Embarking on a profound exploration of our culinary world, we embark on a voyage that delves into the profound significance of sustainable agricultural practices. This journey unraveling the complexities of environmentally friendly nutrition has paved the way for a paradigm shift in the way we perceive our food.
Through conscious choices in cultivation and production, green nourishment offers myriad advantages. From the vast expanse of lush fields, where vibrant crops are nurtured and harvested, to the artistry of transforming these freshly plucked fruits and vegetables into mouthwatering dishes, the path from farm to plate is adorned with sustainable practices that coexist harmoniously with nature.
By embracing an eco-conscious approach, we not only safeguard the Earth’s natural resources but also foster the well-being of both present and future generations. With the instrumental use of innovative techniques and cultivation methods, these green foods promise far-reaching benefits that transcend mere sustenance.
- Exploring the Sustainable Benefits of Green Foods
- The Importance of Sustainable Food Production
- Efficient Resource Utilization
- Reduced Environmental Impact
- From Farm to Plate: The Journey of Green Foods
- Sustainable Agriculture Practices
- Transparent Supply Chains
- Nutritional Benefits of Green Foods
- Embracing a Greener and Healthier Future
- Sustainable Food Choices for Individuals
- Questions and answers
Exploring the Sustainable Benefits of Green Foods
Delving into the myriad of advantages offered by eco-friendly and nourishing green foods, this section takes a deep dive into the sustainable benefits that these natural resources bring to our health and the environment. By embracing the consumption of plant-based products, individuals can unlock a plethora of positive outcomes, meticulously nurtured from the seed to the table, without compromising the delicate balance of nature.
The Importance of Sustainable Food Production
Recognizing the significance of sustainable food production is vital in cultivating a healthier and more environmentally-conscious food system. By adopting sustainable practices from the initial stages of cultivation all the way to the final delivery, we can minimize the negative impacts on the environment while ensuring a stable supply of nutritious food for future generations.
1. Preserving Biodiversity:
- One of the key benefits of sustainable food production lies in its ability to preserve biodiversity.
- Through the utilization of organic farming techniques, such as crop rotation and the avoidance of synthetic pesticides, we can safeguard the delicate balance of ecosystems.
- By maintaining diverse ecological systems, we protect essential pollinators and natural predators, which contribute to the health and fertility of our crops.
2. Conserving Natural Resources:
- Sustainable food production limits the excessive use of natural resources, such as water and soil.
- Implementing efficient irrigation systems and water-recycling methods can minimize water wastage and ensure its availability for the long term.
- Adopting agroforestry practices and promoting soil conservation measures can help prevent erosion and degradation, preserving fertile land for future cultivation.
3. Mitigating Environmental Pollution:
- Achieving sustainable food production is crucial in mitigating the harmful effects of agricultural practices on the environment.
- By prioritizing organic farming methods, we reduce the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and harmful pesticides that can contaminate soil, water sources, and contribute to air pollution.
- Implementing proper waste management systems and reducing food waste can further minimize the environmental impact caused by the food production and distribution process.
4. Promoting Food Security:
- Sustainable food production plays a vital role in ensuring long-term food security.
- By diversifying crop varieties and promoting sustainable farming techniques, we can foster resilience against climate change, crop diseases, and other potential threats to agricultural productivity.
- Additionally, sustainable food production empowers local communities by promoting self-sufficiency and reducing reliance on external food sources.
Overall, embracing sustainable food production practices is imperative for the well-being of both our planet and future generations. By preserving biodiversity, conserving natural resources, mitigating pollution, and promoting food security, we can create a more sustainable and resilient food system that supports a healthier planet for all.
Efficient Resource Utilization
In the context of our discussion on the sustainable benefits of eco-friendly food, another crucial aspect that deserves attention is the efficient utilization of resources. This entails optimizing the use of various inputs such as water, energy, and land, as well as minimizing waste and reducing the environmental impact throughout the entire food production process.
Efficient resource utilization plays a significant role in ensuring long-term sustainability and minimizing the ecological footprint of food production. By employing innovative practices and technologies, farmers and food producers can maximize the productivity of their resources while minimizing resource depletion and environmental degradation.
A key area where efficient resource utilization can be observed is in water management. Adopting water-saving irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation or precision water application systems, allows for targeted water delivery to crops, reducing water wastage and ensuring water is used only where necessary. Additionally, implementing water recycling and wastewater treatment systems can help minimize water usage and prevent the contamination of natural water sources.
Another important aspect of resource utilization is energy efficiency. By integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, into the food production process, farms can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels and minimize greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, implementing energy-efficient technologies in processing and transportation can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower the overall carbon footprint of the food industry.
| Efficient Resource Utilization |
|---|
| Water Management |
| Energy Efficiency |
| Waste Minimization |
| Land Optimization |
Waste minimization is another critical aspect of efficient resource utilization. By implementing strategies such as composting, recycling, and utilization of by-products, food producers can reduce waste sent to landfills and convert organic waste into valuable resources, such as fertilizers or biogas.
Lastly, efficient resource utilization involves optimizing land use. Sustainable farming practices, such as crop rotation, precision agriculture, and agroforestry, can maximize productivity while minimizing soil erosion and preserving biodiversity. By maintaining healthy soils and preserving natural habitats, the impact of food production on the environment can be minimized and ecosystems can be conserved.
In conclusion, efficient resource utilization is a fundamental element in the journey towards sustainable and environmentally-friendly food production. By optimizing the use of water, energy, land, and minimizing waste, the food industry can contribute to a more sustainable future while ensuring high-quality and nutritious food for all.
Reduced Environmental Impact

In today’s ever-changing world, it has become increasingly crucial to prioritize sustainable practices that minimize the negative effects on our environment. The concept of reduced environmental impact encompasses a range of actions and initiatives aimed at mitigating harm to our planet’s ecosystems and natural resources.
One aspect of reduced environmental impact lies in the conservation of natural resources. By adopting green food practices, we can reduce the consumption of precious resources such as water, land, and energy. Through innovative farming techniques such as precision irrigation and vertical farming, we can utilize resources more efficiently, minimizing waste and maximizing output.
Furthermore, embracing sustainable agriculture practices can help mitigate pollution and preserve biodiversity. By avoiding the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers, green food production reduces the contamination of soil, water, and air. This, in turn, protects habitats and ecosystems, allowing flora and fauna to thrive.
Reduced environmental impact is not limited to the production stage alone. In the food processing and distribution stages as well, conscious efforts can be made to minimize waste and emissions. Implementing efficient transportation systems and packaging practices that reduce carbon footprint contribute to a greener food industry.
In conclusion, prioritizing reduced environmental impact in the production, processing, and distribution of green foods is vital to ensuring a sustainable future. By conserving natural resources, mitigating pollution, and embracing responsible practices, we can create a more environmentally friendly food system that benefits both present and future generations.
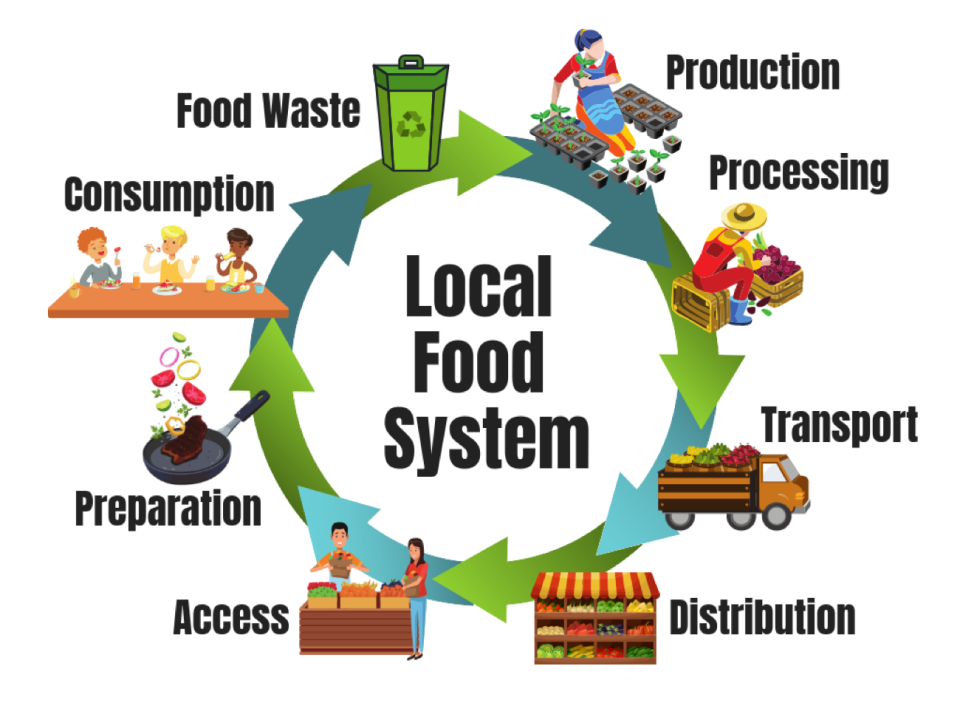
From Farm to Plate: The Journey of Green Foods
In this section, we will explore the fascinating process that green foods go through, starting from their origin on the farm to their final destination on our plates. We will delve into the intricate steps involved in cultivating, harvesting, and delivering these nutritious and environmentally friendly foods.
First and foremost, the journey begins with the dedicated farmers who passionately cultivate these green foods. They sow the seeds, nurture the crops, and employ sustainable farming practices to ensure the health and vitality of the plants. Through their hard work and expertise, they create a foundation for the nutritious and delicious foods that we enjoy.
Once harvested, these green foods embark on a carefully orchestrated journey to reach our plates. They undergo rigorous quality checks to guarantee freshness and safety. From there, they are transported using efficient and eco-friendly methods to minimize their carbon footprint.
- The produce is meticulously sorted and packaged, ensuring only the best and most vibrant specimens make it to the consumer.
- Next, these green foods are carefully transported to distribution centers, where they are stored to maintain optimal conditions.
- From the distribution centers, the green foods are dispatched to various retail locations, including grocery stores and farmers’ markets, where they are made available to the public.
- Finally, we, as consumers, play a crucial role in completing the journey by selecting and purchasing these delightful green foods, ensuring that they fulfill their purpose of providing us with essential nutrients and promoting sustainability.
The journey from farm to plate is a testament to the dedication, innovation, and collaboration involved in bringing green foods to the masses. By understanding and appreciating this journey, we can make informed choices that support the sustainability and well-being of our planet.
Sustainable Agriculture Practices
In the realm of environmentally-friendly and socially-responsible food production, cultivating sustenance through sustainable agriculture practices has emerged as a crucial aspect. These practices encompass a range of strategies and methods that prioritize long-term ecological balance, economic viability, and social justice.
One of the fundamental principles of sustainable agriculture is the emphasis on soil health. This involves employing techniques such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and organic fertilization to enrich the soil, enhance its fertility, and promote biodiversity. By nurturing the soil, farmers can reduce the reliance on synthetic chemicals, enhance water retention capacity, and mitigate erosion.
Another vital aspect of sustainable agriculture practices is the prudent use of water resources. Implementing efficient irrigation systems, conserving rainwater, and adopting precision agriculture techniques can significantly reduce water consumption. Utilizing these methods allows farmers to optimize water usage based on crop needs, conserve this precious resource, and minimize the impact on local water systems.
Integrated pest management (IPM) is another key component of sustainable agriculture practices. Rather than solely relying on chemical pesticides, IPM focuses on a holistic approach that includes the use of natural predators, crop rotation, and the cultivation of pest-resistant varieties. By embracing IPM, farmers can mitigate the detrimental effects of pesticides on ecosystems and human health, while effectively managing pests.
Diversification and the promotion of agroecosystems are vital aspects of sustainable agriculture. By encouraging the cultivation of multiple crop varieties and incorporating livestock into farming practices, farmers can enhance biodiversity, improve soil fertility, and reduce dependence on external inputs. Agroforestry, agroecology, and permaculture are examples of systems that integrate crops, animals, and trees to create sustainable food systems.
- Sustainable agriculture practices prioritize:
- Soil health through crop rotation, cover cropping, and organic fertilization
- Efficient water usage through irrigation methods and rainwater conservation
- Integrated pest management to minimize chemical pesticide usage
- Diversification and agroecosystem development to enhance biodiversity and soil fertility
Embracing sustainable agriculture practices not only ensures the long-term viability of food production but also contributes to the preservation of natural resources, the overall health of ecosystems, and the well-being of communities. By implementing these strategies, we can foster a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system that caters to the needs of both present and future generations.
Transparent Supply Chains
The transparency of supply chains plays a crucial role in the sustainable growth and success of the green foods industry. By embracing transparency, companies and consumers alike can gain a deeper understanding of the journey their food takes from the source to their plates. This section explores the importance of transparent supply chains and how they contribute to building trust, ensuring ethical practices, promoting environmental stewardship, and fostering consumer engagement.
| Building Trust | Ensuring Ethical Practices | Promoting Environmental Stewardship | Fostering Consumer Engagement |
|---|---|---|---|
| By openly sharing information about sourcing, production methods, and certifications, green food companies can build trust with consumers. Transparent supply chains enable customers to verify claims and make informed decisions, knowing that the products they choose align with their values and preferences. | By providing transparency regarding labor practices, fair trade partnerships, and ethical sourcing, companies can demonstrate their commitment to social responsibility. Consumers want assurance that the food they consume is produced in a manner that respects human rights, workers’ welfare, and community well-being. | Transparent supply chains allow companies to showcase their environmentally friendly practices, such as organic farming, sustainable packaging, and responsible waste management. By offering visibility into the entire supply chain, consumers can support brands that prioritize minimizing their environmental impact. | Through transparency, consumers can engage more actively in the green foods movement. By understanding where their food comes from and how it is produced, they can make choices that support sustainable practices. Transparent supply chains empower consumers to demand accountability and drive positive change in the industry. |
In conclusion, transparent supply chains are integral to the success of the green foods industry. By embracing transparency, companies can build trust, ensure ethical practices, promote environmental stewardship, and foster consumer engagement. The journey from farm to plate becomes more than just a mystery–it becomes an opportunity for shared responsibility and a sustainable future.
Nutritional Benefits of Green Foods
Exploring the nutritional advantages of incorporating green foods into your diet reveals a wealth of health benefits. These verdant edibles offer a diverse range of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which contribute to overall well-being and vitality.
One key benefit of consuming green foods is their abundance of micronutrients. Leafy greens, such as spinach and kale, are known for their high concentrations of vitamins A, C, and K, which promote healthy vision, boost the immune system, and support bone health, respectively. These nutrients play crucial roles in various bodily functions, ensuring that your body functions optimally.
Green vegetables are also an excellent source of dietary fiber, aiding in digestion and promoting a feeling of satiety. The insoluble fiber found in these foods helps regulate bowel movements and prevents constipation, while the soluble fiber promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and assists in maintaining a healthy weight.
In addition to their impressive nutritional profile, green foods are often low in calories and fat, making them a suitable choice for those aiming to maintain or lose weight. These nutritious options can be incorporated into meals and snacks without adding excessive calories, offering a guilt-free and satisfying way to nourish your body.
Another notable advantage of green foods is the presence of various antioxidants, such as flavonoids and carotenoids. These compounds help protect the body against harmful free radicals, reducing the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease and certain types of cancer. Antioxidants also contribute to youthful-looking skin by preventing damage caused by oxidative stress.
Moreover, green foods are often associated with a reduced environmental impact compared to other food sources. They require fewer resources to grow and produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions, making them a more sustainable choice for both personal and planetary health.
- High in micronutrients like vitamins A, C, and K
- Excellent source of dietary fiber for better digestion
- Low in calories and fat, suitable for weight management
- Packed with antioxidants to combat free radicals
- Environmentally-friendly choice for sustainable living
Incorporating green foods into your diet not only nourishes your body but also contributes to a healthier planet. By choosing these nutritionally-dense options, you can enjoy a multitude of benefits, supporting your overall well-being while placing less strain on the environment.
Embracing a Greener and Healthier Future
In this section, we will explore the concept of transitioning towards a more environmentally friendly and nutritious way of life. Through the integration of sustainable practices and the adoption of green foods, we have the opportunity to pave the way for a brighter and healthier future.
By embracing a greener and healthier future, we are committing to a lifestyle that prioritizes the well-being of both ourselves and the planet. Through the consumption of green foods, which include organic fruits and vegetables, plant-based protein sources, and sustainably sourced seafood, we can nourish our bodies with nutrient-rich options while minimizing our environmental impact.
A key aspect of embracing a greener and healthier future is appreciating the interconnectedness of our food choices and the health of the planet. By opting for locally sourced produce and supporting sustainable farming practices, we can reduce the carbon emissions associated with long-distance transportation and contribute to the preservation of ecosystems.
Furthermore, embracing a greener and healthier future involves recognizing the benefits of plant-based diets. Plant-based diets have been linked to lower risks of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Additionally, choosing plant-based protein sources over animal products can help reduce land and water usage, minimize greenhouse gas emissions, and alleviate the strain on global food resources.
In conclusion, embracing a greener and healthier future entails making conscious choices that prioritize both our personal well-being and the sustainability of the environment. By incorporating green foods into our diets, supporting sustainable farming practices, and embracing plant-based options, we can contribute to a more sustainable and nourishing future for ourselves and generations to come.
Sustainable Food Choices for Individuals
Exploring the path towards sustainable food choices, this section delves into the various ways individuals can make a positive impact on the environment and their health through their food choices.
By making conscientious decisions regarding the food we consume, we can contribute to a more sustainable future. This involves considering the sources of our food, the production methods employed, and the overall impact it has on the planet. Sustainable food choices align with the principles of environmental preservation, promoting biodiversity, reducing waste, and conserving natural resources.
One key aspect of sustainable food choices is opting for locally sourced ingredients. This supports local farmers and reduces the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation. By choosing local, seasonal produce, individuals can enjoy fresher and more nutritious meals while minimizing the environmental impact of their food consumption.
Another important component of sustainable food choices is reducing meat and dairy consumption. Livestock production has a significant ecological footprint, contributing to deforestation, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. By incorporating more plant-based alternatives into our diets, individuals can decrease their environmental impact and improve their overall health.
| Benefits of Sustainable Food Choices |
|---|
| Conserves natural resources |
| Promotes biodiversity |
| Reduces greenhouse gas emissions |
| Supports local farmers and communities |
| Minimizes food waste |
Furthermore, consciously selecting organic and locally grown foods can help minimize exposure to harmful pesticides and chemicals while supporting a more sustainable agricultural system. Opting for sustainably produced seafood also contributes to the conservation of marine ecosystems.
In conclusion, making sustainable food choices as individuals allows us to be mindful of the environmental impact and promote a healthier and more sustainable future. By choosing locally sourced, plant-based, and ethically produced foods, we can contribute to a more sustainable food system and protect the planet for generations to come.
Questions and answers
What are green foods?
Green foods are a category of foods that are produced using sustainable and environmentally-friendly practices, with a focus on minimizing negative impacts on the planet.
How are green foods produced?
Green foods are produced through organic farming practices that do not use synthetic chemicals or genetically modified organisms. They prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and conservation of natural resources.
What are the advantages of consuming green foods?
Consuming green foods has several advantages. Firstly, they are healthier as they contain higher levels of nutrients and antioxidants. Secondly, they have a lower impact on the environment as they reduce pollution and conserve resources. Lastly, they support sustainable agriculture and local communities.
How do green foods contribute to sustainability?
Green foods contribute to sustainability by promoting organic farming methods that protect soil quality, prevent water pollution, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and conserve biodiversity. They also support local economies and help reduce dependence on fossil fuels in food production and transportation.
Are green foods more expensive than conventional foods?
While green foods may be slightly more expensive due to the higher costs associated with organic farming practices, the long-term benefits they offer, such as improved health and reduced environmental impact, justify the price difference for many consumers. Additionally, as demand for green foods increases, economies of scale may help reduce costs in the future.
What are green foods and why are they sustainable?
Green foods refer to plant-based foods that are grown using sustainable agricultural practices. These practices prioritize environmental conservation, biodiversity, and natural resource preservation. Green foods are sustainable because they have a minimal environmental impact, use fewer chemical inputs, and promote a healthier ecosystem.
How does the journey from farm to plate impact the sustainability of green foods?
The journey from farm to plate has a significant impact on the sustainability of green foods. It involves transportation, packaging, processing, and distribution. These aspects can affect the carbon footprint, waste generation, and resource consumption associated with green foods. Therefore, adopting sustainable practices throughout the entire journey is crucial to maintaining their sustainable advantages.
What are some sustainable agricultural practices used in the production of green foods?
Some sustainable agricultural practices used in the production of green foods include organic farming, permaculture, agroforestry, and integrated pest management. These practices promote soil health, reduce chemical usage, conserve water, and encourage biodiversity, making the production of green foods more sustainable.
Do green foods have any nutritional advantages over non-green foods?
Green foods often have nutritional advantages over non-green foods. They are rich in essential nutrients, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Additionally, most green foods are low in saturated fat and cholesterol while being high in dietary fiber, which supports a healthy digestive system and overall well-being.
How can individuals incorporate green foods into their daily diets?
Individuals can incorporate green foods into their daily diets by including more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and plant-based proteins. They can opt for organic and locally sourced options, support farmers’ markets, and reduce consumption of animal products. It is also important to choose seasonal produce and minimize food waste to maximize the sustainability of green food choices.