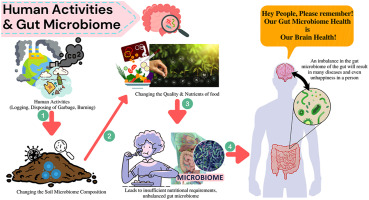
In today’s health-conscious society, there is growing recognition of the fundamental role played by the intricate ecosystem residing within our gastrointestinal tract. The symbiotic relationship between the gut microbiome and the human body is now considered to be pivotal in fostering and preserving overall digestive well-being.
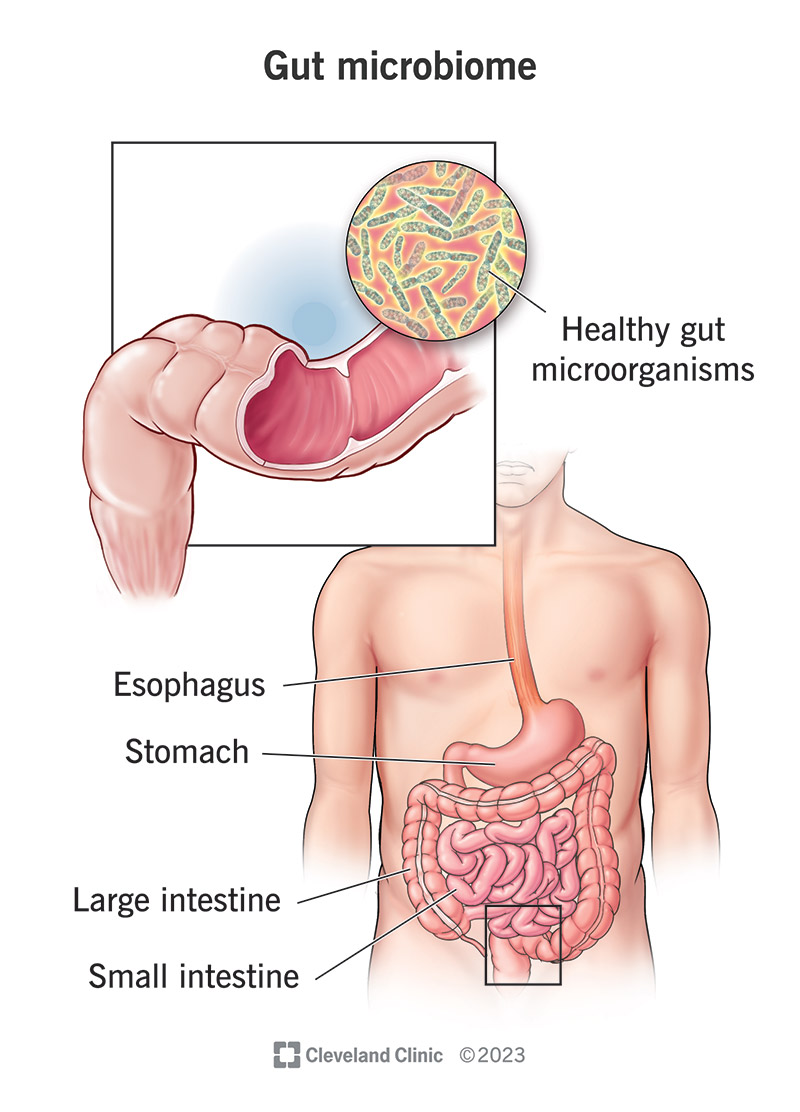
At the core of our digestive system lies an assortment of microorganisms, encompassing bacteria, viruses, and fungi, collectively referred to as the gut microbiome. This rich and diverse community, intricately interwoven with our body, acts as a strong support system, ensuring the smooth functioning of our digestive processes.
An intriguing aspect of the gut microbiome is its ability to modulate various physiological functions, exhibiting an influential impact on our health and vitality. It has emerged as a resilient powerhouse, orchestrating key processes such as nutrient absorption, immune system regulation, and the breakdown of complex compounds that our body alone cannot digest.
The intricate interplay between our gut microbiome and the overall functioning of the digestive system cannot be overstated. The delicate balance within this ecosystem is crucial for the efficient breakdown and absorption of nutrients from the food we consume, ensuring the sustenance of our overall well-being and vitality.
- The Benefits of a Healthy Gut Microbiome for Digestive Health
- The Role of Gut Microbiome in Digestion
- Breaking Down Food into Nutrients
- Supporting Proper Nutrient Absorption
- Enhancing the Immune System
- Factors That Affect Gut Microbiome
- Diet and Nutrition
- Antibiotic Use
- Stress and Mental Health
- Questions and answers
The Benefits of a Healthy Gut Microbiome for Digestive Health
A robust and balanced gut microbiome plays a crucial role in maintaining proper functioning of the digestive system. It is widely recognized that maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is vital for promoting optimal digestion and overall well-being.
One of the key advantages of a healthy gut microbiome is its ability to enhance nutrient absorption. A diverse population of beneficial bacteria in the gut aids in breaking down complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, facilitating their absorption in the intestines. This, in turn, ensures that essential nutrients are effectively absorbed by the body, supporting overall digestive health.
Furthermore, a healthy gut microbiome promotes efficient digestion by regulating bowel movements. The presence of beneficial bacteria helps in maintaining regularity and preventing conditions such as constipation or diarrhea. A well-balanced gut microbiome also assists in the production of necessary digestive enzymes, optimizing digestion and reducing the likelihood of discomfort or bloating after meals.
In addition to digestion, a healthy gut microbiome has a positive impact on the immune system. The gut is home to a significant portion of our immune cells, and a diverse microbiome helps in maintaining a strong immune response. By promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, a healthy gut enhances the body’s ability to defend against harmful pathogens, reducing the risk of digestive infections or inflammations.
The benefits of a healthy gut microbiome extend beyond digestion and immunity. Research has shown a potential link between the gut microbiome and mental health, suggesting that a diverse and balanced gut microbiome may positively influence mood and cognitive function.
| Key Benefits of a Healthy Gut Microbiome: |
|---|
| Enhanced nutrient absorption |
| Regulated bowel movements |
| Improved immune response |
| Potential influence on mental health |
In conclusion, nurturing a healthy gut microbiome is crucial for maintaining optimal digestive health. The benefits extend far beyond digestion, impacting nutrient absorption, bowel movements, immune function, and even mental well-being. By prioritizing the health of our gut microbiome through a balanced diet and lifestyle, we can support a healthier and happier digestive system.
The Role of Gut Microbiome in Digestion
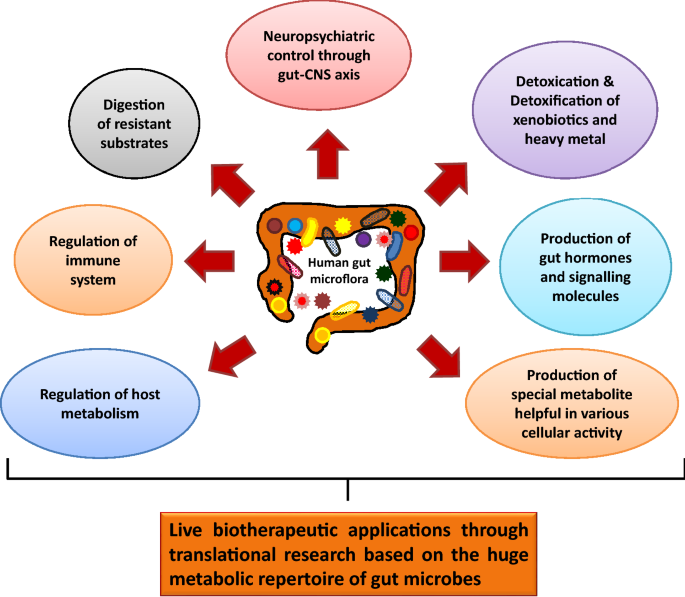
The gut microbiome plays a significant role in the process of digestion, ensuring the efficient breakdown and absorption of nutrients. It contributes to the overall balance and functionality of the digestive system by promoting gut health and supporting various essential processes.
One crucial aspect of the gut microbiome’s role in digestion is its ability to ferment certain dietary fibers and complex carbohydrates that the human body cannot digest on its own. Through this fermentation process, the gut microbiome produces short-chain fatty acids, which provide energy to the cells lining the colon and support the overall health of the digestive tract.
The gut microbiome also aids in breaking down proteins, fats, and other molecules that are ingested through food. It produces specific enzymes that help to break down complex molecules into smaller, more easily absorbable components. Additionally, the gut microbiome is involved in the synthesis of certain vitamins, such as vitamin K and some B vitamins, which are essential for various metabolic processes in the body.
Moreover, the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in the immune system’s function, influencing the development and maintenance of a healthy gut barrier. This barrier helps prevent the entry of harmful pathogens and toxins into the bloodstream, thereby protecting the body from potential infections and inflammation.
Furthermore, the gut microbiome interacts with the enteric nervous system, contributing to the regulation of gut motility and the signaling of hunger and satiety. It communicates with the brain through the gut-brain axis, influencing various aspects of our overall health, including stress response, mood, and cognitive function.
In summary, the gut microbiome is a complex ecosystem that performs a multitude of crucial functions in the process of digestion. From fermenting fibers to breaking down nutrients, supporting the immune system, and communicating with the brain, its role is vital for maintaining optimal digestive health. Understanding and promoting a healthy gut microbiome is therefore essential for overall well-being.
Breaking Down Food into Nutrients
In the process of maintaining a healthy digestive system, one of the fundamental tasks performed by the gut microbiome is breaking down the food we consume into essential nutrients. This intricate process involves various enzymes, bacteria, and acids working together to extract necessary substances from the ingested food, enabling our bodies to function optimally.
- The first step in this breakdown process occurs in the mouth, where chewing and saliva production start breaking down carbohydrates and aiding in their digestion.
- As the food progresses through the digestive tract, it encounters stomach acid and enzymes that further breakdown proteins and fats, ensuring their proper absorption.
- Once the partially broken down food reaches the small intestine, the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in breaking down complex carbohydrates, fiber, and other indigestible substances, converting them into usable energy and essential nutrients.
- Through a process called fermentation, various microorganisms in the gut microbiome assist in breaking down complex molecules that our body cannot digest on its own, releasing beneficial byproducts in the process.
- Lastly, the remaining waste products move through the large intestine, where water is reabsorbed, and the gut microbiome completes the breakdown process by breaking down any remaining fiber and converting it into short-chain fatty acids, which provide additional energy to the body.
Understanding and maintaining a healthy balance of the gut microbiome is vital for the efficient breakdown of food into nutrients. It ensures that the body receives the required vitamins, minerals, and energy necessary for overall well-being and optimal digestive health.
Supporting Proper Nutrient Absorption
In the realm of maintaining a healthy digestive system, one crucial aspect that should not be overlooked is ensuring proper absorption of nutrients. The ability of our bodies to extract essential substances from the food we consume plays a significant role in sustaining our overall well-being.
Achieving optimal nutrient absorption involves a complex interplay of various factors within our digestive system. This intricate process relies on the synergistic actions of different components, including the gut microbiota. The diverse population of microorganisms residing in our gut plays a pivotal role in modulating the effectiveness of nutrient absorption. By maintaining a balanced and diverse gut microbiome, we can support the efficient uptake and utilization of essential nutrients.
One way to promote proper nutrient absorption is by adopting a diet rich in fibers, fruits, and vegetables. These dietary choices contribute to a favorable gut environment, fostering the growth of beneficial bacteria that aid in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients. Additionally, the consumption of probiotic foods and supplements can introduce beneficial bacteria directly, further optimizing nutrient absorption processes.
In addition to dietary considerations, lifestyle factors such as regular physical activity can also bolster nutrient absorption. Engaging in regular exercise has been shown to enhance blood flow to the digestive system, promoting better nutrient absorption. Proper hydration is another crucial aspect to support nutrient absorption, as adequate water intake helps in breaking down and transporting nutrients effectively.
In conclusion, supporting proper nutrient absorption is vital for maintaining a healthy digestive system. By adopting a balanced diet, incorporating probiotics, practicing regular physical activity, and staying adequately hydrated, we can optimize the efficiency of nutrient absorption processes. Prioritizing these practices contributes to overall well-being and long-term digestive health.
Enhancing the Immune System
The synergy between our body’s immune system and the complex community of microorganisms residing within the gut plays a pivotal role in promoting overall well-being. By fostering a robust immune system, we can actively support our body’s defense mechanisms, enabling it to withstand various challenges and maintain optimal health. This section explores ways to bolster our immune system and harness its full potential for a resilient and thriving body.
| 1. Nourishing the Immune System |
| In order to fortify our immune system, it is essential to provide it with the vital nutrients it requires to function optimally. Incorporating a diverse range of nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, ensures that our immune system receives the necessary building blocks to fight off infections and illnesses. A balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and phytochemicals acts as a strong foundation to support the immune system’s vitality. |
| 2. Maintaining a Healthy Gut Microbiota |
| Our gut microbiota, comprising trillions of microbes, has a profound influence on the immune system. By cultivating a diverse and balanced gut microbiome, we can enhance our immunity. Consuming probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt and fermented vegetables, or taking probiotic supplements can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, which in turn stimulates the immune response. Additionally, incorporating prebiotic fiber-rich foods, like onions and oats, nourishes the gut microbiota, providing a favorable environment for beneficial microbes to thrive. |
| 3. Managing Stress and Sleep |
| Chronic stress and inadequate sleep can significantly impair the immune system, leaving the body vulnerable to infections. Prioritizing stress management techniques, such as exercise, meditation, and spending quality time with loved ones, can help reduce stress levels and mitigate its negative impact on the immune system. Equally important is prioritizing sufficient and restorative sleep, as it allows the body to repair and rejuvenate, optimizing immune function. |
| 4. Regular Exercise |
| Engaging in regular physical activity not only enhances overall health but also stimulates the immune system. Exercise promotes the circulation of immune cells, enabling them to reach different parts of the body more efficiently. Furthermore, physical activity has been shown to reduce inflammation, another crucial factor in maintaining a resilient immune system. Incorporating moderate-intensity exercises, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, for at least 30 minutes most days of the week can provide immune-boosting benefits. |
In conclusion, by following strategies that nourish the immune system, optimize gut microbiota, manage stress levels and prioritize quality sleep, and engage in regular exercise, we can enhance our body’s natural defense mechanism. Empowering our immune system paves the way for improved overall health and well-being, enabling us to lead vigorous, fulfilling lives.
Factors That Affect Gut Microbiome
In order to maintain a healthy balance within the complex ecosystem of the gut, various factors play a crucial role. These factors greatly influence the composition and diversity of the gut microbiome, ultimately impacting digestive well-being and overall health. Understanding the numerous elements that affect the gut microbiome is essential for optimizing digestive function and promoting overall wellness.
Dietary Choices: The food we consume has a significant impact on the gut microbiome. A diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria, while a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can disrupt the microbial balance. Making conscious dietary choices can help support a diverse and thriving gut microbiome.
Lifestyle Habits: The lifestyle choices we make can influence the gut microbiome. Regular exercise has been shown to promote a healthy gut microbiota, while chronic stress and lack of sleep can negatively impact microbial diversity. Maintaining a balanced lifestyle that incorporates physical activity and stress management techniques can contribute to a healthy gut environment.
Medications and Antibiotics: Certain medications, such as antibiotics, can have a profound effect on the gut microbiome. While antibiotics are necessary to combat infections, they can also disrupt the delicate balance of gut bacteria. It is important to use antibiotics judiciously under the guidance of a healthcare professional to minimize their impact on the microbiome.
Environmental Factors: Environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins and pollutants, can influence the gut microbiome. Chemicals in food, water, and air can disrupt the microbial balance, affecting digestion and overall health. Taking measures to reduce exposure to environmental toxins can help support a healthy gut environment.
Age and Genetics: Age and genetics also play a role in shaping the gut microbiome. The microbiota composition changes throughout different life stages, and genetic factors can influence the diversity and stability of the gut microbiome. Understanding the impact of age and genetics can provide insights into personalized approaches for maintaining a healthy gut.
In conclusion, numerous factors contribute to the health of the gut microbiome, impacting overall digestive well-being. By considering and addressing these factors, individuals can support a thriving gut microbiome and promote optimal digestive health.
Diet and Nutrition
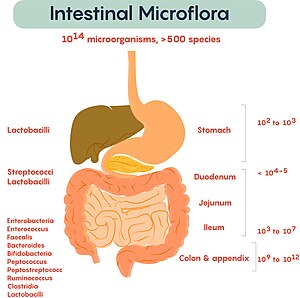
Understanding the role of diet and nutrition is essential for maintaining a healthy and well-functioning gut microbiota, which is crucial for supporting optimal digestive well-being.
|
1. Balanced Diet Eating a diverse range of nutrient-rich foods is key to promoting a harmonious gut environment. Opt for a balanced diet that includes an array of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. |
2. Probiotic-rich Foods Incorporating foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi into your diet can contribute to a healthy gut microbiome. These foods contain beneficial bacteria that support digestion and promote a thriving gut ecosystem. |
|
3. Prebiotic Foods Include prebiotic-rich foods like garlic, onions, asparagus, and bananas in your diet. Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that nourish the beneficial bacteria in your gut, helping them thrive and maintain a balanced gut microbiota. |
4. Fiber Intake Adequate fiber intake is crucial for a healthy gut. Consuming foods high in soluble and insoluble fiber, such as whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, helps regulate bowel movements and provides nourishment for the gut microbiome. |
|
5. Hydration Staying hydrated is important for optimal digestive health. Drinking an appropriate amount of water throughout the day supports the breakdown and absorption of nutrients, aiding in overall gut function. |
6. Limit Processed Foods Reducing the consumption of processed foods, which are often high in refined sugars and unhealthy fats, can help maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Opting for whole, unprocessed foods supports a diverse and thriving gut ecosystem. |
By understanding the significance of diet and nutrition in nurturing a thriving gut microbiome, individuals can make informed choices that promote digestive wellness and overall well-being.
Antibiotic Use
Exploring the Impact of Antibiotics on the Balance of Gut Microorganisms
Antibiotics, a powerful class of medications designed to combat bacterial infections, have revolutionized modern medicine. They have played a critical role in saving countless lives by effectively eliminating harmful bacteria. However, it is essential to recognize that the use of antibiotics can disrupt the delicate balance of microorganisms that reside in our gut.
When antibiotics are administered, they not only target the harmful bacteria causing the infection but also have a significant impact on the beneficial bacteria in our gut. The indiscriminate nature of some antibiotics can disrupt the diversity and composition of the gut microbiome, leading to potential health consequences.
| Potential Effects of Antibiotics on Gut Microbiome |
|---|
| 1. Reduced microbial diversity |
| 2. Imbalanced microbial composition |
| 3. Increased susceptibility to infections |
| 4. Altered metabolism and nutrient absorption |
Studies have shown that the long-term use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, especially during critical periods of early development, can have lasting effects on the gut microbiome. These effects may persist even after the course of antibiotics is complete, potentially impacting overall digestive health.
It is crucial to use antibiotics judiciously and only when necessary to minimize the unintended consequences on the gut microbiome. Healthcare professionals should consider the potential risks and benefits before prescribing antibiotics, taking into account the individual’s specific circumstances.
In conclusion, while antibiotics have undoubtedly revolutionized medicine, their use can disrupt the intricate balance of the gut microbiome. Understanding the potential effects of antibiotics on our digestive health highlights the need for further research and the importance of responsible antibiotic use.
Stress and Mental Health

In today’s fast-paced world, it is evident that the pressures and demands of life can take a toll on our mental well-being. The way we handle stress can have a profound impact on our overall mental health and quality of life.
Chronic feelings of stress and anxiety can lead to a range of mental health issues, such as depression, insomnia, and even cognitive impairments. The effects of stress on the brain can be far-reaching and long-lasting.
Research suggests that stress disrupts the delicate balance of neurotransmitters in our brain, affecting our mood, emotions, and cognition. It can alter the structure and function of various brain regions involved in regulating stress response, memory, and decision-making.
Moreover, stress can influence the gut-brain axis, the bidirectional communication system between the digestive system and the brain. This connection highlights the intricate relationship between our gut microbiome and mental health.
| Effects of Stress on Mental Health: | Ways to Manage Stress: |
|---|---|
| Depression | Regular exercise |
| Anxiety | Meditation and mindfulness |
| Insomnia | Healthy diet and nutrition |
| Cognitive Impairments | Social support and connection |
By understanding the impact of stress on mental health, we can adopt strategies to mitigate its negative effects. Incorporating stress management techniques and promoting a healthy lifestyle can contribute to improved mental well-being and overall quality of life.
It is essential to recognize the significance of addressing stress and maintaining mental health to ensure optimal functioning and personal fulfillment. Remember, taking care of your mind is as crucial as taking care of your body.
Questions and answers
How does the gut microbiome contribute to digestive health?
The gut microbiome plays a crucial role in digestive health by aiding in the breakdown and absorption of nutrients, producing beneficial compounds, regulating the gut immune system, and preventing the growth of harmful bacteria.
Can an unhealthy gut microbiome lead to digestive problems?
Yes, an unhealthy gut microbiome can contribute to various digestive problems such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, constipation, and even more serious conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
What factors can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome?
Several factors can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiome, including a poor diet high in processed foods and sugars, chronic stress, lack of sleep, overuse of antibiotics, and exposure to certain environmental toxins.
Are there any ways to improve and maintain a healthy gut microbiome?
Yes, there are several ways to improve and maintain a healthy gut microbiome. Consuming a diet rich in fiber, probiotic and prebiotic foods, staying hydrated, managing stress levels, getting regular exercise, and avoiding unnecessary use of antibiotics can all contribute to a healthy gut microbiome.
Can the gut microbiome affect overall health beyond digestion?
Yes, the gut microbiome has been linked to various aspects of overall health. It can influence the immune system, brain function, weight management, mood, and even the risk of developing certain diseases such as obesity, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
What is gut microbiome and why is it important?
Gut microbiome refers to the community of bacteria and other microorganisms that inhabit our digestive system. It plays a crucial role in maintaining proper digestive health by aiding in digestion, synthesizing essential nutrients, supporting the immune system, and preventing harmful bacteria from proliferating.
How does an unhealthy gut microbiome affect digestive health?
An unhealthy gut microbiome can lead to various digestive issues such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, constipation, and even more serious conditions like inflammatory bowel disease. It can also have a negative impact on nutrient absorption and weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
What factors can disrupt the balance of gut microbiome?
Several factors can disrupt the balance of gut microbiome, including a poor diet high in processed foods and sugars, overuse of antibiotics, chronic stress, lack of physical activity, and certain medical conditions. These factors can contribute to the overgrowth of harmful bacteria and the depletion of beneficial ones, leading to an imbalanced gut microbiome.
How can we promote a healthy gut microbiome?
To promote a healthy gut microbiome, it is essential to consume a diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods. Regular exercise, adequate sleep, stress management, and avoiding unnecessary use of antibiotics can also contribute to a healthy gut microbiome. Additionally, incorporating probiotics and prebiotics into the diet can help nourish and support beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Can the gut microbiome affect mental health?
Yes, emerging research suggests that the gut microbiome can influence mental health. The gut-brain axis connects the gut and the brain through biochemical signaling, and disruptions in the gut microbiome have been linked to conditions such as anxiety, depression, and even neurodevelopmental disorders. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome can potentially have a positive impact on mental well-being.