Uncovering the intricate relationship between cortisol and weight gain has become a subject of considerable interest for researchers and health enthusiasts alike. Through tireless exploration, scientists have endeavored to shed light on the profound impact that this hormone exerts on metabolism, highlighting its potential role in shaping body composition.
Delving deep into the physiological mechanisms controlled by cortisol, we aim to unravel the intricate network of interactions that governs the body’s response to stress. Often referred to as the stress hormone, cortisol plays a pivotal role in modulating a wide array of processes, ranging from carbohydrate metabolism to inflammation and immune response. Through its multifaceted influence, cortisol has been implicated in the development of weight gain and its associated outcomes.
Steering away from conventional notions, this article aims to challenge prevailing beliefs and foster a comprehensive understanding of the connections between cortisol and weight gain. By examining the intricate interplay between cortisol levels and various metabolic pathways, we can begin to grasp the underlying mechanisms that contribute to alterations in body weight and composition.
- The Relationship Between Cortisol and Weight Gain
- Understanding the Impact of Cortisol on Metabolism
- The Role of Cortisol in Fat Storage
- The Effect of Elevated Cortisol Levels on Appetite
- The Influence of Stress on Cortisol Production
- Managing Cortisol Levels for Weight Management
- Stress Reduction Techniques to Lower Cortisol
- The Importance of Regular Exercise for Cortisol Regulation
- The Role of Nutrition in Balancing Cortisol Levels
- Questions and answers
The Relationship Between Cortisol and Weight Gain
Exploring the connection between cortisol and weight gain uncovers an intricate interplay within the body’s metabolic processes. Understanding how this hormone affects weight regulation sheds light on the potential factors contributing to weight gain and the challenges in maintaining a healthy weight.
Cortisol, also known as the stress hormone, plays a vital role in our body’s response to stress and helps regulate various physiological functions. While cortisol is necessary for our survival, chronically elevated levels can lead to adverse effects on our metabolism and overall health.
Research suggests that high levels of cortisol can influence weight gain by affecting both the quantity and distribution of fat storage in the body. Additionally, cortisol can impact appetite, leading to increased cravings for calorie-dense foods and a preference for comfort foods high in sugar and fat.
Furthermore, cortisol has been found to increase insulin resistance, impair glucose metabolism, and promote fat accumulation, particularly in the abdominal region. This abdominal fat, also known as visceral fat, is associated with a higher risk of developing chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disorders and type 2 diabetes.
Understanding the relationship between cortisol and weight gain is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage and prevent obesity. Implementing stress-reduction techniques, practicing mindful eating, engaging in regular physical activity, and prioritizing quality sleep are all potential approaches to mitigate the effects of cortisol on weight regulation.
In conclusion, the complex relationship between cortisol and weight gain highlights the importance of maintaining a balanced cortisol level for overall health and weight management. By addressing factors that contribute to stress and implementing healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can better navigate the impact of cortisol on their body composition and maintain a healthy weight.
Understanding the Impact of Cortisol on Metabolism
Diving into the intricate relationship between cortisol and metabolism sheds light on the profound influence this hormone has on our body’s fat storage, energy utilization, and overall metabolic processes. Exploring the intricate interplay between cortisol levels and metabolic functions reveals a captivating connection that deepens our comprehension of the intricate nature of the human body.
Examining the Role of Cortisol in Energy Regulation:
Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, plays a crucial role in regulating energy balance within the body. While it is commonly associated with stress responses, cortisol also influences metabolism both directly and indirectly. By studying the mechanisms by which cortisol affects energy regulation, scientists have unraveled the multifaceted impact it has on metabolism.
The Relationship Between Cortisol and Fat Storage:
One of the notable effects of cortisol on metabolism is its ability to stimulate fat storage. When cortisol levels rise, our body’s ability to break down fats for energy is hindered, leading to increased accumulation of adipose tissue. Understanding the underlying mechanisms at play in this process provides key insights into the factors contributing to weight gain and obesity.
Cortisol’s Influence on Glucose Metabolism:
In addition to its role in fat storage, cortisol also affects glucose metabolism. Cortisol assists in maintaining blood sugar levels, ensuring that our cells have an adequate supply of glucose for energy production. However, high levels of cortisol can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism. This disruption can potentially contribute to the development of conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
The Complex Interactions Between Cortisol and Appetite:
An often-overlooked aspect of cortisol’s impact on metabolism is its influence on appetite regulation. Elevated cortisol levels have been found to increase appetite, particularly for high-calorie, nutrient-poor foods. This connection between cortisol and cravings provides insight into the role of stress in unhealthy eating habits and weight management.
The Role of Cortisol in Sleep and Circadian Rhythm:
Cortisol levels follow a daily pattern, peaking in the morning and gradually declining throughout the day. Disruptions in this natural rhythm, such as those caused by stress or shift work, can lead to dysregulation of cortisol production. Understanding the intricate relationship between cortisol, sleep, and circadian rhythm provides a holistic view of metabolism and its susceptibility to external factors.
Conclusion:
Delving into the impact of cortisol on metabolism reveals a complex web of interactions that extend far beyond its association with stress. By understanding the multifaceted role cortisol plays in energy regulation, fat storage, glucose metabolism, appetite, and sleep, we can gain valuable insights into the potential underlying causes of weight gain and metabolic disorders. Equipped with this knowledge, further research and potential interventions can be developed to optimize metabolic health and overall well-being.
The Role of Cortisol in Fat Storage
Cortisol plays a significant role in the accumulation of body fat. This hormone influences the storage and distribution of fat throughout the body, making it an important factor in understanding weight management and metabolism.
One of the primary effects of cortisol on fat storage is its ability to increase the activity of lipoprotein lipase (LPL), an enzyme that plays a crucial role in the uptake and storage of triglycerides in fat cells. When cortisol levels are elevated, LPL activity is stimulated, leading to an increased accumulation of fat in adipose tissue.
Additionally, cortisol promotes the development and growth of visceral fat, which refers to the fat that surrounds internal organs in the abdominal cavity. Visceral fat is known to be more metabolically active and has been linked to increased health risks such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
In times of stress or chronic stress, cortisol levels tend to remain elevated, resulting in a continuous increase in fat storage. This can lead to weight gain over time, especially in the abdominal area. The accumulation of excess fat in this region has been associated with a higher risk of developing metabolic disorders.
To manage cortisol levels and its impact on fat storage, it is important to adopt healthy lifestyle habits such as regular exercise, stress reduction techniques, and a balanced diet. These measures can help regulate cortisol secretion and potentially lead to healthier fat distribution and weight management.
- Understanding cortisol’s role in fat storage is key to addressing weight management challenges.
- Cortisol influences the activity of lipoprotein lipase, which affects the uptake and storage of fat in adipose tissue.
- Elevated cortisol levels promote the growth of visceral fat, which is associated with increased health risks.
- Chronic stress can lead to prolonged elevation of cortisol levels, contributing to continuous fat storage.
- Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including exercise, stress reduction, and a balanced diet, can help regulate cortisol levels and support weight management.
The Effect of Elevated Cortisol Levels on Appetite
Elevated levels of the stress hormone cortisol have been found to significantly influence an individual’s appetite. When cortisol levels are high, the body’s natural response is to increase its hunger signals, leading to a potential increase in food intake. This phenomenon can have an impact on overall energy balance and potentially contribute to weight gain.
Researchers have observed that elevated cortisol levels can alter the regulation of key appetite hormones in the body, including ghrelin and leptin. Ghrelin, often referred to as the hunger hormone, stimulates appetite, while leptin, known as the satiety hormone, helps to regulate feelings of fullness. When cortisol levels are elevated, the balance between ghrelin and leptin can be disrupted, resulting in increased hunger and a decreased sense of satiety.
In addition to directly affecting appetite hormones, elevated cortisol levels can also influence food preferences. Studies have shown that individuals with higher cortisol levels tend to crave energy-dense foods that are high in fat, sugar, and salt. This preference for unhealthy foods can further contribute to weight gain and potentially lead to the development of poor eating habits.
Furthermore, stress-induced cortisol elevation has been associated with emotional eating. During times of stress, individuals may turn to food as a coping mechanism, seeking comfort and distraction from their emotions. This emotional eating, combined with the effects of cortisol on appetite regulation, can create a cycle of overeating and make weight management more challenging.
Understanding the effect of elevated cortisol levels on appetite is essential for developing strategies to maintain a healthy weight. Lifestyle interventions, such as stress management techniques, regular exercise, and a balanced diet, can help regulate cortisol levels and minimize its impact on appetite. By acknowledging the link between cortisol and appetite, individuals can make informed choices to support their overall well-being and achieve a healthier relationship with food.
The Influence of Stress on Cortisol Production
Stress has a significant impact on the production of cortisol, a hormone involved in various metabolic processes within the body. By examining the relationship between stress and cortisol, we can gain a deeper understanding of how stress levels affect metabolism and potentially contribute to weight gain.
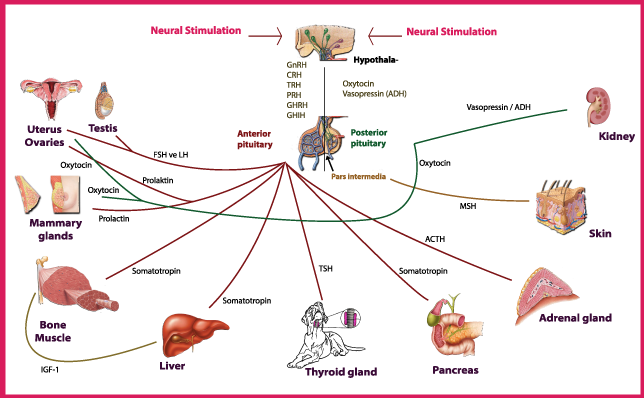
When the body experiences stress, whether it be physical or psychological, it triggers the release of cortisol from the adrenal glands. Cortisol is known as the stress hormone and plays a crucial role in the body’s response to stress. It helps regulate blood pressure, immune function, and the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
Chronic stress can lead to chronically elevated cortisol levels, which can have detrimental effects on metabolism. One way that cortisol influences metabolism is by promoting the breakdown of muscle tissue. This can result in a decrease in lean muscle mass and a potential increase in body fat, as muscle tissue is metabolically active and helps burn calories even at rest.
Cortisol also has an impact on appetite and food choices. High levels of cortisol can stimulate cravings for unhealthy, high-calorie foods, particularly those that are high in sugar and fat. Stress eating, also known as emotional eating, is a common response to stress that can contribute to weight gain. Additionally, cortisol can affect how the body stores and distributes fat, with a tendency to store fat in the abdominal region, which is associated with an increased risk of various health conditions.
It is important to note that the relationship between stress, cortisol, and weight gain is complex and can vary among individuals. Some individuals may be more sensitive to the effects of cortisol, while others may have different coping mechanisms for stress. Nevertheless, understanding the influence of stress on cortisol production can provide valuable insights into the role of hormones in metabolism and weight management.
| Effects of Stress on Cortisol Production |
|---|
| 1. Release of cortisol in response to stress |
| 2. Impact of chronically elevated cortisol levels on metabolism |
| 3. Influence of cortisol on muscle tissue breakdown and body fat accumulation |
| 4. Connection between cortisol, stress eating, and weight gain |
| 5. Individual variations in the response to cortisol and stress |
Managing Cortisol Levels for Weight Management

Evaluating the impact of cortisol on body weight is pivotal in developing effective weight management strategies. This section focuses on techniques and lifestyle modifications aimed at optimizing cortisol levels to support weight maintenance and achieve successful weight loss.
One crucial aspect of managing cortisol levels is adopting stress-reducing techniques. Chronic stress can elevate cortisol levels, leading to increased abdominal fat and weight gain. Implementing stress management practices such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help regulate cortisol production and promote overall well-being.
In addition to stress reduction, prioritizing a balanced and nutritious diet can also play a significant role in managing cortisol levels. Consuming foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and vitamins can support adrenal health and minimize cortisol spikes. Moreover, incorporating regular meals and avoiding prolonged fasting can help stabilize cortisol levels and prevent excessive weight gain.
Ensuring adequate sleep is another essential factor in maintaining healthy cortisol levels. Lack of sleep can disrupt the body’s natural cortisol rhythm, leading to increased appetite and cravings for unhealthy foods. Establishing a consistent sleep routine and aiming for at least 7-8 hours of quality sleep can contribute to cortisol regulation and support weight management efforts.
Physical activity and exercise should also be a part of any cortisol management plan. Engaging in regular moderate-intensity workouts can help reduce cortisol levels and promote the release of endorphins, which are known to enhance mood and alleviate stress. Combining aerobic exercise, strength training, and activities like yoga or tai chi can be particularly beneficial for cortisol management and weight control.
Lastly, fostering a positive and supportive environment is vital for cortisol management and overall weight management success. Surrounding oneself with a network of friends, family, or support groups can provide encouragement and help mitigate stress levels. Engaging in hobbies, practicing self-care, and cultivating a healthy work-life balance are also essential in managing cortisol and maintaining a healthy weight.
By implementing these strategies in daily life, individuals can effectively manage cortisol levels, curb weight gain, and achieve their desired weight management goals. It is important to remember that everyone’s cortisol levels and responses may vary, and seeking professional guidance is advised for personalized cortisol management plans.
Stress Reduction Techniques to Lower Cortisol
In today’s fast-paced society, stress has become an all too familiar aspect of our daily lives. It affects our physical and mental well-being, and can even play a role in weight gain and metabolic changes. Understanding how to effectively manage stress is crucial for maintaining a healthy balance.
Here are some stress reduction techniques that can help lower cortisol levels and promote overall well-being:
- Practice mindfulness meditation: Engaging in regular mindfulness meditation can help reduce stress levels and lower cortisol. Taking the time to focus on the present moment and cultivate a sense of inner calm can have a profound impact on overall well-being.
- Engage in regular exercise: Physical activity has been shown to reduce cortisol levels and improve mood. Whether it’s going for a jog, practicing yoga, or participating in a team sport, finding a form of exercise that you enjoy can be a powerful tool in managing stress.
- Get enough sleep: Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to increased cortisol levels, so it’s important to prioritize getting enough quality sleep. Establishing a regular sleep routine and creating a relaxing bedtime routine can help improve sleep quality and reduce stress.
- Connect with nature: Spending time outdoors and connecting with nature has been shown to reduce stress levels and lower cortisol. Whether it’s taking a walk in the park, going for a hike, or simply spending time in your garden, immersing yourself in nature can provide a much-needed respite from daily stressors.
- Practice deep breathing exercises: Deep breathing exercises can activate the body’s relaxation response and help lower cortisol levels. Taking slow, deep breaths and focusing on your breath can help calm the mind and reduce stress.
By incorporating these stress reduction techniques into your daily routine, you can effectively lower cortisol levels and promote overall well-being. Remember, managing stress is a key component of maintaining a healthy lifestyle and achieving optimal metabolic function.
The Importance of Regular Exercise for Cortisol Regulation
Exercise plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of cortisol levels in the body. Engaging in regular physical activity is essential for effectively regulating this hormone, which is often associated with weight gain and other metabolic factors. By incorporating consistent exercise into your routine, you can help manage cortisol levels and promote overall well-being.
Regular exercise serves as a natural way to modulate cortisol production and release. Physical activity elicits various physiological responses in the body, including the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which is responsible for cortisol secretion. Through regular exercise, this intricate system can be regulated, ensuring optimal cortisol levels and preventing potential imbalances.
Engaging in aerobic activities such as running, swimming, or cycling has been shown to have a positive impact on cortisol regulation. These types of exercises stimulate the production of endorphins, which are known as feel-good hormones, and help reduce cortisol levels. Incorporating strength training into your routine, such as weightlifting or resistance exercises, can also assist in cortisol regulation by promoting muscle growth and enhancing metabolic function.
- Include at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking or dancing, in your daily routine to help regulate cortisol levels.
- Participate in activities that you enjoy and find motivating, as this can help reduce stress and consequently influence cortisol regulation.
- Consider incorporating relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises into your exercise routine, as these practices have been shown to effectively reduce cortisol levels.
- Remember that consistency is key when it comes to exercise and cortisol regulation. Regular physical activity yields more substantial and lasting effects on your overall health and hormone balance.
In conclusion, regular exercise is a vital component in maintaining healthy cortisol levels and promoting overall well-being. By incorporating aerobic activities, strength training, and relaxation techniques into your routine, you can effectively regulate cortisol, thereby reducing the risk of weight gain and other metabolic imbalances. Prioritizing exercise as part of your daily routine can have significant benefits on both physical and mental health.
The Role of Nutrition in Balancing Cortisol Levels

Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy balance of cortisol, a hormone involved in various metabolic processes. By making mindful dietary choices and adopting healthy eating habits, individuals can positively impact their cortisol levels and support overall well-being.
Consuming a well-balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and fresh fruits and vegetables can help regulate cortisol production. These nutrient-dense foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote hormonal balance and reduce the risk of cortisol-related weight gain.
Incorporating foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish, nuts, and seeds, can also aid in cortisol regulation. Omega-3 fatty acids possess anti-inflammatory properties and help counteract the negative effects of chronic stress on the body, thereby supporting healthy cortisol levels.
Furthermore, managing carbohydrate intake is essential for cortisol control. Choosing complex carbohydrates, like whole grains and legumes, over refined sugars and processed foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels and prevent spikes in cortisol production. This approach assists in maintaining a consistent cortisol profile throughout the day, promoting a more balanced metabolism.
Additionally, staying adequately hydrated is vital for cortisol regulation. Drinking enough water supports optimal cortisol function and helps flush out toxins from the body. Avoiding excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption is also recommended, as they can disrupt cortisol production and contribute to increased stress levels.
Lastly, adopting stress-reducing techniques, such as mindfulness practices, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep, can complement a nutritious diet in balancing cortisol levels. When combined with proper nutrition, these lifestyle factors work synergistically to support a healthy cortisol response and promote overall metabolic harmony.
Questions and answers
What is cortisol and how does it affect weight gain?
Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress. It can affect weight gain by increasing appetite, promoting the storage of fat, and inhibiting the breakdown of stored fat.
Can high levels of cortisol lead to weight gain?
Yes, high levels of cortisol can lead to weight gain. When cortisol is consistently elevated, it can disrupt the balance of other hormones involved in metabolism, leading to increased appetite and the accumulation of fat in the abdominal area.
Are there any natural ways to lower cortisol levels?
Yes, there are several natural ways to lower cortisol levels. These include practicing stress-reducing techniques such as yoga and meditation, getting regular exercise, ensuring an adequate amount of sleep, and maintaining a healthy diet.
Are there any medications or supplements that can help regulate cortisol levels?
While there are medications available that can help regulate cortisol levels in certain medical conditions, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before taking any medications or supplements. They can provide guidance based on individual circumstances.
Can cortisol levels affect metabolism in other ways besides weight gain?
Yes, cortisol levels can affect metabolism in other ways besides weight gain. High cortisol levels can lead to muscle breakdown, reduced bone density, impaired immune function, and increased blood pressure.
Does cortisol affect weight gain?
Yes, cortisol can indeed affect weight gain. When cortisol levels in the body are consistently high, it can lead to an increase in appetite and cravings for unhealthy, high-calorie foods. Additionally, cortisol promotes the storage of fat, especially in the abdominal area.
How does cortisol affect metabolism?
Cortisol influences metabolism by stimulating the breakdown of proteins into amino acids, which can be converted into glucose for energy. This process is known as gluconeogenesis. However, prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol can disrupt normal metabolism and lead to weight gain.
What are some negative effects of high cortisol levels on weight?
High cortisol levels can have several negative effects on weight. Firstly, it can increase the deposition of fat in the abdominal region, leading to an increase in waist circumference. Secondly, cortisol can stimulate the production of insulin, which can result in higher blood sugar levels and weight gain. Lastly, elevated cortisol levels can disrupt the balance of other hormones involved in weight regulation.
Can stress cause weight gain through cortisol?
Yes, stress can indeed cause weight gain through the release of cortisol. When we experience stress, our body’s natural response is to produce cortisol. Chronic stress can lead to continuously high cortisol levels, which can result in increased appetite, cravings for unhealthy foods, and ultimately weight gain.
Are there any ways to lower cortisol levels and prevent weight gain?
Yes, there are several effective ways to lower cortisol levels and prevent weight gain. Engaging in regular physical exercise, practicing stress management techniques such as meditation or yoga, getting enough sleep, and maintaining a healthy diet with balanced meals can all help in reducing cortisol levels and promoting a healthy weight.