Within the realm of medical science, there exists a profound fascination with the intricate workings of the human body. In particular, researchers have been captivated by the perplexing nature of autoimmune illnesses, which can provoke a myriad of symptoms that elude easy classification. These enigmatic conditions, bestowed upon individuals through a complex interplay of genetic predispositions and environmental factors, encompass an assortment of disorders affecting various bodily systems.
While each autoimmune disease presents a distinct set of challenges, it is the diverse array of symptoms that truly sets them apart. From joint pain and inflammation to skin disorders and debilitating fatigue, these symptoms manifest in a myriad of ways, often leaving patients and even medical professionals bewildered. The proverbial map of symptoms associated with autoimmune conditions spans a cornucopia of bodily manifestations, at times intertwining and intermingling to create a veritable maze of diagnostic puzzles.
What further adds to the intrigue of autoimmune diseases is the unpredictable nature in which symptoms emerge and evolve over time. An individual may experience intermittent episodes of symptoms, only to be followed by extended periods of remission. This unpredictability poses challenges not only for patients who endure the physical and emotional rollercoaster ride but also for clinicians aiming to uncover the underlying mechanisms and develop effective treatment strategies.
As our understanding of the complexities surrounding autoimmune diseases grows, it becomes increasingly evident that unraveling the diverse symptoms and their triggers is crucial for advancing our knowledge and improving patient outcomes. Through a combination of cutting-edge research, collaborative efforts among healthcare professionals, and the empowerment of individuals living with autoimmune conditions, we inch closer to deciphering the intricate web of symptoms that these diseases can conjure.
- Exploring Autoimmune Diseases Symptoms
- Common Symptoms Associated with Autoimmune Diseases
- Fatigue and Malaise
- Joint Pain and Stiffness
- Skin Rashes and Lesions
- Less Known Symptoms That Could Indicate Autoimmune Conditions
- Hair Loss and Nail Changes
- Digestive Issues and Food Intolerances
- Neurological Problems and Cognitive Impairment
- Questions and answers
Exploring Autoimmune Diseases Symptoms
Delving into the Spectrum of Manifestations in Autoimmune Conditions
In this section, we will embark on a comprehensive exploration of the multitude of symptoms that can arise from various autoimmune diseases. By examining the diverse range of manifestations, we aim to gain a deeper understanding of the complex nature of these conditions.
Highlighting the Wide Array of Symptoms
Autoimmune diseases can present with an extensive array of symptoms that can affect multiple organ systems and bodily functions. These symptoms can vary greatly depending on the specific disease and the affected part of the body.
Unveiling the Varied Clinical Presentations
Autoimmune diseases can manifest as joint pain and inflammation, skin rashes, fatigue, fever, muscle weakness, and gastrointestinal disturbances, among many others. These symptoms can be chronic, intermittent, or fluctuate over time, making diagnosis and management challenging.
Examining the Overlapping Symptoms
Furthermore, there can be significant overlap in symptoms between different autoimmune diseases, making it essential for healthcare professionals to conduct thorough assessments and investigations to accurately identify the underlying condition.
Understanding the Impact on Quality of Life
The diverse symptoms associated with autoimmune diseases can have a profound impact on individuals’ quality of life, causing physical discomfort, emotional distress, and limitations in daily activities. A holistic approach to treatment is crucial to address not only the physical symptoms but also the psychological well-being of patients.
Exploring the Importance of Individualized Care
Recognizing the variability in symptoms and their impact, healthcare providers must tailor treatment plans to the specific needs of each patient. By understanding the diverse symptoms triggered by autoimmune diseases, we can strive towards improved management, disease control, and enhanced overall well-being.
Common Symptoms Associated with Autoimmune Diseases
Prevalent Signs Linked to Autoimmune Disorders
Autoimmune diseases are characterized by a wide range of symptoms that vary in severity and manifestation. These conditions can affect different organs and tissues in the body, leading to various health issues. It is crucial to recognize and understand the common signs associated with autoimmune diseases in order to facilitate early diagnosis and proper management.
Joint pain and inflammation
One of the most commonly observed symptoms in autoimmune diseases is joint pain and inflammation. Individuals affected by these conditions often experience swollen and tender joints, making it difficult to carry out daily tasks. The pain in the joints can range from mild to severe, impacting mobility and overall quality of life.
Fatigue and general weakness
Feeling constantly tired and having a general sense of weakness are frequent symptoms experienced by individuals with autoimmune diseases. This persistent fatigue can be debilitating and may significantly reduce a person’s ability to engage in regular activities. It is important to address these symptoms to prevent further deterioration of physical and mental well-being.
Skin abnormalities
Autoimmune diseases can also manifest through various skin abnormalities. These may include rashes, redness, itching, and the development of skin lesions or ulcers. Some individuals may even experience hair loss or changes in nail appearance. Recognizing these dermatological symptoms can aid in the identification and management of underlying autoimmune conditions.
Gastrointestinal issues
Many autoimmune diseases affect the digestive system, leading to gastrointestinal problems. These may range from mild stomach discomfort to chronic diarrhea, vomiting, or bowel irregularities. Individuals experiencing such symptoms should consult a medical professional to determine the potential presence of an autoimmune disorder.
Neurological manifestations
Autoimmune diseases can also affect the nervous system, resulting in various neurological symptoms. These may include headaches, dizziness, numbness or tingling sensations, muscle weakness, and cognitive difficulties. Recognizing these signs is crucial for early intervention and the prevention of potential complications.
Other common symptoms
In addition to the aforementioned symptoms, autoimmune diseases may also present with a wide range of other signs. These can include fever, weight loss or gain, swollen glands, difficulty breathing, and eye problems. Paying attention to these general indicators can aid in the diagnosis and management of underlying autoimmune conditions.
In conclusion, understanding the common symptoms associated with autoimmune diseases is vital for timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Recognizing the prevalence of joint pain, fatigue, skin abnormalities, gastrointestinal issues, neurological manifestations, and other general symptoms can facilitate early intervention and improve the overall well-being of individuals affected by autoimmune disorders.
Fatigue and Malaise
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/3232847_color1-5c0191cec9e77c00013b3053.png)
Exhaustion and weariness are common symptoms experienced by individuals with various autoimmune conditions. This section will explore the debilitating effects of fatigue and malaise in relation to autoimmune diseases, shedding light on the overwhelming sense of physical and mental exhaustion that can often accompany these conditions.
Joint Pain and Stiffness
Joint discomfort and limited mobility are commonly encountered symptoms in individuals affected by various autoimmune conditions. These manifestations can present distinct challenges, hindering daily activities and negatively impacting quality of life. This section aims to explore the multifaceted nature of joint pain and stiffness, delving into the underlying mechanisms and potential management options.
Joint pain, also referred to as arthralgia, refers to the unpleasant sensation experienced in the joints, ranging from a dull ache to sharp, intense pain. Stiffness, on the other hand, pertains to a sensation of reduced flexibility and difficulty in initiating or maintaining movements. Both symptoms often accompany each other, and their severity can vary widely among individuals.
Autoimmune diseases can trigger joint pain and stiffness through several mechanisms. Inflammation plays a crucial role, as the immune system erroneously attacks healthy joint tissues, leading to swelling and pain. Moreover, autoimmune processes can result in damage to the protective cartilage that cushions the joints, further exacerbating symptoms. The exact mechanisms underlying joint pain and stiffness in autoimmune diseases can vary, depending on the specific condition.
Effective management of joint pain and stiffness requires a comprehensive approach. Medical professionals may prescribe anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate symptoms and reduce inflammation. Physical therapy and exercises tailored to improve joint mobility and strength can also be beneficial. In some cases, lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding activities that strain the joints, may help manage symptoms.
Furthermore, complementary therapies, like acupuncture or massage, may provide relief for some individuals. It is important to note that treatment plans should be personalized, taking into account the specific autoimmune disease and its associated symptoms. Regular communication with healthcare providers is crucial to ensure optimal management of joint pain and stiffness.
In conclusion, joint pain and stiffness are prevalent symptoms in autoimmune diseases that significantly impact the well-being of affected individuals. Understanding the underlying mechanisms and implementing appropriate management strategies can greatly enhance the quality of life for those experiencing these symptoms.
Skin Rashes and Lesions
Characterized by a range of visual abnormalities on the skin, skin rashes and lesions are prevalent manifestations linked to autoimmune disorders. These distinct symptoms showcase the diverse ways in which the immune system can react and target the skin.
One of the common outcomes of autoimmune diseases is the emergence of skin rashes and lesions, signifying the intricate relationship between the immune system and the skin. These manifestations can vary greatly in appearance, location, and severity, further emphasizing the complexity of autoimmune disorders.
Various factors contribute to the development of skin rashes and lesions in autoimmune diseases. The immune system’s misguided attack on healthy skin cells leads to the formation of rashes, which may present as red, inflamed patches or raised, scaly areas. Lesions, on the other hand, can appear as blisters, sores, or ulcers, reflecting the destructive nature of the immune response.
- The type and location of the skin rash or lesion can provide valuable diagnostic information for specific autoimmune disorders. For instance, psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory autoimmune condition, often manifests as raised, reddened patches covered with silvery scales.
- Autoimmune blistering disorders, such as pemphigus and bullous pemphigoid, result in the formation of blisters on the skin and mucous membranes, contributing to pain and discomfort.
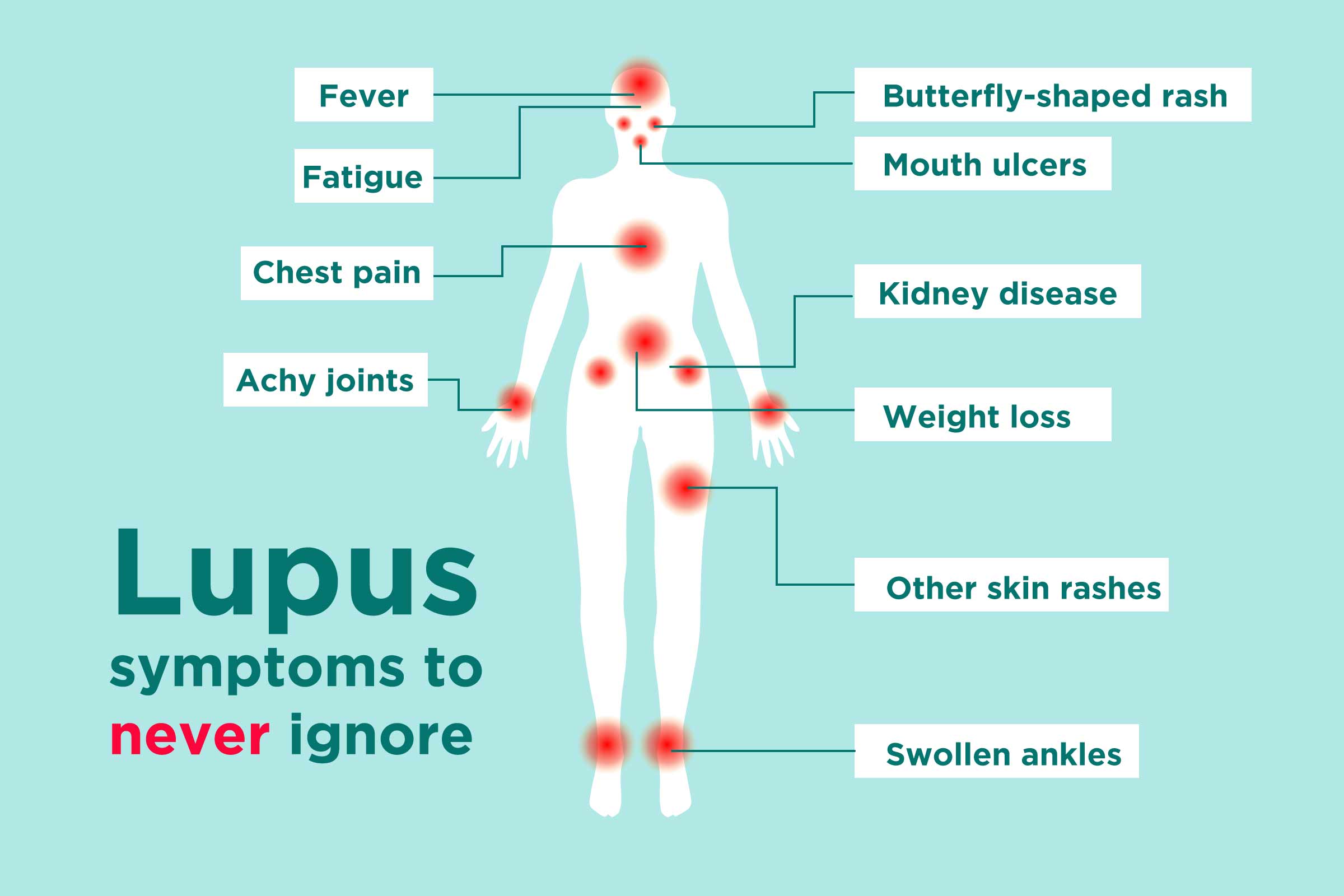
- Lupus, another autoimmune disease, can cause a wide range of skin-related symptoms, including a butterfly-shaped rash on the face, lesions triggered by photosensitivity, and discoid lupus lesions that lead to scarring.
Understanding the distinct characteristics and patterns of skin rashes and lesions in autoimmune diseases plays a crucial role in both diagnosis and treatment. Novel research is continuously uncovering the underlying mechanisms behind these symptoms, paving the way for targeted therapies to alleviate the discomfort and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by autoimmune diseases.
Less Known Symptoms That Could Indicate Autoimmune Conditions
In addition to the well-known symptoms typically associated with autoimmune diseases, such as inflammation, pain, and fatigue, there exist a myriad of lesser-known symptoms that can also serve as indicators of these conditions. These often overlooked symptoms may vary greatly depending on the specific autoimmune condition and the individual affected.
- Unexplained weight loss or gain: Fluctuations in weight that cannot be explained by diet or lifestyle changes may be an indication of an underlying autoimmune disorder.
- Changes in hair texture and growth: Individuals with autoimmune conditions may experience hair thinning, brittle hair, or changes in hair growth patterns.
- Oral ulcers and dry mouth: Recurrent mouth sores and a persistent dry mouth may be early warning signs of an autoimmune condition.
- Brain fog and cognitive difficulties: Some individuals with autoimmune diseases may experience difficulties with memory, concentration, and overall cognitive function.
- Joint pain and stiffness: Joint pain and stiffness, similar to symptoms seen in arthritis, can manifest as a result of certain autoimmune diseases.
The manifestation of these less known symptoms can differ significantly from person to person, making the diagnosis of autoimmune diseases challenging. It is crucial to be aware of the potential range of symptoms and to seek medical attention if any persistent or unusual symptoms arise.
By increasing awareness of these less known symptoms, both individuals and healthcare professionals can better identify potential autoimmune conditions and provide timely intervention and management strategies for those affected.
Hair Loss and Nail Changes
Signs of the Impact on Hair and Nails
Within the intricate world of autoimmune diseases, certain symptoms manifest in diverse ways, affecting various aspects of the body. One such manifestation involves the changes that occur in hair and nails. These alterations can be observed in different forms, including hair loss and abnormal nail growth. In individuals battling autoimmune diseases, disruptions in the normal growth cycle of hair follicles and nail beds often emerge, resulting in visible transformations.
Effects on Hair
One of the prominent indicators of autoimmune diseases is the distressing occurrence of hair loss. This condition, known as alopecia, can present itself in different patterns and extents, ranging from patchy baldness to complete hair loss on the scalp or even the entire body. Hair follicles, essential in the growth and maintenance of hair, become the target of the immune system, leading to their inflammation and subsequent shedding. It is crucial to note that this form of hair loss is not permanent in all cases, as hair regrowth can occur once the underlying autoimmune condition is addressed and managed.
Changes in Nails
Similar to hair, autoimmune diseases can have an impact on the appearance and health of nails. The alterations may manifest as pitting, which refers to the formation of small depressions or dents on the surface of the nails. Additionally, the nails can become brittle, thin, or discolored. Changes in nail growth patterns, such as slowed growth or irregular shape, may also occur. These nail changes can cause discomfort and, in some cases, lead to pain or infection. Appropriate management of the underlying autoimmune condition is crucial to alleviate these nail abnormalities and promote healthier nail growth.
Digestive Issues and Food Intolerances
Exploring the Impact of Gastrointestinal Dysfunctions and Incompatibilities with Food
When it comes to autoimmune diseases, the effects on the gastrointestinal system and the body’s ability to tolerate certain foods can be quite diverse. This section aims to delve into the various digestive issues that can arise as a result of autoimmune conditions, as well as the development of food intolerances.
One of the most common symptoms experienced by individuals with autoimmune diseases is digestive discomfort. This can manifest in different ways, from abdominal pain and bloating to diarrhea and constipation. The gut, being a crucial component of the immune system, is often targeted by autoimmune attacks, leading to inflammation and disruptions in its normal functioning.
Furthermore, individuals with autoimmune diseases may develop food intolerances, where certain foods trigger adverse reactions in their bodies. These sensitivities can range from mild to severe, with symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, and even systemic reactions like hives or difficulty breathing. Identifying and managing these food intolerances is essential to maintaining overall well-being and reducing the frequency and severity of autoimmune flare-ups.
Understanding the precise mechanisms behind the development of digestive issues and food intolerances in autoimmune diseases is a complex task. Researchers are actively investigating the interplay between genetics, gut microbiota, and immune responses to gain more insights into this intricate relationship. By deciphering these mechanisms, it may be possible to develop targeted interventions and therapeutic approaches that can alleviate digestive symptoms and enhance the quality of life for individuals living with autoimmune conditions.
Neurological Problems and Cognitive Impairment
Exploring the intricate world of autoimmune diseases reveals an array of symptoms that extend beyond the expected physical manifestations. Often overshadowed, but equally significant, are the unique challenges presented by neurological problems and cognitive impairment. These manifestations can have a profound impact on a person’s daily life, affecting their ability to think clearly, remember information, and perform daily tasks that once came effortlessly.
Neurological problems encompass a wide range of conditions that affect the nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. One such condition is encephalitis, which refers to the inflammation of the brain. This can lead to a plethora of symptoms, such as headaches, seizures, and even personality changes. Furthermore, autoimmune disorders can also result in the development of neuropathies, disrupting the proper functioning of the peripheral nerves and causing numbness, tingling, and muscle weakness.
Cognitive impairment involves a decline in cognitive abilities, such as memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. This can manifest in various ways, ranging from mild forgetfulness to severe dementia-like symptoms. Individuals with autoimmune diseases may experience difficulties in processing information, concentrating, and multitasking, significantly impacting their overall cognitive function.
It is crucial to note that the emergence of neurological problems and cognitive impairment in autoimmune diseases is highly diverse and complex. The specific symptoms that arise may vary greatly depending on the particular autoimmune disorder, the affected area of the nervous system, and the individual’s unique genetic makeup. This intricate interplay highlights the need for further research and understanding in the field to effectively diagnose, treat, and manage these challenges.
In conclusion, the intricate nature of autoimmune diseases goes beyond physical symptoms, with an intricate web of neurological problems and cognitive impairment. Acknowledging and comprehending the diverse manifestations in these realms is crucial in providing comprehensive care and support to individuals living with autoimmune disorders.
Questions and answers
What are autoimmune diseases?
Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own healthy cells and tissues, causing various symptoms and health issues.
What are the common symptoms of autoimmune diseases?
The symptoms of autoimmune diseases can vary greatly depending on the specific condition, but some common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, skin rashes, inflammation, fever, and organ dysfunction.
How are autoimmune diseases diagnosed?
Autoimmune diseases are often diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies. In some cases, a biopsy of affected tissue may be necessary.
Can autoimmune diseases be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for autoimmune diseases. Treatment options aim to manage symptoms, control inflammation, and suppress the immune system to prevent further damage.
Are autoimmune diseases hereditary?
There is a genetic component to autoimmune diseases, and some conditions tend to run in families. However, not everyone with a family history of autoimmune disease will develop the condition.
What are autoimmune diseases and how do they affect the body?
Autoimmune diseases are conditions caused when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells. This can lead to various symptoms and affect different organs or systems in the body.
What are the common symptoms of autoimmune diseases?
The symptoms of autoimmune diseases vary greatly depending on the specific condition, but some common symptoms include fatigue, joint pain, inflammation, skin rashes, and digestive issues.
Is it possible to have multiple autoimmune diseases at the same time?
Yes, it is possible for an individual to have multiple autoimmune diseases simultaneously. This is known as having a comorbidity of autoimmune diseases.
Are there any specific tests to diagnose autoimmune diseases?
There are various tests that can be done to diagnose autoimmune diseases, such as blood tests to measure certain autoantibodies, imaging tests to examine affected organs, and biopsies to analyze tissue samples.
Can autoimmune diseases be treated or cured?
While there is no known cure for autoimmune diseases, symptoms can often be managed through medications, lifestyle changes, and therapies that aim to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation.