Stress can disrupt our bodies in ways we may not even realize, impacting our physiological functions and influencing our overall wellbeing. In today’s fast-paced world, where demands and pressures seem to be ever-increasing, understanding the link between cortisol and weight gain becomes essential. Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, plays a significant role in our body’s response to stress and can have profound effects on our metabolism.
What is cortisol, you may ask? Well, cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress. It is a natural part of our fight-or-flight response, designed to help us survive dangerous situations. However, in our modern lives, cortisol can be released in excess, leading to various health implications, including weight gain.
So, how exactly does cortisol contribute to weight gain? When stress levels rise, cortisol is released into the bloodstream, signaling the body to store energy as fat. This evolutionary mechanism served our ancestors well when they needed energy reserves to survive famine or physical threats. However, in today’s society, chronic stress and high cortisol levels can lead to weight gain, particularly around the abdominal area, also known as visceral fat.
What’s more, cortisol can influence our metabolism in other ways as well. It can increase our appetite, leading to cravings for high-calorie, comfort foods, which can further contribute to weight gain. Additionally, cortisol can interfere with insulin function, leading to insulin resistance and potentially increasing the risk of developing conditions such as type 2 diabetes.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the intricate relationship between cortisol and weight gain, exploring the mechanisms through which stress affects metabolism. We will also discuss strategies to help manage stress levels and mitigate its impact on our bodies. By understanding this connection, we can take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy weight and overall well-being.
- The Impact of Stress on Your Metabolism: Understanding the Relationship Between Cortisol and Weight Gain
- Understanding the Role of Cortisol in Metabolism
- How Cortisol Affects Your Body’s Fat Storage
- Exploring the Connection Between Cortisol and Hunger
- Stress-Induced Changes in Eating Habits
- The Influence of Cortisol on Food Cravings
- Stress Eating: An Unhealthy Coping Mechanism
- Breaking the Cycle: Managing Stress to Support Healthy Weight
- The Importance of Stress Management in Weight Loss
- Questions and answers
The Impact of Stress on Your Metabolism: Understanding the Relationship Between Cortisol and Weight Gain
Discovering the intricate connection between stress and metabolism can provide insights into how cortisol, a hormone released during stressful situations, affects weight management and potential weight gain. By delving into this relationship, we can gain a better understanding of how stress impacts our bodies and why it often leads to unwanted changes in weight.
When we experience stress, our bodies release cortisol, a natural response that is meant to help us cope with the situation. However, prolonged or chronic stress can lead to consistently elevated cortisol levels, which can disrupt our metabolism and have various effects on our bodies. One of these effects is an increase in appetite, particularly for high-calorie and comfort foods, leading to weight gain over time.
Furthermore, cortisol can affect the way our bodies store and break down fat. High cortisol levels promote the accumulation of visceral fat, which is stored around our organs and linked to various health issues. Additionally, cortisol can interfere with insulin production and sensitivity, potentially leading to imbalances in blood sugar levels and an increased risk of developing conditions such as insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Understanding the relationship between stress, cortisol, and weight gain is crucial for developing strategies to mitigate the negative effects of stress on our metabolism. By managing stress levels through techniques such as exercise, mindfulness, and relaxation techniques, we can potentially reduce the release of cortisol and its impact on our bodies. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet and regular physical activity can help support a healthy metabolism and weight management, even when faced with stressful situations.
In conclusion, the connection between stress and metabolism, primarily mediated by the hormone cortisol, plays a significant role in weight gain and overall health. By exploring and comprehending this relationship, we can take proactive steps towards maintaining a healthy metabolism and managing our weight, even in the face of stress.
Understanding the Role of Cortisol in Metabolism
In this section, we will explore the crucial role that cortisol plays in the intricate processes of metabolism. Cortisol, also known as the stress hormone, significantly influences various aspects of metabolic function. By delving into its impact, we can gain insight into the intricate relationship between cortisol and the body’s ability to efficiently utilize and store energy.
First and foremost, cortisol serves as a key regulator of energy metabolism. It affects the breakdown of macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, ultimately influencing the body’s ability to extract energy from these sources. Additionally, cortisol plays a vital role in glucose metabolism, helping to maintain stable blood sugar levels. This hormone also contributes to the intricate balance between anabolic and catabolic processes, influencing the synthesis and breakdown of molecules within the body.
Beyond its direct influence on macronutrient metabolism, cortisol also exerts significant control over appetite and food intake. During periods of stress, cortisol can lead to an increase in appetite and cravings for energy-dense foods, particularly those high in sugar and fat. This response is believed to be a result of cortisol’s ability to modulate the brain’s reward circuitry, leading to a heightened desire for pleasurable foods.
Moreover, cortisol influences metabolic rate, determining the speed at which the body burns calories. It can lead to alterations in resting metabolic rate, potentially resulting in weight gain or difficulties in losing weight. Additionally, chronically elevated cortisol levels have been linked to the accumulation of visceral fat, which carries an increased risk of metabolic disorders.
It is important to note that while cortisol plays a crucial role in energy regulation, chronic stress can disrupt the delicate balance of cortisol production. Prolonged elevation of cortisol levels, commonly seen in individuals experiencing chronic stress, can lead to dysregulation of metabolism, contributing to weight gain and metabolic dysfunction.
Overall, understanding the intricate role of cortisol in metabolism allows us to grasp the complex interplay between stress, hormone regulation, and the body’s ability to effectively manage energy. By examining the impact of cortisol on various aspects of metabolism, we can develop targeted interventions and strategies to promote optimal metabolic health and mitigate the potential negative effects of stress.
How Cortisol Affects Your Body’s Fat Storage
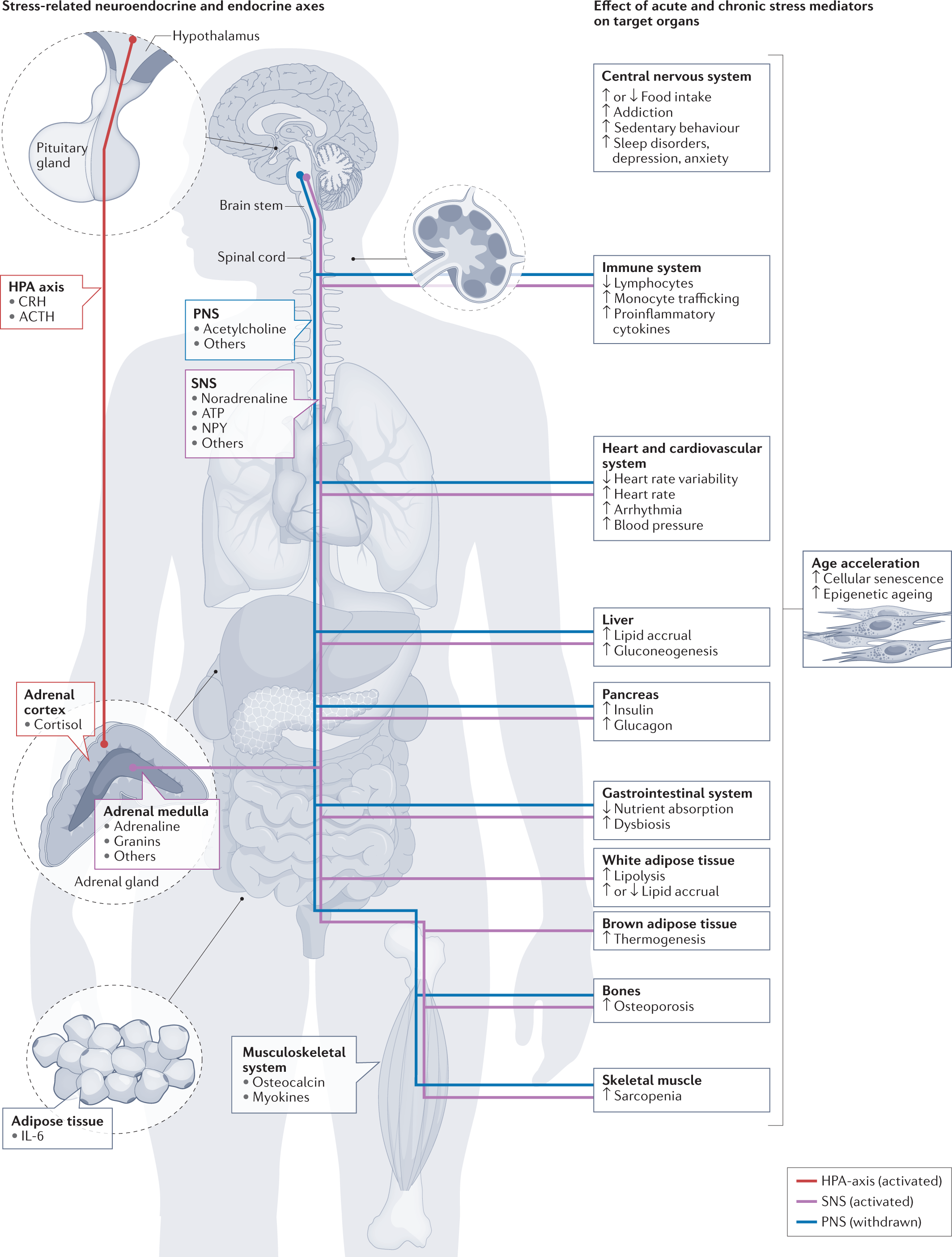
In this section, we will delve into the impact of cortisol on the storage of fat in your body. Cortisol, commonly referred to as the stress hormone, plays a significant role in regulating various physiological processes, including metabolism. When your body experiences stress, cortisol levels rise, triggering a series of changes in your body that can lead to an increase in fat storage.
One of the key ways cortisol affects your body’s fat storage is by promoting the accumulation of visceral fat. Visceral fat is the type of fat that surrounds internal organs, and excessive amounts of it can increase the risk of various health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes. Elevated cortisol levels can stimulate the storage of visceral fat in your abdomen, leading to a more pronounced and visible belly fat.
Apart from promoting the storage of visceral fat, cortisol can also influence the distribution of fat in your body. It has been observed that chronic stress and high cortisol levels are associated with a preferential accumulation of fat in the abdominal region. This means that even if you have an overall healthy body weight, persistent stress can still contribute to an unhealthy distribution of fat, potentially impacting your body composition and overall health.
In addition to affecting where fat is stored in your body, cortisol can also impact the rate at which your body burns calories. High levels of cortisol have been shown to slow down metabolism, making it more difficult for your body to burn calories efficiently. This can lead to weight gain and difficulty in losing weight, even with a healthy diet and regular exercise.
- Elevated cortisol levels can promote the storage of visceral fat.
- Chronic stress and high cortisol levels can lead to an unhealthy distribution of fat.
- Cortisol can slow down metabolism, making it harder to burn calories.
Understanding how cortisol affects your body’s fat storage is crucial in managing weight and overall health. By reducing stress levels and implementing healthy lifestyle habits, such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, you can help regulate cortisol levels and mitigate the negative effects it has on your body’s fat storage.
Exploring the Connection Between Cortisol and Hunger

In this section, we delve into the correlation between elevated levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, and its impact on appetite regulation. Research has shown that cortisol plays a crucial role in influencing our hunger levels, albeit in complex ways that are not fully understood. By examining the effects of cortisol on appetite, we can gain insight into the underlying mechanisms that contribute to weight gain and potentially develop strategies to manage appetite in stressful situations.
| Hormonal Regulation | Psychological Factors | Individual Variations |
|---|---|---|
| Studies have indicated that cortisol is involved in the intricate hormonal pathways that control appetite. It interacts with various hormones, including leptin, ghrelin, and insulin, which are key players in hunger and satiety signals. | Furthermore, the connection between cortisol and hunger extends beyond its hormonal impact. Psychological factors, such as emotional eating and stress-induced cravings, can influence the intensity and frequency of food cravings, leading to overeating and potential weight gain. | However, it is important to note that the relationship between cortisol and hunger can vary among individuals. Some people may experience an increase in appetite during periods of stress, while others may lose their appetite altogether. Understanding these individual variations can aid in developing personalized strategies for managing stress-related eating behaviors. |
By unraveling the intricate connection between cortisol and hunger, we can shed light on the complexities of appetite regulation and its role in weight management. This knowledge can pave the way for interventions and lifestyle modifications that target stress-induced overeating, ultimately promoting overall well-being and optimal metabolic health.
Stress-Induced Changes in Eating Habits
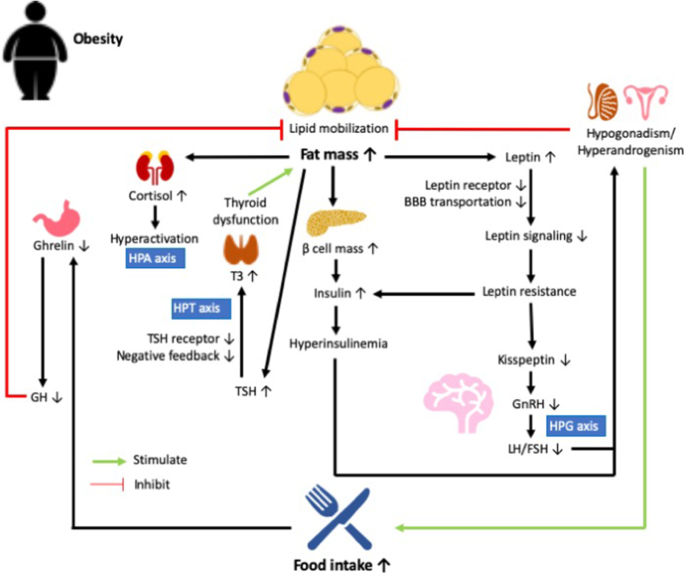
When faced with stressful situations, individuals often experience alterations in their dietary patterns and food preferences. Stress has been observed to have a significant impact on eating habits, leading to changes in food choices, portion sizes, and overall food intake. These stress-induced shifts in eating habits can influence an individual’s metabolism and have implications for weight management and overall health.
One effect of stress on eating habits is the tendency to seek out comfort foods. These are typically high in sugar, fat, and calories, providing a temporary feeling of relief or pleasure. The desire for these types of foods during times of stress can be attributed to the activation of reward pathways in the brain, which link stress relief to the consumption of certain foods. As a result, individuals may exhibit a preference for indulgent and unhealthy food options when they are under stress.
In addition to the preference for comfort foods, stress can also lead to changes in portion sizes and overall food intake. Some individuals may experience an increase in appetite and consume larger quantities of food when they are stressed. This overeating can be driven by the dysregulation of appetite-controlling hormones, such as ghrelin and leptin, which are influenced by stress and cortisol levels. Consequently, stress-induced alterations in eating habits can contribute to weight gain and the development of obesity.
Furthermore, stress can have an impact on meal frequency and eating patterns. Some individuals may develop irregular eating habits, skipping meals or eating at irregular times due to the demands of stress. This disruption in meal timing and frequency can disrupt the body’s metabolic processes and lead to difficulties in maintaining a healthy weight. Stress-related changes in eating habits may not only affect the quantity and quality of food consumed but also the timing and regularity of meals.
While stress-induced changes in eating habits are a common response to challenging situations, understanding the mechanisms behind these alterations is crucial for developing strategies to manage stress-related weight gain. By recognizing the influence of stress on food choices, portion sizes, and eating patterns, individuals can make conscious efforts to prioritize healthy eating, develop stress management techniques, and maintain a balanced lifestyle to mitigate the potential negative effects on metabolism and weight.
The Influence of Cortisol on Food Cravings
Exploring the impact of cortisol on our dietary habits and desires.
When it comes to our relationship with food, there is more at play than just our taste buds and hunger signals. Cortisol, a hormone released in response to stress, has been found to have a significant influence on our food cravings and consumption patterns. Understanding the connection between cortisol and our desire for certain foods can shed light on why stress often leads to unhealthy eating habits.
First and foremost, cortisol stimulates the release of glucose into the bloodstream. This increase in blood sugar triggers the brain to crave quick sources of energy, such as sugary or high-carbohydrate foods. These food choices not only provide an immediate energy boost but also lead to a temporary mood improvement due to the release of neurotransmitters like serotonin. It’s important to note that this craving for comfort foods is not solely driven by taste preferences but can be a biological response to stress.
Furthermore, cortisol promotes fat storage, especially around the abdominal region. This is because prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol can increase insulin resistance and hinder the breakdown of fat cells. As a result, individuals under chronic stress may find themselves more prone to weight gain, particularly in the form of visceral fat. Unfortunately, this abdominal fat is not only aesthetically undesirable but also poses significant health risks, including heart disease and diabetes.
In addition to its effects on metabolism and fat storage, cortisol also disrupts the balance of hunger-regulating hormones in the body. Specifically, it increases levels of ghrelin, a hormone that stimulates appetite, while decreasing levels of leptin, a hormone that suppresses appetite. This hormonal imbalance can lead to constant feelings of hunger and difficulty in feeling satisfied, driving individuals to consume more food than their bodies actually require.
- Increased food cravings, particularly for sugary and high-carbohydrate foods
- Promotion of fat storage, especially around the abdominal region
- Disruption of hunger-regulating hormones, leading to constant feelings of hunger
Overall, the influence of cortisol on food cravings is a complex interplay between hormonal responses to stress and the biological urge for energy. By understanding how stress affects our food preferences and metabolic processes, we can develop strategies to better manage our dietary choices and mitigate the negative impact of stress on our health.
Stress Eating: An Unhealthy Coping Mechanism
In times of stress, individuals often turn to food as a means of soothing their emotions and finding temporary relief. This instinctual response, commonly known as stress eating, can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms and disrupt our body’s natural balance. By examining the relationship between stress and our dietary habits, we can gain a deeper understanding of the impact that stress can have on our overall well-being.
During periods of high stress, the body releases cortisol, a hormone that helps regulate our response to stressful situations. This surge in cortisol can trigger cravings for foods that are high in sugar, fat, and salt, which provide a temporary sense of comfort and pleasure. Unfortunately, indulging in these cravings can lead to weight gain and other negative health consequences.
In addition to the physical effects, stress eating often perpetuates a cycle of emotional distress. Over time, relying on food as a coping mechanism can create feelings of guilt, shame, and frustration, which in turn can lead to further stress and perpetuate the unhealthy behavior. Breaking this cycle requires finding alternative, healthier coping strategies that address the underlying causes of stress.
Exploring the reasons behind stress eating is crucial in order to develop effective strategies for breaking free from this harmful habit. It is important to recognize that stress eating is not a sign of weakness or lack of self-control, but rather a complex response to the demands and pressures of modern life. By seeking support, practicing mindfulness, and implementing stress management techniques, we can develop healthier ways to cope with stress and restore the balance in our lives.
In conclusion, stress eating is an unhealthy coping mechanism that can have a detrimental impact on our physical and emotional well-being. By understanding the relationship between stress and our dietary habits, we can begin to break free from the cycle of stress eating and adopt healthier coping strategies that promote a balanced, sustainable lifestyle.
Breaking the Cycle: Managing Stress to Support Healthy Weight
Discover effective strategies to break the connection between stress and weight gain, and learn how managing stress can contribute to maintaining a healthy weight.
Understanding the Impact of Stress on Weight:
Uncontrolled stress can disrupt the delicate balance of the body’s metabolism, leading to weight imbalances. Chronic stress triggers the release of cortisol, a hormone that influences how the body stores and uses energy. In this section, we will explore the intricate relationship between stress, cortisol levels, and weight gain.
Exploring Stress Management Techniques:
By adopting stress management techniques, individuals can minimize the negative influence of stress on their weight. This section will delve into effective strategies for stress reduction, such as regular exercise, meditation, and deep breathing. We will highlight the importance of self-care and provide practical tips on incorporating these techniques into daily routines.
Building Resilience to Combat Stress:
Developing resilience is an essential component of managing stress for maintaining a healthy weight. Through techniques such as cognitive reframing and fostering social support networks, individuals can enhance their ability to cope with stressors. This section will provide insights into building psychological resilience and equipping individuals with the tools to face stressful situations with better mental and emotional strength.
Cultivating Healthy Habits in Stressful Environments:
In this section, we will explore strategies to cultivate healthy habits while navigating stressful environments. This includes optimizing nutrition and meal planning, getting quality sleep, and incorporating physical activity into a busy schedule. By actively managing stress and making positive choices, individuals can support their weight goals and overall well-being.
Maintaining Long-Term Balance:
Lastly, we will discuss the importance of consistent stress management for long-term weight maintenance. This section will provide practical guidance on creating sustainable lifestyle changes and adapting stress management techniques for different life stages. By breaking the cycle of stress and weight gain, individuals can achieve a healthier weight and enjoy improved overall health and well-being.
The Importance of Stress Management in Weight Loss

In today’s fast-paced world, the correlation between stress and weight gain has become increasingly evident. Stress, whether caused by work pressure, personal issues, or other factors, can have a significant impact on our metabolism and overall health. Understanding the importance of stress management in weight loss is crucial for achieving successful and sustainable results.
One of the key factors that contribute to weight gain is the hormone cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone. When we experience stress, cortisol levels in our body rise, leading to a range of physiological changes that can affect our metabolism. Higher levels of cortisol can cause an increase in appetite, particularly for unhealthy, high-calorie foods. This can lead to overeating and weight gain, undermining our weight loss efforts.
Additionally, chronic stress can disrupt our sleep patterns, further exacerbating weight gain. Poor sleep has been linked to increased hunger, decreased satiety, and altered metabolism, making it more challenging to maintain a healthy weight. Stress management techniques, such as meditation, exercise, or engaging in hobbies, can help reduce stress levels and promote better sleep, aiding in weight loss.
Moreover, stress can trigger emotional eating as a coping mechanism. Many individuals turn to food for comfort or as a way to alleviate stress. This reliance on food as a source of comfort can lead to a cycle of emotional eating, weight gain, and negative emotional well-being. By incorporating stress management strategies into our daily lives, we can find healthier ways to cope with stress and break this detrimental cycle.
When it comes to weight loss, managing stress is as essential as adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity. By reducing stress levels, we can minimize the impact of cortisol on our metabolism, improve sleep quality, and reduce emotional eating episodes. Incorporating stress management techniques into our weight loss journey can promote overall well-being and increase the likelihood of achieving lasting results.
Questions and answers
How does stress affect metabolism?
Stress can have a significant impact on metabolism. When the body is under stress, it releases cortisol, also known as the stress hormone. Cortisol increases the release of glucose into the bloodstream, providing a quick source of energy. However, prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol can lead to weight gain and metabolic disturbances.
Can stress directly cause weight gain?
Yes, stress can directly contribute to weight gain. Elevated cortisol levels associated with chronic stress can lead to increased appetite, especially for sugary and high-fat foods. Many people also engage in emotional eating as a coping mechanism for stress, which can further contribute to weight gain.
What are the long-term effects of cortisol on weight?
Long-term exposure to high levels of cortisol can have detrimental effects on weight. It can lead to increased abdominal fat deposition, as cortisol stimulates the storage of fat in this area. Abdominal fat, in turn, is associated with a higher risk of developing obesity-related diseases such as diabetes and cardiovascular problems.
Is there a way to reduce cortisol levels and prevent weight gain?
Yes, there are strategies that can help reduce cortisol levels and prevent weight gain associated with stress. Regular exercise, especially aerobic exercise, has been shown to lower cortisol levels. Practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can also help in managing stress and reducing cortisol production.
How can I manage stress to prevent cortisol-related weight gain?
Managing stress is essential for preventing cortisol-related weight gain. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as hobbies, spending time with loved ones, and practicing relaxation techniques can be helpful. It’s also important to prioritize self-care, get enough sleep, and maintain a healthy lifestyle overall to mitigate the effects of stress on weight.
Can stress cause weight gain?
Yes, stress can contribute to weight gain. When you’re stressed, your body produces cortisol, a hormone that increases appetite and can lead to overeating. Additionally, high levels of cortisol can promote the storage of fat, particularly in the abdominal area.
How does cortisol affect metabolism?
Cortisol plays a role in regulating metabolism. When cortisol levels are elevated due to stress, it can lead to an increase in insulin resistance, which can result in the accumulation of fat. Additionally, cortisol can affect the breakdown of fats and proteins, leading to changes in energy expenditure and potentially affecting weight management.
What are some strategies to reduce stress-related weight gain?
There are several strategies that can help reduce stress-related weight gain. Engaging in regular physical activity has been shown to lower cortisol levels and improve overall well-being. Additionally, adopting stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help reduce stress levels and prevent emotional eating. Prioritizing sleep, maintaining a balanced diet, and seeking social support are also helpful strategies.
Is cortisol bad for the body?
Cortisol is a hormone that is essential for the body’s response to stress and plays a role in various bodily functions. However, consistently high levels of cortisol due to chronic stress can have negative effects on health. It can lead to weight gain, increased blood pressure, weakened immune function, and disruptions in sleep patterns, among other potential negative consequences. It’s important to manage stress levels to maintain a healthy cortisol balance.
Can stress lead to weight gain even if I don’t overeat?
Yes, stress can contribute to weight gain even without overeating. When you’re under stress, your body releases cortisol, which can promote the storage of fat and cause weight gain, particularly around the abdominal area. Additionally, stress can disrupt sleep patterns and negatively affect metabolism, leading to changes in energy expenditure. Therefore, it’s important to address stress levels and implement healthy coping mechanisms to prevent weight gain, even if you don’t overeat.