In our bustling lives, it is crucial to be cognizant of our wellbeing and recognize early symptoms that may indicate underlying health issues. One such category of conditions that requires our attention is autoimmune diseases. These conditions arise when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells and tissues, leading to a myriad of complications.
Identifying the initial warning signs of autoimmune diseases can play a pivotal role in early detection, diagnosis, and effective management. While autoimmune diseases can manifest in diverse ways, there are some common symptoms that one should be aware of. By recognizing these indications, individuals can seek timely medical assistance and take proactive steps towards preserving their well-being.
Although autoimmune diseases encompass a wide spectrum, it is important to note that they often share similar early warning signs. These symptoms, ranging from mild to severe, may vary depending on the type of autoimmune disease and the affected organ. By being vigilant and observant of changes in our bodies, we can potentially mitigate the impact of these conditions and improve our quality of life.
Understanding Autoimmune Diseases
Getting to grips with autoimmune conditions can provide valuable insights into the complex nature of these diseases. Autoimmune disorders are characterized by an overactive immune response, which mistakenly attacks and damages healthy cells and tissues in the body. While each autoimmune disease manifests differently, they share common underlying mechanisms that drive their development and progression.
- Autoimmune diseases arise when the body’s immune system malfunctions and fails to distinguish between self and non-self.
- An array of triggers, including genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors, can contribute to the onset of these conditions.
- Understanding the interplay between the immune system, genetic predispositions, and external triggers is crucial in deciphering the underlying causes of autoimmune diseases.
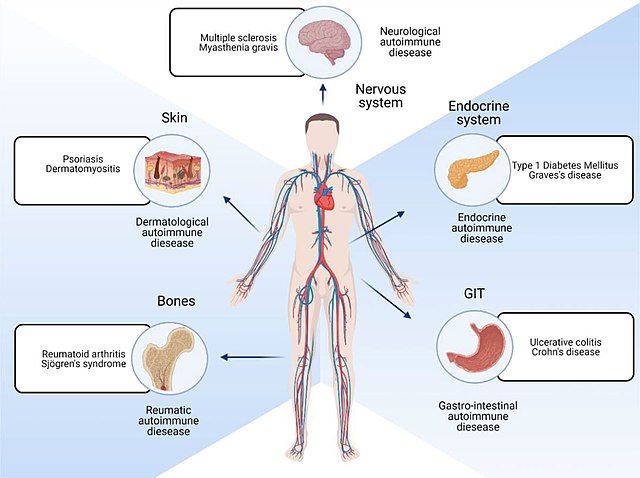
- The spectrum of autoimmune disorders encompasses a wide range of conditions affecting various organs and systems in the body, such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, and type 1 diabetes.
- Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of autoimmune diseases is essential for early intervention and proper management of these chronic conditions.
- Promising research efforts are underway to unravel the intricate mechanisms at play in autoimmune diseases, with the hope of developing targeted treatments and improving the quality of life for those affected.
By delving into the underlying mechanisms, triggers, and diversity of autoimmune diseases, we can deepen our understanding of these complex conditions and work towards better diagnosis, treatment, and ultimately, prevention.
What are Autoimmune Diseases?
Autoimmune diseases are a group of medical conditions that occur when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells and tissues. These diseases can affect various organs and systems within the body, leading to inflammation, tissue damage, and dysfunction.
In autoimmune diseases, the immune system loses its ability to differentiate between foreign substances and the body’s own cells. As a result, it launches an immune response against self-components, treating them as if they were foreign invaders. This abnormal immune response can have detrimental effects on the body and manifest as a wide range of symptoms, depending on the specific autoimmune disease involved.
Autoimmune diseases can target specific organs or affect multiple organs simultaneously. Some examples of autoimmune diseases include rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, and celiac disease. Each of these diseases has its unique set of symptoms and complications, but they all share the underlying characteristic of an overactive immune response against self.
While the exact cause of autoimmune diseases is not fully understood, researchers believe that a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors plays a role in their development. Factors such as infections, hormonal imbalances, and exposure to certain chemicals or drugs can trigger the onset or exacerbation of autoimmune diseases.
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases can often be challenging as many of the early symptoms are nonspecific and can overlap with other medical conditions. However, identifying and treating these diseases early is crucial to prevent further damage and manage symptoms effectively.
If you experience persistent unexplained symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional who can evaluate your symptoms, conduct appropriate diagnostic tests, and provide appropriate treatment options. Early recognition and intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with autoimmune diseases.
The Impact of Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases have a profound effect on individuals and society as a whole. These conditions, characterized by the body’s immune system mistakenly attacking its own healthy cells and tissues, can result in a wide range of symptoms and complications. The impact of autoimmune diseases can be both physical and emotional, affecting various aspects of a person’s life.
- Physical Well-being: Autoimmune diseases can cause chronic fatigue, pain, and inflammation throughout the body. The symptoms can vary widely depending on the specific condition but often include joint pain, muscle weakness, skin rashes, and gastrointestinal issues. These physical symptoms can significantly impair a person’s ability to carry out daily activities, work, and engage in social interactions.
- Mental and Emotional Health: Dealing with the challenges of an autoimmune disease can take a toll on a person’s mental and emotional well-being. The chronic pain and discomfort can lead to feelings of frustration, helplessness, and anxiety. Additionally, the unpredictable nature of autoimmune diseases can cause uncertainty and stress, impacting a person’s overall quality of life.
- Financial Burden: Managing autoimmune diseases often involves frequent doctor visits, laboratory tests, and ongoing medication. The cost of these medical expenses can quickly add up, placing a significant financial burden on individuals and families. Moreover, the physical limitations caused by autoimmune diseases may lead to reduced work productivity or the need for disability support, further impacting financial stability.
- Social Impact: Autoimmune diseases can affect a person’s social life and relationships. The chronic symptoms and limitations may make it challenging for individuals to participate in social activities or maintain a regular social life. This can lead to feelings of isolation, as well as strain on personal relationships and support networks.
- Increased Healthcare Utilization: The presence of autoimmune diseases contributes to the overall burden on healthcare systems. As the prevalence of these conditions continues to rise, there is a greater demand for medical resources, including specialized healthcare professionals, diagnostic tests, and treatment options. This increased healthcare utilization places strain on healthcare systems and can potentially impact access to care for individuals with autoimmune diseases.
Overall, the impact of autoimmune diseases extends beyond the physical symptoms experienced by individuals. These conditions have far-reaching effects on various aspects of life, including physical health, mental well-being, finances, social interactions, and healthcare systems. Recognizing the early signs and symptoms of autoimmune diseases is crucial for timely diagnosis and management, with the aim of minimizing the impact and improving the quality of life for those affected.
Early Indications of Autoimmune Disorders
Discovering the initial signs of autoimmune diseases can be crucial for early intervention and proper management. These indications often manifest in various ways, alerting individuals to potential underlying health issues. Early symptoms may point towards potential autoimmune disorders, prompting individuals to seek medical attention and receive an accurate diagnosis.
It is imperative to remain vigilant for any unusual shifts in bodily functions or alarming sensations that may indicate the onset of autoimmune diseases. Recognizing possible early signs and seeking prompt medical guidance can aid in early detection and subsequent treatment of these conditions.
Observable changes in the immune system functionality: Through self-awareness, individuals may notice fluctuations in their immune system, such as persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, or changes in appetite. These variations may suggest underlying autoimmune disorders that warrant medical investigation.
Alterations in the musculoskeletal system: Autoimmune diseases often affect the musculoskeletal system, leading to joint pain, stiffness, and swelling. Uncharacteristic muscle weakness or limited mobility could also indicate an autoimmune condition that requires careful examination by a healthcare professional.
Unusual skin and hair changes: Individuals may experience unexpected redness, rashes, or itchiness on their skin, which can serve as potential early indicators of autoimmune diseases. Furthermore, hair loss or sudden hair thinning may be additional signs that should not be disregarded.
Disruptions in gastrointestinal functions: Persistent abdominal pain, irregular bowel movements, or significant changes in appetite and digestion may be early signs of autoimmune disorders affecting the gastrointestinal tract. Paying attention to these symptoms can facilitate the early diagnosis and management of potential diseases.
Potential neurologological indications: Some autoimmune diseases can impact the nervous system, resulting in symptoms such as frequent headaches, dizziness, or cognitive difficulties. Recognizing these indicators and consulting with a healthcare professional can help identify and address potential underlying autoimmune disorders.
It is important to remember that these early signs do not confirm the presence of an autoimmune disease, but rather serve as potential red flags that prompt further investigation. Seeking professional medical advice when any of these signs become apparent is essential for accurate diagnosis and timely intervention in autoimmune disorders.
Fatigue and Low Energy Levels
Feeling tired and lacking energy are common indicators of an underlying health issue that should not be ignored. When experiencing fatigue and low energy levels, it may be a sign that there could be an autoimmune disease present. These symptoms often go beyond the normal tiredness that can be relieved with rest and can persist for an extended period of time, potentially affecting one’s daily activities and overall quality of life.
The exact cause of fatigue and low energy levels in autoimmune diseases varies depending on the specific condition. However, it is believed that the immune system’s abnormal response is a contributing factor. In autoimmune diseases, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells instead of foreign substances, leading to inflammation and damage to various organs and tissues. This constant immune response can result in fatigue and a feeling of constant tiredness.
It is important to note that fatigue and low energy levels can be associated with other medical conditions as well, so it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. It is also advisable to keep a record of fatigue levels and any other accompanying symptoms to provide your doctor with a comprehensive understanding of your condition.
| Common symptoms of fatigue and low energy levels in autoimmune diseases: |
|---|
| – Persistent tiredness that does not improve with rest |
| – Difficulty concentrating and brain fog |
| – Unexplained muscle and joint pain |
| – Depression and mood swings |
| – Increased sensitivity to cold or heat |
If you are experiencing chronic fatigue and low energy levels, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause. Early detection and treatment of autoimmune diseases can significantly improve the management of symptoms and overall quality of life.
Unexplained Weight Loss or Gain
Weight changes that cannot be attributed to a specific cause can sometimes be an early indicator of an underlying autoimmune condition. These fluctuations in weight can be either unexplained weight loss or unexplained weight gain.
Unexplained weight loss refers to a significant decrease in body weight without a conscious effort to lose weight. It is important to note that while weight loss can occur for a variety of reasons, such as dietary changes or increased physical activity, unexplained weight loss is characterized by a loss of 5% or more of total body weight within a span of six to twelve months without any apparent reason.
On the other hand, unexplained weight gain refers to a significant increase in body weight that cannot be explained by an increase in calorie intake or decrease in physical activity. This can be particularly concerning if it happens rapidly or if it is disproportionate to the individual’s lifestyle or eating habits.
Unexplained weight loss or gain can be indicative of an autoimmune disease due to the body’s immune system attacking healthy tissues, which can disrupt normal bodily functions, including metabolism. It is crucial to pay attention to these changes and consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and diagnosis.
While unexplained weight loss or gain alone does not necessarily indicate an autoimmune disease, recognizing and addressing this symptom early on can help identify any underlying conditions and facilitate timely medical intervention and treatment.
Joint Pain and Stiffness
One of the most prevalent symptoms experienced by individuals with autoimmune diseases is joint pain and stiffness. This condition affects the mobility and flexibility of the joints, causing discomfort and limitation of movement. Identifying and understanding the early signs of joint pain and stiffness is crucial in recognizing the presence of an autoimmune disease.
The sensation of joint pain can vary from mild discomfort to intense and debilitating pain. Individuals may experience stiffness in one or multiple joints, which can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks or engage in physical activities. This symptom is often characterized by a feeling of tightness or difficulty in moving the affected joint.
Joint pain and stiffness can occur in various parts of the body, including the fingers, wrists, elbows, shoulders, knees, and ankles. It is essential to pay attention to any persistent or recurring pain or stiffness, as this may indicate an underlying autoimmune condition.
In addition to joint pain and stiffness, individuals with autoimmune diseases may also experience other related symptoms such as swelling, redness, and warmth in the affected joints. These symptoms can worsen over time, leading to decreased joint function and increased disability if left untreated.
If you are experiencing persistent joint pain, stiffness, or any other concerning symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. Early detection and management of autoimmune diseases can help prevent further complications and improve overall quality of life.
Recurring Skin Rashes or Lesions
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/scleroderma-signs-symptoms-and-complications-4177037_color2-5c0f2d9046e0fb00017d0aa2.png)
Recurrent skin rashes or lesions can often serve as an early indicator of an underlying autoimmune condition. These persistent dermatological manifestations can manifest in various forms, such as redness, itching, swelling, blisters, or raised bumps on the skin. Identifying and recognizing these recurring skin issues is crucial for timely diagnosis and management of potential autoimmune diseases.
Questions and answers
What are the early signs of autoimmune disease?
Some common early signs of autoimmune disease include fatigue, joint pain, muscle weakness, recurring fever, and skin rashes. It is important to note that these symptoms can vary greatly depending on the specific autoimmune disease a person may have.
How can I recognize the early signs of an autoimmune disease?
Recognizing the early signs of an autoimmune disease can be challenging as the symptoms can be vague and easily mistaken for other health issues. However, if you experience persistent fatigue, frequent joint pain or muscle weakness, persistent fever, or unexplained skin rashes, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for a comprehensive evaluation and diagnosis.
Why is it important to recognize the early signs of autoimmune disease?
Early recognition of autoimmune disease is crucial because it allows for prompt medical intervention and management. Many autoimmune diseases have no cure, but early treatment can help control symptoms, prevent further damage to organs or tissues, and improve quality of life.
What should I do if I suspect I have an autoimmune disease based on the early signs?
If you suspect that you may have an autoimmune disease based on the early signs, it is recommended to consult a healthcare professional. They can perform a thorough physical examination, review your medical history, and order relevant tests to determine the cause of your symptoms and provide appropriate treatment options.
Are these early signs of autoimmune disease specific to a particular age group?
No, the early signs of autoimmune disease can occur in people of all age groups. While certain autoimmune diseases may be more prevalent in specific age groups, experiencing symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, muscle weakness, fever, or skin rashes should not be disregarded solely based on age.
What are the early signs of autoimmune disease?
Early signs of autoimmune disease can vary depending on the specific condition, but common symptoms to watch for include fatigue, joint pain and stiffness, unexplained weight loss or gain, skin rashes, and chronic inflammation.
How can I recognize if I have an autoimmune disease?
Recognizing an autoimmune disease can be challenging as symptoms may overlap with other conditions. However, if you experience persistent or unusual symptoms such as chronic fatigue, joint pain, or recurring skin issues, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if further evaluation is necessary.
What should I do if I suspect I have an autoimmune disease?
If you suspect that you may have an autoimmune disease, it is important to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can evaluate your symptoms, medical history, and perform diagnostic tests if needed to determine the appropriate course of action.
Are there any specific tests to diagnose autoimmune diseases?
There is no single test that can diagnose all autoimmune diseases. However, healthcare professionals may use a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests to check for autoantibodies or markers of inflammation, and imaging studies to help diagnose an autoimmune condition.
What are the treatment options for autoimmune diseases?
Treatment for autoimmune diseases depends on the specific condition and its severity. It may involve a combination of medications to manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and suppress the immune system. Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet and managing stress, may also be recommended. In some cases, physical therapy or other supportive therapies may be beneficial.