeper understanding of the role of fat consumption, individuals can make informed choices regarding their dietary habits and optimize their overall well-being.
The Effect of High-Fat Dinners on Body Weight and Obesity
Exploring the influence of consuming meals high in fat on body weight and the development of obesity is the focal point of this research. A comprehensive investigation into the potential consequences of indulging in such meals aims to shed light on the relationship between high-fat dinners and their impact on body weight management.
When individuals regularly consume high-fat dinners, there is evidence suggesting a correlation with increased body weight and a higher risk of developing obesity. The excessive intake of fatty foods can lead to weight gain due to their calorie-dense nature and a potential disruption in the body’s metabolism. Such meals often contain high levels of saturated fats, which are associated with a higher risk of obesity and related health conditions.
- One potential mechanism contributing to the impact of high-fat dinners on body weight is their influence on satiety and hunger. Studies have shown that meals rich in fats tend to be less satiating compared to those with a balanced macronutrient composition. As a result, individuals may consume larger portions or additional snacks, leading to an overall increase in daily calorie intake.
- In addition to affecting satiety, high-fat dinners can also play a role in altering the body’s fat storage and utilization. Consuming excessive amounts of fat prompts the body to prioritize storing and retaining fat, potentially contributing to weight gain and the accumulation of adipose tissue.
- Furthermore, the consumption of high-fat dinners can impact various hormones involved in appetite regulation, such as leptin and ghrelin. Imbalances in these hormones can disrupt the body’s ability to regulate hunger and fullness cues, potentially leading to overeating and a higher risk of weight gain.
Addressing the effect of high-fat dinners on body weight and obesity is essential for understanding the potential risks associated with dietary choices. By investigating the mechanisms through which such meals can influence weight gain and obesity development, it becomes possible to develop strategies for promoting healthier eating habits and weight management.
Potential Health Risks Associated with High-Fat Dinners

Exploring the potential hazards linked to consuming meals with a high-fat content can provide valuable insights into their impact on health. When individuals indulge in dinners abundant in fats, various health risks may emerge, affecting overall well-being. This section highlights some of the possible negative effects that may arise from the consumption of high-fat dinners.
1. Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: Regularly consuming high-fat dinners can contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases such as heart attacks and strokes. The consumption of excessive saturated and trans fats can raise cholesterol levels, leading to the buildup of plaque in arteries, thus increasing the risk of these potentially life-threatening conditions.
2. Weight Gain and Obesity: High-fat dinners often consist of calorie-dense foods that can promote weight gain and potentially lead to obesity. Fatty meals tend to be more energy-dense, providing more calories per gram compared to protein or carbohydrates. Moreover, these meals can be less satiating, making individuals more prone to overeating and causing an imbalance in energy intake.
3. Impaired Blood Sugar Control: The consumption of high-fat dinners can negatively impact blood sugar control. Foods rich in unhealthy fats can lead to insulin resistance, preventing the body from effectively utilizing and regulating blood sugar levels. In the long run, this can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
4. Digestive Issues: High-fat dinners can also pose risks to digestive health. Fatty foods are generally harder to digest, requiring a more significant effort from the digestive system. This can result in discomfort, bloating, and potentially impact the absorption of essential nutrients, leading to deficiencies over time.
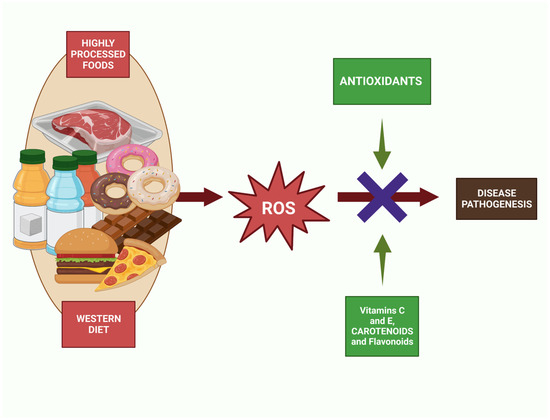
5. Increased Inflammation: The consumption of high-fat dinners, particularly those containing unhealthy fats, can trigger inflammatory responses within the body. Chronic inflammation is associated with various health issues, including an increased risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders.
It is crucial to be mindful of the potential health risks associated with high-fat dinners. Striving for a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrients can help mitigate these risks and promote overall well-being.
Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases

Consuming a rich and fatty evening meal has been linked to a heightened susceptibility to cardiovascular diseases. This section explores the potential negative effects that are associated with a diet high in fat content, examining the impact it may have on the cardiovascular system.
1. Elevated cholesterol levels: Regular intake of high-fat meals can lead to increased levels of cholesterol in the blood. This can contribute to the build-up of plaque in the arteries, restricting blood flow and potentially leading to various cardiovascular conditions.
2. Inflammation: A diet high in fat can trigger chronic inflammation within the body, particularly in the blood vessels and arteries. This inflammation can damage the inner lining of the blood vessels, making them more susceptible to the development of atherosclerosis and increasing the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
3. Impaired endothelial function: Endothelial cells play a crucial role in maintaining the health of blood vessels. Consuming a high-fat dinner can impair the function of these cells, affecting the vasodilation process and potentially leading to increased blood pressure and compromised cardiovascular function.
4. Oxidative stress: A high-fat meal can induce oxidative stress in the body, causing an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants. Over time, this imbalance can lead to damage to the blood vessels and arteries, further promoting the development of cardiovascular diseases.
5. Increased risk of obesity: Regular consumption of high-fat dinners can contribute to weight gain and the development of obesity. Obesity is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, as it is associated with other metabolic abnormalities such as insulin resistance, hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
6. Impaired lipid metabolism: A high-fat diet can disrupt the normal metabolism of lipids in the body, leading to elevated levels of triglycerides and LDL cholesterol. These alterations in lipid profile can increase the risk of atherosclerosis and consequently raise the likelihood of cardiovascular diseases.
- To summarize, a high-fat dinner can have detrimental effects on cardiovascular health by increasing cholesterol levels, promoting inflammation, impairing endothelial function, inducing oxidative stress, contributing to obesity, and disrupting lipid metabolism.
It is crucial to consider the long-term impact of dietary choices, as addressing and modifying high-fat dinner habits may help mitigate the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
Impacts on Cholesterol Levels and Blood Pressure
Examining the influence of a rich, lipid-laden meal on our overall well-being reveals intriguing effects on two vital physiological markers: cholesterol levels and blood pressure. Unveiling the consequences of consuming a highly saturated dinner sheds light on how it may perturb our body’s lipid profile and vascular dynamics. Let us delve into these intricate ramifications and explore the intricate relationship between dietary fat intake and these key elements of our cardiovascular health.
Cholesterol Levels: The consumption of a meal abundant in fat can induce noteworthy alterations in cholesterol levels, particularly with regards to low-density lipoprotein (LDL), commonly referred to as bad cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein (HDL), known as good cholesterol. While elevated LDL levels have been associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease, the intricate interplay between dietary fats and cholesterol metabolism remains complex and multifaceted. By teasing apart these intricate associations, we aim to shed light on the delicate balance between fat intake, cholesterol synthesis, and their potential impact on the overall lipid profile.
Blood Pressure: The influence of a high-fat dinner on blood pressure levels presents an interesting avenue of investigation in understanding the immediate and long-term effects on cardiovascular health. Numerous studies have demonstrated an acute rise in blood pressure after consumption of a fatty meal, suggesting a transient physiological response to high-fat intake. However, the long-term implications on blood pressure regulation, endothelial function, and vascular health require further exploration. Understanding the underlying mechanisms that link dietary fat intake to alterations in blood pressure can provide valuable insights into the optimization of our dietary patterns to support cardiovascular well-being.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the impacts of a high-fat dinner on cholesterol levels and blood pressure, we can inform dietary recommendations and interventions aimed at reducing cardiovascular risk. Designing targeted strategies to mitigate the potential adverse effects while harnessing any potential benefits of a high-fat meal is crucial in promoting optimal health outcomes.
Potential Health Benefits of High-Fat Dinners
Exploring the Potential Positive Effects of Rich Fat Content in Evening Meals
Indulging in a nourishing and flavorful evening meal rich in healthy fats may unveil an array of potential health benefits. Research suggests that consuming a substantial amount of dietary fat at dinnertime can contribute to various favorable outcomes. Although traditionally viewed as detrimental to health, high-fat dinners might actually promote satiety, enhance nutrient absorption, and support overall well-being.
One potential advantage of incorporating high-fat dinners into a balanced diet is the potential for increased satiety. Foods containing healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, tend to be more filling and satisfying, allowing individuals to feel content and less likely to overeat. This may aid in weight management and reduce the risk of overindulging on unhealthy snacks or desserts later in the evening.
In addition, having a high-fat dinner could potentially enhance the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and other nutrients. Fat plays a crucial role in the absorption of vitamins A, D, E, and K, which are essential for various bodily functions. By including healthy fats in evening meals, individuals may optimize the assimilation of these vital nutrients, aiding overall health and supporting proper organ functioning.
Furthermore, studies have shown that certain healthy fats, such as omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, can provide various benefits for cardiovascular health. These beneficial fats have been associated with reducing inflammation, improving cholesterol levels, and lowering the risk of heart disease. Including such fats in high-fat dinners may contribute to a well-balanced cardiovascular profile and potentially decrease the incidence of heart-related complications.
While further investigation is necessary to fully comprehend the extent of the potential health benefits of high-fat dinners, early research highlights promising outcomes. Incorporating a variety of healthy fats into evening meals might offer advantages such as increased satiety, enhanced nutrient absorption, and improved cardiovascular health. Nevertheless, it is essential to consider individual dietary needs and consult healthcare professionals to ensure a well-rounded and personalized approach to nutrition.
The Role of Healthy Fats in Nutrient Absorption
When it comes to the intake of a nourishing meal, the incorporation of healthy fats plays a vital role in facilitating optimum nutrient absorption. These beneficial fats, which are commonly found in foods such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are instrumental in aiding the body in absorbing essential vitamins and minerals. Through their unique properties, healthy fats enhance the bioavailability of nutrients, allowing for their efficient utilization by the body.
A critical aspect of healthy fats lies in their ability to enhance the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, such as vitamins A, D, E, and K. These vitamins, which are crucial for various bodily functions, including immune system health, bone maintenance, and antioxidant protection, require the presence of dietary fat to be absorbed effectively. Healthy fats act as carriers, transporting these vitamins across the intestinal lining and into the bloodstream, where they can exert their beneficial effects.
Beyond vitamins, healthy fats also play a significant role in the absorption of other essential nutrients, such as carotenoids and phytochemicals. Carotenoids, which are plant pigments responsible for the vibrant colors in fruits and vegetables, have been associated with numerous health benefits, including reducing the risk of chronic diseases. However, their absorption is greatly enhanced when consumed alongside healthy fats. Similarly, phytochemicals, which are bioactive compounds found in plant-based foods, exhibit greater bioavailability when combined with dietary fats.
Furthermore, the inclusion of healthy fats in a meal not only enhances nutrient absorption but also contributes to satiety and overall diet satisfaction. Unlike unhealthy fats, which can lead to weight gain and negative health outcomes, healthy fats provide a sense of fullness and promote balanced energy levels. This satiating effect helps prevent overeating and supports the maintenance of a balanced diet.
| Benefits of Healthy Fats in Nutrient Absorption: |
|---|
| Enhancement of fat-soluble vitamin absorption |
| Improved uptake of carotenoids and phytochemicals |
| Promotion of satiety and balanced energy levels |
Possible Benefits for Brain Health and Cognitive Function
Exploring the potential advantages associated with the consumption of a high-fat meal can also extend to the realm of brain health and cognitive function. By delving into this particular aspect, researchers have started to uncover various noteworthy findings that are worth considering.
- Aiding in Brain Development: Consuming a high-fat dinner has been hypothesized to contribute positively to brain development, particularly during early stages of life. It is believed that specific types of fats can enhance neural connections and help in the formation of a healthy brain structure.
- Promoting Cognitive Performance: Certain components found in high-fat meals have been associated with potential benefits for cognitive performance. Studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids, for instance, may enhance memory, attention, and overall cognitive functioning.
- Protective Effects Against Age-Related Decline: Some research suggests that the consumption of certain fats, such as those found in nuts and avocados, may have protective effects against age-related cognitive decline. These fats are thought to support brain health and potentially reduce the risk of cognitive impairments as individuals age.
- Substantial Nutrient Support: High-fat dinners that incorporate nutrient-rich sources, like fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, can provide essential nutrients such as vitamin E, which plays a vital role in maintaining brain health. These nutrients act as important building blocks for brain tissues and assist in overall cognitive functions.
- Improving Mood and Mental Well-being: Emerging evidence hints at a link between the consumption of certain fats and improved mood and mental well-being. A diet rich in healthy fats, such as those found in olive oil, may potentially enhance mood regulation and contribute to reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Although further research is needed to fully understand the specific mechanisms and long-term effects associated with a high-fat dinner on brain health and cognitive function, these preliminary findings offer interesting insights into the potential benefits that warrant further investigation.
Questions and answers
Is it true that eating a high-fat dinner can be harmful to your health?
Yes, according to the study mentioned in the article, consuming a high-fat dinner can have negative impacts on health. It can lead to increased inflammation, impaired blood vessel function, and an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
What are the potential benefits of consuming a high-fat dinner?
Although a high-fat dinner is generally associated with negative health effects, some studies suggest that it may have certain benefits. For example, a meal rich in healthy fats can provide a feeling of satiety, help maintain stable blood sugar levels, and improve nutrient absorption.
Which types of fats are considered healthy for consumption?
Healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, are recommended for consumption. These include fats found in avocados, nuts, seeds, fatty fish, and olive oil. These fats have been associated with various health benefits, including improved heart health and brain function.
Does consuming a high-fat dinner affect sleep quality?
Yes, studies have shown that consuming a heavy meal high in fat before bedtime can negatively impact sleep quality. It can lead to indigestion, heartburn, and discomfort, which can disrupt normal sleep patterns and affect the overall quality of sleep.
Can a high-fat dinner contribute to weight gain?
Yes, consuming a high-fat dinner can contribute to weight gain. Fats are calorie-dense, and if a person consistently consumes more calories than they burn, it can lead to weight gain over time. Additionally, high-fat meals tend to be less filling, which can result in overeating and further weight gain.
What are the potential risks of consuming a high-fat dinner?
Consuming a high-fat dinner can have several potential risks for health. Firstly, it can lead to weight gain and increase the risk of obesity. High-fat diets are often high in calories, and when these excess calories are not burned off, they can be stored as fat. Secondly, a high-fat dinner can negatively impact cardiovascular health by raising cholesterol levels and increasing the risk of heart disease. Lastly, a high-fat dinner can cause digestive issues such as indigestion, bloating, and constipation.
Are there any benefits to consuming a high-fat dinner?
While high-fat dinners are generally associated with risks, there can be certain benefits as well. Firstly, consuming healthy fats such as avocados, nuts, and olive oil can contribute to better brain function and improved cognitive health. Secondly, fats are essential for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K, so consuming a small amount of healthy fats in the dinner can enhance the body’s ability to absorb these important nutrients.
What are some examples of high-fat dinner options?
Some examples of high-fat dinner options include cheeseburgers, steak with butter sauce, fried chicken, creamy pasta dishes, and deep-fried foods like french fries. These meals often contain high levels of saturated and trans fats, which can contribute to health problems if consumed in excess.
How does a high-fat dinner affect cholesterol levels in the body?
A high-fat dinner can lead to an increase in cholesterol levels, particularly LDL or bad cholesterol. Foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as fried foods and fatty meats, can raise LDL cholesterol levels in the blood. This increase in LDL cholesterol can contribute to the development of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Is it recommended to completely avoid fats in dinner for good health?
No, it is not recommended to completely avoid fats in dinner for good health. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and oily fish, are important for overall health. These fats provide essential fatty acids, support brain function, and help with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. The key is to consume fats in moderation and choose healthier options rather than those high in saturated and trans fats.

I’m Jake Morgan, a 23-year-old Keto diet and fitness expert from sunny California. Passionate about helping you achieve your dream body with the right nutrition and workout. Connect or consult via Telegram.