In a society that glorifies productivity and rewards constant busyness, have you ever stopped to consider the toll it takes on our bodies? We often push ourselves to the brink, chasing after success and achievements, but rarely do we pause to understand the intricate mechanisms at play within us. One such mechanism is the cortisol belly, an often overlooked consequence of our fast-paced lifestyles.
Our bodies are incredibly adaptable machines, designed to respond to stress and keep us safe. One of the key players in this intricate dance is cortisol, a hormone that helps regulate our body’s response to stress. When faced with a perceived threat, cortisol floods our system, preparing us to fight or flee. This essential hormone can be a lifesaver in the short term, but when constantly elevated, it can wreak havoc on our bodies.
Unbeknownst to many, sustained high levels of cortisol can lead to the accumulation of abdominal fat, commonly known as the cortisol belly. This dangerous phenomenon occurs when our bodies are overwhelmed by chronic stress, causing cortisol levels to remain elevated for prolonged periods. The excess cortisol not only encourages fat storage in the abdominal area but also disrupts the balance of other hormones, magnifying the issue further.
But how can one recognize the presence of a cortisol belly? While each body is unique and reacts differently, there are common signs and symptoms to watch out for. The most obvious indicator is a persistent, stubborn belly fat that refuses to budge despite your best efforts. Additionally, you may find yourself battling increased cravings for high-calorie, comfort foods, or experience difficulty in falling asleep or staying asleep through the night.
Fortunately, there are steps you can take to prevent or minimize the risks associated with a cortisol belly. By prioritizing self-care and stress management, you can keep cortisol levels in check and mitigate the negative effects it has on your body. Incorporating regular exercise, practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga, and adopting a balanced and nutritious diet can all contribute to a healthier cortisol balance. Remember, the journey towards a stress-free life and a slimmer waistline begins with understanding the subtle but significant impact of cortisol on our bodies.
- Understanding Cortisol Belly
- Causes of Cortisol Belly
- Stress and Cortisol
- Poor Diet and Cortisol Belly
- Lack of Physical Activity and Cortisol Belly
- Symptoms of Cortisol Belly
- Weight Gain in the Abdominal Area
- Increased Appetite and Food Cravings
- Difficulty Losing Weight
- Prevention and Management of Cortisol Belly
- Questions and answers
Understanding Cortisol Belly
In this section, we will delve into the concept of cortisol belly, exploring the underlying factors that contribute to its development. We will explore the various manifestations and consequences of cortisol belly, and discuss effective strategies for prevention and management. Through a comprehensive understanding of cortisol belly, we can empower ourselves with the knowledge and tools necessary to maintain a healthy and balanced lifestyle.
| Table of Contents |
|---|
| 1. Introduction |
| 2. The Impact of Cortisol |
| 3. Identifying the Symptoms |
| 4. Exploring the Causes |
| 5. Understanding the Consequences |
| 6. Prevention and Management Strategies |
When it comes to our overall well-being, understanding cortisol belly is essential. This term refers to the accumulation of excess abdominal fat caused by elevated levels of cortisol, a stress hormone. An increase in cortisol levels can be triggered by various factors, including chronic stress, poor sleep patterns, unhealthy eating habits, and lack of physical activity.
The impact of cortisol on our bodies can be far-reaching, affecting not only our physical appearance but also our overall health. Excessive cortisol can disrupt the balance of various hormones, leading to weight gain, increased appetite, and a higher likelihood of storing fat in the abdominal region. Understanding the symptoms associated with cortisol belly is crucial for early detection and intervention.
Identifying the causes of cortisol belly is essential for effective prevention and management. As mentioned earlier, stress is a major contributor, but hormonal imbalances, poor dietary choices, and sedentary lifestyles can also play a significant role. By addressing the root causes and adopting healthier habits, we can work towards reducing cortisol belly and improving our overall well-being.
The consequences of cortisol belly extend beyond aesthetics. Excess abdominal fat has been linked to an increased risk of various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, insulin resistance, and metabolic disorders. Understanding these potential consequences can serve as a powerful motivator for making positive lifestyle changes.
Prevention and management strategies for cortisol belly involve a multi-faceted approach. This includes incorporating stress reduction techniques, such as mindfulness and exercise, into daily routines, adopting a balanced and nutritious diet, optimizing sleep patterns, and engaging in regular physical activity. By implementing these strategies, we can actively mitigate the effects of cortisol belly and maintain a healthy weight and body composition.
Causes of Cortisol Belly

The accumulation of excess fat in the abdominal region, commonly known as cortisol belly, can be attributed to various factors. Understanding these causes can help individuals take appropriate measures to prevent or combat this condition.
One of the primary causes of cortisol belly is chronic stress. When a person experiences prolonged periods of stress, the body produces higher levels of cortisol, a hormone that is involved in the body’s stress response. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to increased appetite and cravings for unhealthy, high-calorie foods, which can result in the accumulation of fat in the abdominal area.
Another contributing factor to cortisol belly is lack of sleep. Inadequate or poor-quality sleep can disrupt the body’s hormonal balance, including cortisol regulation. Sleep deprivation can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which can promote the deposition of fat in the abdominal region.
Additionally, an unhealthy diet and lifestyle can also contribute to cortisol belly. Consuming a diet high in refined carbohydrates, processed foods, and sugary drinks can lead to weight gain and an increase in cortisol levels. Lack of exercise and sedentary behavior further exacerbate the accumulation of abdominal fat.
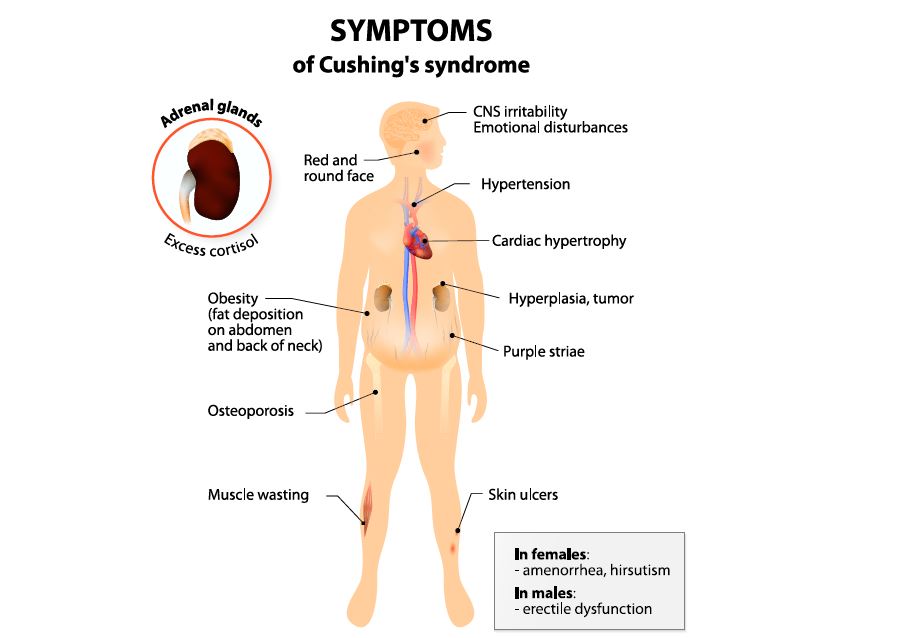
Hormonal changes, such as those associated with aging or certain medical conditions, can also play a role in cortisol belly. As individuals age, hormonal imbalances can occur, including an increase in cortisol production. Certain medical conditions, such as Cushing’s syndrome, can lead to excessive cortisol production, resulting in abdominal weight gain.
In conclusion, cortisol belly can be caused by chronic stress, lack of sleep, an unhealthy diet and lifestyle, and hormonal changes. Understanding these causes can empower individuals to make positive changes to prevent or address this condition. Incorporating stress-management techniques, practicing good sleep hygiene, adopting a balanced diet, and engaging in regular physical activity can all contribute to reducing the accumulation of abdominal fat associated with cortisol belly.
Stress and Cortisol
In today’s fast-paced world, stress has become an all too familiar companion for many individuals. It is a response triggered by various factors and can manifest in different forms. One of the key players in the body’s stress response is cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Understanding the relationship between stress and cortisol is crucial in managing the impact they have on our overall well-being.
When we experience stress, whether it be due to work pressures, relationship difficulties, or financial worries, our body releases cortisol as part of its natural response. This hormone helps prepare the body for the fight or flight response, increasing blood sugar levels, suppressing the immune system, and enhancing the brain’s alertness. While cortisol is essential for short-term stress adaptation, prolonged exposure to stress can lead to chronic elevated cortisol levels.
Chronic stress can result in a cascade of negative effects on the body, including the accumulation of visceral fat, commonly known as cortisol belly. This type of fat tends to accumulate around the abdominal area, leading to an increase in waist circumference. Other symptoms associated with high cortisol levels include increased appetite, cravings for sugary and high-fat foods, difficulty in losing weight, and disrupted sleep patterns.
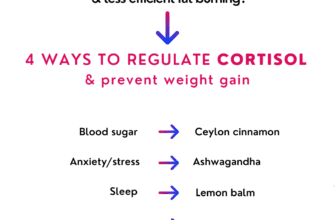
To prevent and manage cortisol belly, it is important to adopt stress management techniques. This can include regular exercise, practicing mindfulness and meditation, getting ample sleep, and engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation. Additionally, incorporating a balanced and nutritious diet can support overall health and help regulate cortisol levels.
- Engage in regular physical activity such as walking, jogging, or yoga.
- Practice deep breathing exercises and relaxation techniques to reduce stress levels.
- Ensure an adequate amount of sleep each night, aiming for 7-8 hours of quality rest.
- Find activities that bring joy and serve as a form of stress relief, such as hobbies or spending time with loved ones.
- Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains in your diet to support balanced nutrition.
- Avoid excessive consumption of sugary and high-fat foods, as they can contribute to weight gain and cortisol imbalances.
By actively managing stress levels and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals can reduce the impact of cortisol on their bodies, promoting overall well-being and preventing the development of cortisol belly.
Poor Diet and Cortisol Belly
A detrimental eating routine can significantly contribute to the development of cortisol belly, a condition characterized by excess abdominal fat associated with elevated cortisol levels. The correlation between an unhealthy diet and the accumulation of visceral fat in the midsection is well established. The way we nourish our bodies plays a pivotal role in regulating the release and impact of cortisol, a hormone responsible for various bodily functions.
When we consistently consume a poor diet lacking essential nutrients and composed of processed foods, sugary beverages, saturated fats, and high levels of refined carbohydrates, it can lead to hormonal imbalances, including increased cortisol production. The excessive intake of these detrimental food choices often results in weight gain, particularly in the abdominal region.
Processed foods laden with artificial additives and preservatives can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones in the body, triggering an increase in cortisol levels. Regular consumption of these convenience foods can lead to inflammation, insulin resistance, and metabolic dysregulation, which all contribute to the deposition of visceral fat.
The consumption of excessive sugar and sugary beverages can have adverse effects on cortisol levels. The rapid spikes in blood sugar caused by high sugar intake stimulate cortisol secretion, which ultimately promotes fat accumulation, especially in the abdominal area.
Saturated fats found in fatty meats, full-fat dairy products, and processed snacks can also trigger cortisol belly. These unhealthy fats not only contribute to weight gain but also induce inflammation in the body, leading to an increased release of cortisol and subsequent abdominal fat deposition.
High levels of refined carbohydrates such as white bread, pasta, and pastries can significantly disrupt cortisol levels and contribute to cortisol belly. These refined carbs cause rapid rises in blood sugar, triggering an insulin response that results in increased cortisol secretion and encourages the storage of abdominal fat.
In summary, poor dietary choices can disrupt the delicate balance of cortisol in the body and contribute to the development of cortisol belly. The regular consumption of processed foods, excessive sugar, saturated fats, and refined carbs can lead to hormonal imbalances and increased cortisol production, ultimately resulting in abdominal fat deposition. Adopting a healthy eating pattern that focuses on nutrient-dense, whole foods is essential in preventing cortisol belly and promoting overall well-being.
Lack of Physical Activity and Cortisol Belly
Lack of physical activity plays a significant role in the development of cortisol belly, a condition characterized by excess abdominal fat accumulation. Engaging in regular exercise not only helps to maintain a healthy weight but also plays a crucial role in regulating cortisol levels in the body.
When individuals lead sedentary lifestyles without incorporating physical activity into their daily routines, cortisol, commonly known as the stress hormone, tends to increase. Higher cortisol levels can lead to weight gain, particularly in the abdomen area, resulting in the formation of cortisol belly.
Regular physical activity helps to decrease cortisol levels, promoting overall well-being and reducing the risk of cortisol belly. Exercise has been shown to stimulate the release of endorphins, which are known as feel-good hormones. These endorphins help to alleviate stress, reducing cortisol levels in the body.
Additionally, engaging in physical activity increases muscle mass, which helps to boost metabolism. A higher metabolic rate aids in burning calories and reducing body fat, including abdominal fat. By incorporating exercise into one’s daily routine, individuals can actively prevent the formation of cortisol belly.
Incorporating a variety of exercises, such as cardiovascular activities, strength training, and flexibility exercises, can be beneficial in reducing cortisol belly. It is essential to find physical activities that are enjoyable and sustainable to ensure consistency.
To prevent cortisol belly, individuals should aim for a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises at least twice a week. It is equally important to break up long periods of sitting with short bursts of physical activity throughout the day.
By prioritizing regular physical activity, individuals can effectively manage cortisol levels, maintain a healthy weight, and prevent the development of cortisol belly.
Symptoms of Cortisol Belly
When it comes to conditions like cortisol belly, understanding the symptoms is crucial for early detection and prevention. By recognizing and addressing these symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps towards reducing cortisol levels and regaining control of their overall health and well-being.
| 1. Increased Abdominal Fat | Excessive cortisol production can lead to an accumulation of abdominal fat. This can manifest as a thicker waistline and an overall increase in belly size. |
| 2. Persistent Weight Gain | Cortisol belly is often associated with persistent weight gain, despite efforts to maintain a healthy lifestyle. Individuals may find it challenging to lose weight, even with exercise and proper diet. |
| 3. Insomnia or Poor Sleep | Elevated cortisol levels can disrupt normal sleep patterns, leading to difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night. Insomnia or poor-quality sleep may contribute to increased cortisol production, forming a vicious cycle. |
| 4. Constant Fatigue | Individuals with cortisol belly often experience persistent fatigue, regardless of adequate rest and sleep. This can impact daily activities, productivity, and overall quality of life. |
| 5. Mood Swings and Irritability | Elevated cortisol levels can affect neurotransmitter balance, leading to mood swings, irritability, and emotional instability. Individuals may find themselves experiencing heightened stress, anxiety, or even depression. |
| 6. Digestive Issues | Cortisol imbalances can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system, leading to symptoms such as bloating, indigestion, constipation, or diarrhea. |
| 7. Weakened Immune System | Chronically elevated cortisol levels can suppress the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections, illnesses, and slower healing processes. |
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of cortisol belly is the first step towards addressing this condition. By being aware of these indicators and seeking appropriate medical advice, individuals can take proactive steps towards reducing cortisol levels, improving overall health, and achieving a balanced body composition.
Weight Gain in the Abdominal Area
Excess weight accumulation in the abdominal area is a common concern for many individuals. This particular type of weight gain is often associated with various health issues and can be caused by a variety of factors. Understanding the causes and symptoms of weight gain in the abdominal area is crucial in order to prevent its negative effects on overall well-being.
Excessive abdominal fat, often referred to as visceral fat, surrounds the internal organs and can lead to serious health complications. Increased levels of cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands, have been linked to the development of belly fat. Cortisol acts on fat cells, promoting storage of excess fat in the abdominal area. Moreover, certain lifestyle factors, such as high-stress levels, poor diet, lack of physical activity, and inadequate sleep patterns, can contribute to increased cortisol production and subsequent weight gain in the abdominal region.
Identifying the symptoms of weight gain in the abdominal area is important for early detection and intervention. Individuals experiencing excessive weight in this region may notice a protruding belly, increased waist circumference, and a feeling of heaviness or discomfort. Additionally, abdominal weight gain can be accompanied by other symptoms such as indigestion, bloating, and hormonal imbalances.
To prevent weight gain in the abdominal area, it is essential to address the underlying causes and adopt healthy lifestyle habits. Incorporating regular exercise into your routine, particularly activities that target the core muscles, can help reduce belly fat and strengthen the abdominal area. Additionally, implementing stress-management techniques, such as mindfulness or relaxation exercises, can assist in lowering cortisol levels. Paying attention to your diet by consuming nutrient-dense foods, limiting processed and sugary foods, and practicing portion control can also contribute to maintaining a healthy weight in the abdominal region.
Ultimately, understanding the factors contributing to weight gain in the abdominal area and taking proactive steps towards prevention can lead to improved overall health and well-being. By incorporating healthy habits and managing stress effectively, individuals can reduce their risk of developing excessive abdominal fat and its associated health complications.
Increased Appetite and Food Cravings
One common issue often associated with cortisol belly is an increase in appetite and intense food cravings. Individuals who experience this may find themselves constantly thinking about food and feeling hungry, especially for high-calorie and sugary foods.
These cravings can be difficult to resist and may lead to overeating, which can contribute to weight gain and a worsening of the cortisol belly. The hormonal changes caused by increased cortisol levels can directly impact appetite and food preferences, making it challenging to maintain a balanced and healthy diet.
When cortisol levels rise, it can interfere with the body’s regulation of appetite-controlling hormones such as leptin and ghrelin. Leptin is responsible for signaling fullness, while ghrelin stimulates hunger. When cortisol levels are elevated, the body may become less responsive to these hormones, leading to an increased appetite.
In addition to hormonal changes, stress can also play a significant role in triggering food cravings. Many individuals turn to food as a source of comfort or distraction when feeling stressed or overwhelmed. The combination of stress-induced cravings and hormonal imbalances can create a cycle of overeating and weight gain.
To prevent and manage increased appetite and food cravings associated with cortisol belly, it is essential to focus on stress management techniques and adopt a healthy and balanced diet. Strategies such as regular exercise, mindfulness practices, and getting enough sleep can help reduce stress levels and regulate hormone production.
Additionally, incorporating nutrient-dense foods into meals and snacks can help maintain satiety and reduce cravings. Choosing whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can provide the body with essential nutrients while promoting a feeling of fullness.
By addressing the underlying causes of increased appetite and food cravings, individuals can take steps towards managing cortisol belly and achieving overall health and well-being.
Difficulty Losing Weight
Struggling with shedding those extra pounds can be frustrating and disheartening. Many individuals find it challenging to achieve their desired weight, despite putting in significant effort and adopting various weight loss methods.
The journey to losing weight can be influenced by several factors that may make it difficult to reach your goals. It’s important to understand these underlying reasons to effectively address and overcome them.
- Metabolism: A slow metabolic rate can hinder weight loss progress. It refers to the rate at which your body converts food into energy. Individuals with a sluggish metabolism tend to burn fewer calories, making it more challenging to create a calorie deficit required for weight loss.
- Hormonal imbalance: Hormones play a crucial role in regulating body weight. An imbalance in hormones like insulin, thyroid hormones, and cortisol can disrupt the body’s ability to effectively burn fat and reduce weight.
- Stress and emotional eating: Emotional and psychological factors can greatly affect weight loss efforts. Chronic stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone associated with increased abdominal fat storage. This can lead to cravings for unhealthy food and emotional eating habits, making it harder to lose weight.
- Inadequate sleep: Lack of quality sleep can impact weight loss. Sleep deprivation affects hormones involved in appetite regulation, leading to increased hunger and cravings for high-calorie foods. It also affects energy levels and may decrease motivation for physical activity.
- Inconsistent exercise routine: Physical activity is essential for weight loss, but inconsistency in exercising can hinder progress. Regular exercise helps burn calories, build muscle, and improve overall metabolism.
To overcome the difficulties in losing weight, it’s crucial to create a comprehensive approach that addresses these underlying factors. This may involve implementing lifestyle changes such as adopting a balanced diet, managing stress levels, ensuring sufficient sleep, and maintaining a consistent exercise routine. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals or certified nutritionists can provide personalized strategies to navigate through the challenges and achieve successful weight loss.
Prevention and Management of Cortisol Belly
In this section, we will explore effective strategies for preventing and managing the condition commonly known as cortisol belly. By implementing simple lifestyle changes and adopting healthy habits, individuals can aid in reducing cortisol levels and promote a flatter abdomen.
Mindful Stress Management: Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can help regulate cortisol production. By managing stress levels, individuals may prevent the accumulation of abdominal fat associated with elevated cortisol levels.
Dietary Modifications: Making healthy food choices is crucial in managing cortisol belly. Opting for whole and unprocessed foods while reducing the intake of refined sugars and carbohydrates can help regulate cortisol levels. Also, consuming foods rich in vitamins C and E, magnesium, and omega-3 fatty acids can help support a healthy response to stress and reduce cortisol secretion.
Regular Exercise Routine: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercises, strength training, or high-intensity interval training, can aid in reducing cortisol levels and reducing abdominal fat. Exercise not only helps burn calories but also promotes the release of mood-boosting hormones, thereby alleviating stress and cortisol-related abdominal weight gain.
Adequate Sleep: Getting enough quality sleep is essential in managing cortisol belly. Lack of sleep can disrupt the body’s cortisol regulation, leading to an increase in appetite, cravings for unhealthy foods, and weight gain. Creating a nighttime routine conducive to relaxation and ensuring a consistent sleep schedule are vital for maintaining a healthy cortisol balance.
Social Support: Building a strong network of friends, family, or support groups can have a positive impact on managing cortisol belly. Having a support system to rely on and engage in meaningful connections can help reduce stress levels and provide emotional comfort during challenging times.
Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Engaging in healthy coping mechanisms, such as journaling, spending time in nature, practicing hobbies, or seeking professional help when needed, can contribute to managing cortisol belly. These activities can provide individuals with a sense of relaxation, improve emotional well-being, and help in reframing stressful situations.
Consistency and Patience: It’s important to remember that managing cortisol belly takes time and consistency. By consistently following the recommended strategies and being patient with the progress, individuals can gradually achieve a flatter abdomen and lead a healthier life overall.
In conclusion, prevention and management of cortisol belly requires a holistic approach encompassing stress management, healthy eating, regular exercise, sleep, social support, and healthy coping mechanisms. By implementing these strategies, individuals can effectively regulate cortisol levels, reduce abdominal fat, and achieve a healthier body composition.
Questions and answers
What is cortisol belly and how is it caused?
Cortisol belly refers to the accumulation of excess fat around the abdominal area due to high levels of the stress hormone cortisol. This can be caused by chronic stress, a poor diet, lack of exercise, and sleep deprivation.
What are the symptoms of cortisol belly?
Common symptoms of cortisol belly include increased belly fat, bloating, weight gain, difficulty losing weight, and a tendency to store fat around the midsection.
Can cortisol belly be prevented?
Yes, cortisol belly can be prevented by managing stress levels through techniques like meditation, exercise, and deep breathing. A healthy diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep also play a crucial role in preventing cortisol belly.
How does cortisol affect belly fat?
Cortisol is a hormone released by the adrenal glands in response to stress. High levels of cortisol lead to an increase in appetite, especially for unhealthy, high-calorie foods. It also promotes the storage of fat, particularly around the abdomen, which can result in a cortisol belly.
Are there any medical conditions related to cortisol belly?
Yes, prolonged high cortisol levels due to chronic stress can lead to a condition called Cushing’s syndrome, which is characterized by excessive weight gain and a rounded face and neck. However, cortisol belly can also occur in individuals without any underlying medical conditions.
What is cortisol belly?
Cortisol belly refers to the accumulation of fat around the abdominal area caused by high levels of cortisol, a stress hormone.
What are the common causes of cortisol belly?
The common causes of cortisol belly include chronic stress, poor diet, lack of exercise, and insufficient sleep.
What are the symptoms of cortisol belly?
The symptoms of cortisol belly may include increased waist circumference, bloating, weight gain in the abdominal area, and difficulty losing belly fat.
How does cortisol contribute to belly fat?
Cortisol contributes to belly fat by promoting the breakdown of protein into glucose, increasing appetite, and slowing down the metabolism.
What are some ways to prevent cortisol belly?
To prevent cortisol belly, it is important to manage stress levels through relaxation techniques, engage in regular exercise, maintain a balanced diet, get enough sleep, and practice mindfulness or meditation.