Delving into the mysteries that surround the consumption of detrimental sustenance, one cannot help but be startled by the profound ramifications it bestows upon our mental prosperity. In a world saturated with an overwhelming abundance of food choices, it becomes imperative to comprehend the intricate connections between our dietary habits and the intricate fabric of our emotional well-being. Unlocking the enigmatic dangers lurking in the shadows of unhealthy food, it becomes evident that the effects reach far beyond mere physical health; they extend into the realm of the mind, impacting our moods, thoughts, and overall psychological equilibrium.
Unbeknownst to many, the perilous implications of ingesting deleterious edibles rear their heads in a myriad of ways that often elude our conscious perception. While the physical repercussions are widely recognized and well-documented, the profound link between our dietary choices and our emotional state remains a lesser-explored frontier. It is here, in the depths of our neural network, that unhealthy food wields its insidious might, infiltrating the channels through which our emotions are channeled. By peering beneath the surface of common perception, we unveil a disturbing reality – the detrimental substances present in our diets insidiously erode our mental resilience and compromise our ability to navigate the complexities of daily life with grace and equanimity.
Indeed, it is through a deeper understanding of the intricate interplay between mind and gut that we can begin to fathom the intriguing mechanisms by which unwholesome victuals cast their maleficent shadow over our psychological panorama. As the saying goes, you are what you eat, and nowhere is this sentiment truer than in the realm of our mental well-being. The foods we consume not only impact the physical composition of our bodies but also shape our cognitive processes, emotional stability, and overall mental health. It is this unseen connection, this harmonious dance between our nutritional choices and our intricate psyche, that forms the crux of the hidden dangers that lie within our plates and bowls.
- Understanding the Link Between Unhealthy Food and Mental Well-being
- The Role of Diet in Mental Health
- Exploring the Connection
- Scientific Studies and Findings
- Unhealthy Food and its Effects on the Brain
- How Junk Food Hijacks the Brain
- The Influence on Cognitive Functions
- Psychological Consequences of Unhealthy Food Consumption
- Mood Disorders and Food Choices
- Eating Disorders and Emotional Well-being
- Questions and answers
Understanding the Link Between Unhealthy Food and Mental Well-being
Exploring the Correlation Between Harmful Food Choices and Emotional Wellness
Recent studies have shed light on the intricate relationship between the types of food we consume and our mental well-being. It is widely acknowledged that the diet we maintain plays a significant role in determining our physical health. However, emerging research suggests that the impact stretches far beyond the surface-level effects on our bodies. In fact, the consumption of unhealthy food may have profound implications on our mental state, affecting our emotions, cognitive abilities, and overall psychological well-being.
An Unhealthy Diet and its Psychological Consequences
Contrary to popular belief, the consequences of an unhealthy diet extend beyond physical health concerns such as obesity and heart disease. The excessive intake of processed foods, sugary snacks, and fast food has been linked to a range of mental health issues. These may include but are not limited to depression, anxiety, mood swings, and decreased cognitive function. The prevalence of such negative effects emphasizes the importance of understanding the link between our dietary choices and our emotional well-being.
The Role of Gut Health in Mental Wellness
One plausible explanation for the connection between unhealthy food and mental well-being lies in the intricate relationship between our gut and our brain. Recent studies suggest that our gut, often referred to as our second brain, plays a crucial role in regulating our emotions, thanks to the millions of neurons it contains. Consequently, consuming a diet high in processed and unhealthy foods can disrupt the delicate balance of gut microbiota, leading to inflammation and ultimately adversely impacting our mental health.
The Influence of Nutrient Deficiencies on Mood
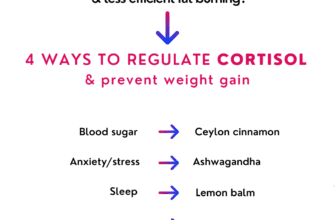
Another aspect worth exploring is the role of nutrient deficiencies in shaping our mood and mental well-being. An unhealthy diet lacking essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients can contribute to imbalances in neurotransmitters, which are crucial for maintaining stable moods and overall mental wellness. Specifically, deficiencies in omega-3 fatty acids, B vitamins, zinc, magnesium, and antioxidants have been associated with an increased risk of mental health disorders, highlighting the significance of a balanced and nutrient-rich diet.
Concluding Thoughts
As researchers delve deeper into the complex relationship between unhealthy food and mental well-being, it becomes increasingly evident that our dietary choices have far-reaching consequences. From the impact on our gut health to nutrient deficiencies and their effects on neurotransmitters, the link between what we eat and how we feel cannot be ignored. Educating ourselves about the potential risks and the benefits of a wholesome diet can empower us to make informed decisions for our overall well-being, both physically and mentally.
The Role of Diet in Mental Health
Diet plays a crucial role in influencing mental well-being. The food we consume has a significant impact on our mental health, affecting our mood, emotions, cognitive function, and overall mental state. It is important to recognize the close relationship between nutrition and mental well-being, as poor dietary choices can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health issues.
Firstly, a healthy diet rich in essential nutrients is essential for supporting brain function, neurotransmitter synthesis, and maintaining stable mental health. Consuming a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides the necessary vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that promote optimal brain health and function.
- Furthermore, specific nutrients play vital roles in mental well-being. For example, omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, nuts, and seeds have been linked to improved mood and reduced risk of depression. Similarly, B vitamins, found in foods like leafy greens, legumes, and whole grains, are involved in neurotransmitter production and can influence mood regulation.
- In contrast, a diet high in processed foods, added sugars, and unhealthy fats can have detrimental effects on mental health. These foods are often lacking in essential nutrients while being high in refined carbohydrates and artificial additives. Such a diet has been associated with increased risk of depression, anxiety, and cognitive decline.
Moreover, the gut-brain connection highlights another aspect of the relationship between diet and mental health. The gut microbiome, made up of trillions of microorganisms, plays a crucial role in maintaining mental well-being. A healthy diet supports a diverse and balanced gut microbiome, which in turn positively influences brain function and reduces the risk of mental health disorders.
In conclusion, adopting a nutritious diet is essential for maintaining optimal mental health. By consuming a wide range of nutrient-dense foods, we can support brain function, neurotransmitter production, and the overall well-being of our mental state. Conversely, a poor diet lacking in essential nutrients can contribute to the development or worsening of mental health issues. It is crucial to prioritize a healthy diet as part of a holistic approach to mental well-being.
Exploring the Connection

In this section, we delve into the intricate relationship between our mental well-being and the consumption of unhealthy food. By examining the underlying factors and exploring the intricacies of this connection, we aim to shed light on the significant impact that our dietary choices can have on our emotional and psychological state.
It is no secret that what we eat plays a crucial role in our overall health. However, the effects of unhealthy food extend beyond physical well-being, stretching into the realm of mental and emotional wellness. Through a comprehensive exploration of this connection, we seek to uncover the intricate mechanisms at play, revealing the profound impact that nutrition has on our psychological state.
By understanding the various ways in which unhealthy food influences our mental well-being, we can gain insights into how our dietary habits may be contributing to cognitive decline, mood disorders, and even the development of mental illnesses. The exploration of this connection will bring to light the significance of making informed food choices and the potential for improving our mental well-being through a balanced and nutritious diet.
We will examine the psychological effects of consuming additives, preservatives, and artificial ingredients commonly found in unhealthy food. Additionally, we will delve into the impact of high sugar and saturated fat intake on our brain function and emotional stability. Through this comprehensive exploration, we hope to highlight the need for a more holistic approach to nutrition and mental health, promoting a greater awareness of the potential dangers hidden within our everyday food choices.
It is important to remember that our diet not only affects our physical health but also has a profound influence on our mental well-being. By exploring the connection between unhealthy food and its impact on our emotional and psychological state, we can strive for a better understanding of the hidden dangers lurking within our plates, and ultimately make more informed choices for our overall well-being.
Scientific Studies and Findings
In this section, we will explore the extensive research conducted and the significant discoveries made regarding the detrimental effects of consuming unhealthy food on our mental well-being. These studies have shed light on the profound impact that our dietary choices can have on our overall mental health.
Researchers have delved into various aspects, investigating the intricate relationship between nutrition and mental well-being. Their findings have revealed a compelling correlation between an unhealthy diet and a higher risk of developing mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, and even cognitive decline.
Scientific investigations have uncovered that the consumption of unhealthy food, characterized by high levels of saturated fats, sugars, and processed ingredients, is associated with increased inflammation in the body. This chronic inflammation can trigger changes in the brain’s chemistry, disrupting neurotransmitter signaling and leading to mood disturbances.
Moreover, studies have shown that diets lacking essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids, can compromise brain function and impair cognitive abilities. The deficiency of these crucial elements has been linked to decreased concentration, memory problems, and a higher vulnerability to mental health disorders.
Furthermore, enlightening research has demonstrated how unhealthy food can contribute to the development of addictive behaviors, similar to those induced by drugs. Certain components in processed foods, such as artificial additives and excessive amounts of sugar, have been found to stimulate the brain’s reward center, leading to cravings, binge eating, and an unhealthy cycle of dependency.
These scientific studies and findings serve as a wake-up call, emphasizing the importance of adopting a balanced and nutritious diet for the sake of our mental well-being. While the allure of unhealthy food may be tempting, being mindful of its detrimental impact can empower individuals to make informed choices and prioritize their mental health.
Unhealthy Food and its Effects on the Brain
The Impact of Unhealthy Dietary Choices on Cognitive Function
The brain, the command center of our bodies, is greatly influenced by the foods we consume. A growing body of research suggests that unhealthy food choices can have detrimental effects on our cognitive function, affecting our memory, attention span, and overall mental well-being. In this section, we delve into the hidden dangers of unhealthy food and how they can impact the brain.
Impaired Cognitive Processing
Consuming unhealthy food regularly can lead to impaired cognitive processing, impacting our ability to think, learn, and make decisions effectively. Such foods, high in processed sugars and unhealthy fats, can disrupt neurotransmitter levels in the brain, hindering proper communication between neurons. As a result, cognitive processes such as memory retention, attention span, and problem-solving skills may be compromised.
Increased Risk of Mental Disorders
Mounting evidence suggests that diets high in unhealthy foods are associated with an increased risk of mental disorders, such as depression and anxiety. The chronic inflammation and oxidative stress caused by these diets can negatively impact neurotransmitter function and alter mood regulation. Additionally, the lack of essential nutrients and antioxidants in unhealthy foods can contribute to the development and progression of mental health disorders.
Effects on Brain Structure
Unhealthy food choices have been linked to alterations in brain structure, particularly in areas responsible for reward and motivation. These regions, such as the prefrontal cortex and hippocampus, can experience reduced volume and impaired functioning when regularly exposed to unhealthy foods. Such structural changes can contribute to addictive behaviors, difficulties in impulse control, and increased vulnerability to mental health disorders.
The Role of Gut Health
Emerging research indicates that the gut microbiota, the diverse community of bacteria residing in our digestive system, plays a crucial role in brain health. Unhealthy food choices can negatively affect the composition of the gut microbiota, leading to an imbalance known as dysbiosis. This imbalance can facilitate the production of harmful substances that can cross the blood-brain barrier, potentially causing inflammation and further impairing brain function.
In conclusion, it is evident that our dietary choices have a significant impact on the health of our brain. By understanding the effects of unhealthy food on cognitive function and mental well-being, we can make informed choices for a healthier brain and overall well-being.
How Junk Food Hijacks the Brain
In this section, we delve into the captivating influence that unhealthy food has on our brain. The allure of junk food goes beyond its mere taste, as its consumption can lead to an astonishing takeover of our neural pathways. It enslaves our minds without us even realizing it, making it crucial to understand how this hijacking occurs and the detrimental consequences it poses for our mental health.
The Intricate Web of Junk Food Addiction
The consumption of junk food triggers a complex series of chemical reactions in our brain, drawing us into a cycle of craving and indulgence. As we indulge in these processed and high-sugar foods, the brain releases dopamine, a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure and reward. This surge of dopamine creates a sense of euphoria, reinforcing the desire to seek out and consume more unhealthy food.
The Role of Hyperpalatability
Junk food manufacturers meticulously engineer their products to be hyperpalatable, combining layers of sugar, fat, salt, and additives that hyperstimulate our taste buds and overload our sensory systems. These flavors and textures surpass the natural range found in wholesome foods, captivating our senses and creating a heightened desire for these artificially enhanced culinary creations.
Impairing Cognitive Functions
Overconsumption of junk food leads to detrimental effects on cognitive functions, such as memory, learning, and decision-making. The excessive intake of unhealthy food disrupts the delicate balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, impairing communication between neurons and compromising our ability to focus, retain information, and make rational choices.
Unveiling the Emotional Consequences
Beyond its impact on cognitive functioning, the hijacking of the brain by junk food has far-reaching emotional consequences. The temporary feelings of pleasure experienced during consumption quickly give way to guilt, shame, and even depression. These negative emotions further perpetuate the cycle of addictive behavior, creating a vicious circle that affects our overall mental well-being.
Breaking Free from the Grip
By understanding the powerful hold that junk food has on the brain, we can take steps to regain control of our mental and physical health. Building awareness, making informed food choices, and incorporating a balanced diet can help us break free from the clutches of unhealthy food and nurture our mental well-being.
The Influence on Cognitive Functions
Delving deeper into the realm of unhealthy dietary choices and their impact on our minds, it becomes evident that our cognitive functions are not immune to the effects. The choices we make regarding what we consume can have far-reaching consequences on our ability to think, reason, remember, and concentrate.
It is crucial to recognize that the repercussions of consuming unhealthy food extend beyond physical health. The mind, too, is intricately intertwined with the body, and the foods we consume can either nurture or impair our cognitive functions. Mental clarity, focus, and the ability to process information efficiently are all crucial aspects that can be influenced by our dietary choices.
The link between nutrition and cognition lies in the fact that our brains require specific nutrients to function optimally. Essential vitamins, minerals, and fatty acids play a crucial role in the development and maintenance of cognitive abilities. Conversely, a diet lacking in these vital components can lead to deficits in attention, memory, problem-solving, and overall cognitive performance.
Moreover, the negative impact of unhealthy foods on cognitive functions is not limited to the short-term. Prolonged exposure to a poor diet can have cumulative effects, leading to long-lasting cognitive decline and an increased vulnerability to mental disorders. Conditions such as depression, anxiety, and even neurodegenerative diseases have been linked to an unhealthy diet and impaired cognitive functions.
Therefore, it is imperative to acknowledge the significant influence our food choices can have on our minds. By prioritizing a balanced and nutritious diet, we can safeguard and enhance our cognitive abilities, fostering a resilient and thriving mental state.
Psychological Consequences of Unhealthy Food Consumption

Delving into the realm of psychological consequences associated with the intake of unhealthy food provides valuable insights into the intricate relationship between what we consume and our mental well-being. By examining the impact of unhealthy food on our psychological state, we can uncover the potential adverse effects it has on various aspects of our cognition, emotions, and overall mental health.
| Consequence | Definition |
|---|---|
| Impaired Cognitive Functioning | Decreased ability to focus, concentrate, and retain information due to the consumption of inadequate and nutritionally deficient food. |
| Mood Instability | Fluctuations in emotions, such as irritability, anxiety, and depressive symptoms, as a result of consuming unhealthy food that lacks essential nutrients needed for optimal brain function. |
| Reduced Stress Coping Mechanisms | Diminished ability to effectively manage stress and cope with everyday challenges due to the negative impact of unhealthy food on neurotransmitter systems involved in stress regulation. |
| Increased Risk of Mental Disorders | Elevated likelihood of developing mental health conditions, such as depression, anxiety disorders, and eating disorders, resulting from prolonged consumption of unhealthy food. |
| Impaired Sleep Quality | Disrupted sleep patterns and decreased sleep quality due to the consumption of unhealthy food that disrupts the production of sleep-regulating hormones and neurotransmitters. |
These psychological consequences emphasize the significance of adopting a balanced and nutritious diet to promote not only physical well-being but also mental health. Incorporating healthier food choices can enhance cognitive functioning, stabilize mood, improve stress resilience, reduce the risk of mental disorders, and promote better sleep quality.
Mood Disorders and Food Choices
Exploring the intricate relationship between our emotional state and dietary preferences is crucial in understanding the impact of food choices on mood disorders. The connection between these two elements goes beyond a simple correlation and delves into the complex interplay of biological, psychological, and social factors.
When it comes to mood disorders, individuals may exhibit distinct patterns in their food choices. Some people may find solace in consuming sugary and processed foods, seeking temporary pleasure and comfort. Others may experience a loss of appetite or engage in emotional eating, where food becomes a coping mechanism to deal with negative emotions.
Research has shown that certain components found in unhealthy food options, such as high levels of refined sugars, trans fats, and artificial additives, can have detrimental effects on mental well-being. These substances can disrupt neurotransmitter function, including serotonin and dopamine, influencing mood regulation. Furthermore, the imbalance caused by these ingredients may contribute to increased inflammation and oxidative stress, both of which have been linked to the development and exacerbation of mood disorders.
| Negative Effects | Positive Impact |
|---|---|
| Increased risk of depression | Reduced risk of depression |
| Aggravation of anxiety symptoms | Improved stress management |
| Impaired cognitive function | Enhanced cognitive performance |
| Reduced motivation and energy levels | Increased vitality and motivation |
On the other hand, incorporating nutrient-dense foods into our diet can have a positive impact on our mental well-being. Adequate intake of essential vitamins and minerals, omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and phytochemicals can support brain health and promote stable moods. Moreover, certain natural compounds present in food, such as tryptophan and magnesium, play crucial roles in the synthesis of mood-stabilizing neurotransmitters.
Understanding the connection between mood disorders and food choices empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their diet and overall mental well-being. By adopting a balanced and nutritious approach to eating, individuals can potentially mitigate the negative effects of unhealthy food choices and improve their emotional resilience and overall quality of life.
Eating Disorders and Emotional Well-being
Emotional well-being can be significantly affected by the presence of eating disorders, which refer to a range of unhealthy relationships with food and body image. In this section, we explore the intricate connection between eating disorders and emotional well-being, focusing on the psychological impacts they can have on individuals.
The emotional effects of eating disorders can be profound, leading to distress and a diminished sense of self-worth. Individuals with eating disorders often experience a constant preoccupation with food, weight, and body shape, which can result in feelings of anxiety, guilt, and shame. Moreover, the intense focus on physical appearance can contribute to poor body image and distorted perceptions of self, further exacerbating emotional distress.
These emotional challenges often create a vicious cycle, as negative emotions can trigger disordered eating behaviors and vice versa. The connection between the mind and the body becomes blurred, with emotions driving unhealthy food choices and eating habits. The repetitive cycle of emotional turmoil and disordered eating can lead to a deteriorating emotional well-being, affecting various aspects of one’s life.
Furthermore, eating disorders can have significant social implications on emotional well-being. The constant comparison to societal ideals and internalization of unrealistic beauty standards can lead to feelings of inferiority and social isolation. The emotional toll of these disorders can strain relationships, as individuals may withdraw from social events or struggle to express their emotions effectively.
Recognizing the detrimental impact of eating disorders on emotional well-being is crucial in promoting better understanding and support for individuals affected by these conditions. By addressing the underlying emotional distress and providing psychological interventions alongside nutritional assistance, holistic recovery becomes attainable. Understanding the complex interplay between emotional well-being and eating disorders is vital for fostering healthier relationships with food and cultivating positive self-esteem.
Questions and answers
Why is unhealthy food bad for mental well-being?
Unhealthy food, such as processed and sugary foods, lacks the essential nutrients needed for proper brain function. These foods can lead to inflammation in the brain, which can negatively impact mental well-being and increase the risk of mental health disorders.
Can unhealthy food affect mood?
Yes, unhealthy food can affect mood. Consuming foods high in sugar and fats can cause rapid spikes and drops in blood sugar levels, leading to mood swings, irritability, and fatigue. Additionally, a diet lacking in essential nutrients can contribute to feelings of low mood and depression.
Are there any specific types of unhealthy food that are particularly detrimental to mental well-being?
Highly processed foods, fast food, sugary snacks, and beverages are particularly detrimental to mental well-being. These foods are generally low in essential nutrients and high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and additives, which can negatively affect brain function and overall mental health.
Is there a connection between unhealthy food and anxiety?
Yes, there is a connection between unhealthy food and anxiety. Research has shown that a diet high in unhealthy fats and sugars can increase the risk of developing anxiety disorders. Additionally, the inflammation caused by consuming unhealthy foods can also contribute to anxiety symptoms.
How can unhealthy food impact cognitive function?
Unhealthy food can negatively impact cognitive function. A diet lacking in essential nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals, can impair memory, concentration, and overall cognitive performance. Consuming excessive amounts of sugar and unhealthy fats can also lead to brain fog and difficulty in thinking clearly.
How does unhealthy food affect mental well-being?
Unhealthy food can have a negative impact on mental well-being. Studies have shown that a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can contribute to feelings of depression, anxiety, and stress. These foods may disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to mood swings and reduced overall mental well-being.
What are some specific examples of unhealthy foods that can affect mental well-being?
Unhealthy foods that can have a negative impact on mental well-being include sugary beverages, fast food, processed snacks, fried foods, and foods high in artificial additives and preservatives. These foods often lack essential nutrients and can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, which are detrimental to brain health and mental well-being.
Are there any healthy alternatives to unhealthy foods that can improve mental well-being?
Absolutely! Choosing a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can significantly improve mental well-being. These foods provide essential nutrients, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids, which are known to support brain health and promote a positive mood. Incorporating foods like salmon, nuts, seeds, leafy greens, and berries into your diet can have a positive impact on mental well-being.
Can regular consumption of unhealthy food lead to long-term mental health problems?
Yes, regular consumption of unhealthy food can contribute to long-term mental health problems. Eating a diet high in processed and unhealthy foods over an extended period can increase the risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. It can also impair cognitive function and increase the likelihood of developing neurodegenerative diseases in the future.
How quickly can a change in diet positively affect mental well-being?
The time it takes for a change in diet to positively affect mental well-being can vary from person to person. However, some individuals have reported improvements in their mood and overall mental well-being within a few weeks of adopting a healthier diet. The key is to be consistent with consuming nutrient-dense foods and avoiding unhealthy options for a sustained period of time.