Within the delicate ecosystem of our minds, there exists a complex interplay between various biological elements that shape our mental equilibrium. A key player in this intricate symphony is the hormone cortisol, a crucial component of our stress response system. When the delicate balance of cortisol levels is disturbed, it can have a profound impact on our mental well-being, leading to a myriad of symptoms and potential long-term consequences.
Factors contributing to cortisol imbalance:
An assortment of factors can disrupt the delicate equilibrium of our cortisol levels. From environmental stressors to genetic predispositions, imbalances in cortisol can arise from a multitude of causes. Chronic stress, unhealthy lifestyle choices, and certain medical conditions can all contribute to dysregulation of cortisol production and release. Furthermore, alterations in the body’s natural circadian rhythm, as well as hormonal disorders, may also play a role in disrupting the steady state of cortisol.
Indications of cortisol imbalance:
When cortisol levels deviate from their ideal range, individuals may experience a range of symptoms that directly affect their mental state. Heightened anxiety, mood swings, and irritability are some of the telltale signs of cortisol imbalance. Additionally, cognitive difficulties, such as impaired memory and concentration, may manifest, further impacting daily functioning. Sleep disturbances, alterations in appetite, and a weakened immune response are also common potential indications of cortisol dysregulation.
Exploring potential therapies:
Recognizing the impact of cortisol imbalance on mental well-being, researchers have delved into the development of therapeutic interventions to restore equilibrium. Dietary modifications, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques have shown promise in managing cortisol levels. Additionally, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and mindfulness-based practices have been found to be effective in alleviating symptoms associated with cortisol imbalance. Pharmacological options, such as cortisol-lowering medications, may be considered in severe cases, although their use is typically a last resort due to potential side effects.
In conclusion, the intricate dance of cortisol within our minds holds significant sway over our mental well-being. Understanding the factors that contribute to cortisol imbalance, recognizing its indications, and exploring potential therapeutic options are essential steps in addressing this crucial aspect of mental health. By restoring the delicate balance of cortisol, individuals can pave the way towards a more harmonious state of mental well-being.
- The Role of Cortisol Imbalance in Mental Health
- Understanding the Causes and Effects
- Chronic Stress as a Trigger
- Hormonal Imbalances and the HPA Axis
- Genetic Predisposition and Cortisol Dysregulation
- Recognizing the Symptoms
- Mood Disorders and Depression
- Anxiety and Panic Attacks
- Cognitive Impairment and Memory Problems
- Exploring Treatment Options
- Questions and answers
The Role of Cortisol Imbalance in Mental Health

In considering the connection between cortisol levels and overall mental well-being, it becomes apparent that the delicate balance of this hormone plays a significant role in the intricate web of our mental health. Essentially, cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands, exerts its influence on various aspects, including mood regulation, stress response, cognitive function, and emotional stability.
Imbalances in cortisol levels can result in a host of mental health issues. When cortisol is excessively elevated, it can manifest as anxiety, agitation, and even panic attacks. Conversely, insufficient levels of cortisol may lead to symptoms such as depression, fatigue, apathy, and a sense of emotional flatness. These imbalances can create a cascading effect, impacting cognitive abilities, impairing decision-making, and exacerbating overall mental well-being.
Identifying the root causes of cortisol imbalances is crucial in order to develop effective treatment strategies. Chronic stress, traumatic experiences, sleep disturbances, unhealthy lifestyle choices, and certain medical conditions can all contribute to disruptions in cortisol levels. Recognizing the symptoms associated with cortisol imbalance, such as mood swings, memory issues, decreased resilience to stress, and changes in appetite and sleep patterns, is instrumental in seeking early interventions.
When addressing cortisol imbalances, treatment options are multifaceted and can incorporate pharmacological interventions, psychotherapy, and lifestyle modifications. Medications such as cortisol receptor antagonists and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors can help regulate cortisol levels and alleviate associated mental health symptoms. Additionally, cognitive-behavioral therapy and stress management techniques can provide individuals with coping mechanisms to manage cortisol imbalances effectively.
In conclusion, cortisol imbalance wields a profound influence on mental health, impacting emotional well-being, cognitive function, and overall psychological stability. Understanding the intricacies of cortisol’s role in mental well-being empowers individuals to recognize the symptoms associated with imbalances and seek appropriate treatment options. By addressing cortisol imbalances, individuals can work towards achieving optimal mental health and well-being.
Understanding the Causes and Effects
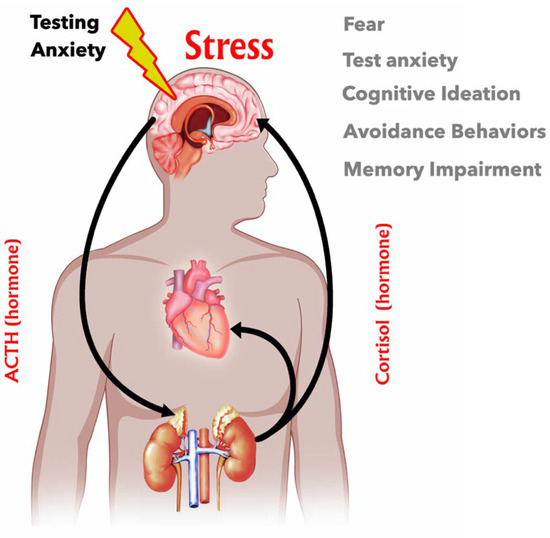
In this section, we will explore the underlying factors that contribute to the development of cortisol imbalances and the subsequent effects it has on mental well-being. By deepening our understanding of the causes and effects, we can better comprehend the complex relationship between cortisol and mental health.
1. Factors Influencing Cortisol Levels:
- Environmental stressors
- Chronic illness or medical conditions
- Genetic predispositions
- Lifestyle choices
The intricate interplay of these factors can disrupt the delicate equilibrium of cortisol production in the body and lead to imbalances. While environmental stressors can vary from person to person, they commonly include work-related pressures, relationship difficulties, financial strain, or traumatic events. Chronic illnesses and medical conditions, such as Cushing’s syndrome or Addison’s disease, can also affect cortisol levels. Additionally, genetic factors can make some individuals more susceptible to cortisol imbalances. Lifestyle choices, such as poor diet, lack of exercise, insufficient sleep, or substance abuse, can further contribute to the development of cortisol imbalances.
2. Effects of Cortisol Imbalance on Mental Health:
- Increased anxiety and depression
- Impaired cognitive function
- Changes in appetite and weight
- Sleep disturbances
When cortisol levels are disrupted, it can have a profound impact on mental health. An excessive or insufficient amount of cortisol can contribute to heightened feelings of anxiety and depression. Cognitive function may also be affected, leading to difficulties in concentration, memory, and decision-making. Cortisol imbalances can disrupt the balance of hunger hormones, resulting in changes in appetite and weight. Additionally, sleep disturbances, such as insomnia or excessive sleep, can occur as a result of cortisol imbalances.
This section aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the various causes that can lead to cortisol imbalances and the effects it can have on mental health. By recognizing these causes and effects, individuals can take proactive steps towards managing cortisol levels and promoting overall well-being.
Chronic Stress as a Trigger
Chronic stress, an enduring and overwhelming emotional strain, has a significant impact on mental well-being. It acts as a catalyst for various mental health issues, exacerbating symptoms and creating a vicious cycle of imbalance. Understanding the role of chronic stress in mental health is crucial in order to develop effective strategies for prevention and treatment.
When individuals experience prolonged periods of stress, their body’s stress response system becomes dysregulated. This dysregulation disrupts the normal functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, leading to irregular cortisol production. Chronically elevated or diminished levels of cortisol can disrupt overall brain chemistry and contribute to the development of mental health disorders.
- Increased vulnerability: Persistent stress weakens the body’s defenses against mental health disorders, making individuals more susceptible to conditions such as anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
- Impaired cognitive function: Chronic stress can impair cognitive function, affecting memory, concentration, and decision-making abilities. This can further contribute to feelings of frustration, helplessness, and decreased overall functioning.
- Altered emotional regulation: The dysregulation of cortisol due to chronic stress can disrupt the regulation of emotions, causing individuals to experience heightened sensitivity, irritability, and difficulty in managing their emotional responses.
- Physical health complications: Prolonged exposure to chronic stress can also result in various physical health complications, such as cardiovascular issues, weakened immune system, and gastrointestinal problems, which further impact overall well-being.
Addressing chronic stress as a trigger for mental health issues requires a comprehensive approach. Effective interventions may include stress management techniques, lifestyle modifications, therapy, and medication, depending on the severity and individual needs. By targeting chronic stress, individuals can better regulate cortisol levels and restore balance to their mental and emotional well-being.
Hormonal Imbalances and the HPA Axis
In this section, we will explore the intricate relationship between hormonal imbalances and the HPA (hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal) axis, shedding light on the significant impact these imbalances can have on mental well-being. Unstable hormone levels can disrupt the delicate equilibrium within the HPA axis, leading to potential health problems and psychological distress.
The HPA axis, often referred to as the stress response system, plays a crucial role in regulating our body’s reaction to stress and maintaining overall physiological balance. When faced with stressors, the HPA axis initiates a cascade of signals among the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal glands, ultimately resulting in the release of cortisol, the primary stress hormone.
An alteration in hormone levels, especially cortisol, can arise due to various factors, including genetic predispositions, external stressors, or underlying medical conditions. These hormonal imbalances can disrupt the HPA axis, leading to an array of symptoms that may manifest both physically and psychologically.
Some individuals with hormonal imbalances and HPA axis dysregulation may experience symptoms such as chronic fatigue, irritability, anxiety, or depression. Others may struggle with disrupted sleep patterns, weight fluctuations, or difficulties in maintaining focus and concentration. These symptoms can significantly impact one’s quality of life, leading to impaired functioning and overall well-being.
Fortunately, there are treatment options available to address hormonal imbalances and restore balance within the HPA axis. It is crucial to consider a comprehensive approach that incorporates targeted therapies, lifestyle modifications, and stress management techniques. By addressing the underlying hormonal imbalances and improving HPA axis function, individuals can potentially alleviate their symptoms and improve their mental health.
Overall, understanding the complex interplay between hormonal imbalances and the HPA axis provides valuable insights into the potential causes and effects of these imbalances on mental well-being. Recognizing the symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances and exploring effective treatment options is essential in promoting optimal mental health and overall quality of life.
Genetic Predisposition and Cortisol Dysregulation
Understanding the Role of Genetics in Cortisol Regulation
Genetic predisposition plays a significant role in the dysregulation of cortisol levels, which can have profound effects on mental health. The interplay between genetic factors and cortisol imbalance is a complex phenomenon that contributes to the development of various mental health disorders. This section aims to explore the intricate relationship between genetic predisposition and the dysregulation of cortisol, shedding light on how these factors interact to impact mental well-being.
Unraveling the Genetic Factors
Researchers have identified specific gene variants that are associated with abnormalities in cortisol regulation. These genetic variations can influence the functioning of key components involved in the synthesis, metabolism, and transportation of cortisol within the body. The dysregulation of cortisol due to genetic predisposition can lead to an overproduction or underproduction of this hormone, creating an imbalance that contributes to mental health issues.
The Role of Genetic Expression
Genetic predisposition alone is not always sufficient to cause cortisol dysregulation. Rather, environmental factors and lifestyle choices often interact with genetic predisposition to trigger the expression of specific genes related to cortisol regulation. These factors can include chronic stress, poor diet, lack of exercise, and exposure to certain toxins. Understanding the interplay of genetic expression and environmental influences is crucial in determining the full picture of how cortisol dysregulation manifests and its impact on mental health.
Implications for Treatment
Recognizing the role of genetic predisposition in cortisol dysregulation provides valuable insights for the development of targeted treatment options. Personalized interventions that take into account an individual’s specific genetic makeup can help restore cortisol balance and improve mental health outcomes. By addressing the underlying genetic factors contributing to cortisol dysregulation, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment approaches to address the unique needs of each individual, leading to more effective and personalized care.
Recognizing the Symptoms

Identifying indications of an irregularity in the cortisol hormone levels is essential for early intervention and appropriate management of mental health conditions. The following signs and manifestations can provide crucial insights into the presence of cortisol imbalance.
| Physical Symptoms |
|
| Emotional and Behavioral Signs |
|
| Changes in Cognitive Functioning |
|
Recurrent or persistent experience of these symptoms may indicate the presence of a cortisol imbalance in an individual’s system. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for a comprehensive assessment and appropriate treatment intervention.
Mood Disorders and Depression
Mood disorders and depression are conditions that can have a significant impact on an individual’s emotional well-being. These conditions, stemming from a state of hormonal imbalance, can manifest in various ways and affect different aspects of a person’s life.
Individuals experiencing mood disorders and depression often struggle with negative emotions, such as sadness, hopelessness, and a general lack of interest or pleasure in activities. They may also experience changes in appetite, sleep patterns, and energy levels. These symptoms can lead to difficulties in functioning socially, academically, and professionally, making it crucial to seek appropriate treatment and support.
While the exact causes of mood disorders and depression can vary from person to person, cortisol imbalance is believed to play a significant role in their development. Cortisol, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands, helps regulate stress response and maintain overall balance in the body. However, when cortisol levels become imbalanced, it can disrupt neurotransmitters and other essential processes in the brain, ultimately contributing to mood disorders and depression.
Treatment options for mood disorders and depression focus on addressing both the physiological and psychological aspects of the condition. Medications, such as antidepressants, may be prescribed to help regulate cortisol levels and stabilize mood. Additionally, therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can provide individuals with coping mechanisms and strategies to manage their symptoms effectively.
It is important to note that seeking professional help is crucial for individuals experiencing mood disorders and depression. A healthcare provider can conduct a thorough evaluation, identify any underlying causes, and create a personalized treatment plan to address the individual’s unique needs. With the right support and treatment, individuals can regain control over their mental health and improve their overall well-being.
Anxiety and Panic Attacks

Anxiety and panic attacks are common symptoms of an imbalance in cortisol levels and can have a significant impact on mental well-being. These conditions are characterized by feelings of intense fear, apprehension, and unease, often accompanied by physical symptoms such as rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and sweating.
Individuals experiencing anxiety may find themselves constantly worrying about future events or situations, even if there is no immediate threat. This persistent state of unease can interfere with daily life and lead to difficulties in concentration, sleep disturbances, and impaired social interactions.
Panic attacks, on the other hand, are sudden and intense episodes of overwhelming fear, often accompanied by physical symptoms such as chest pain, dizziness, and a sense of impending doom. These attacks can be triggered by specific situations or occur unexpectedly, causing individuals to feel a loss of control and a deep sense of terror.
While there can be various causes of anxiety and panic attacks, an imbalance in cortisol levels can play a significant role. Cortisol, commonly known as the stress hormone, is responsible for regulating the body’s response to stress. When cortisol levels are consistently high or low, it can disrupt the delicate balance needed for optimal mental health and contribute to the development of anxiety and panic disorders.
Treatment options for anxiety and panic attacks aim to restore cortisol balance and alleviate symptoms. These may include medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or benzodiazepines, which can help regulate neurotransmitters and manage anxiety. Additionally, therapy and counseling can provide individuals with coping mechanisms and strategies to manage stress and anxiety triggers.
Overall, anxiety and panic attacks are complex conditions that can have a profound impact on an individual’s mental well-being. Understanding the role of cortisol balance in these disorders and seeking appropriate treatment can help individuals regain control of their lives and improve their overall quality of life.
Cognitive Impairment and Memory Problems
Cognitive function and memory play crucial roles in our daily lives, influencing our ability to learn, reason, and remember. However, certain imbalances in the body’s hormonal system can have a notable impact on these cognitive functions. This section delves into the intricacies of cognitive impairment and memory problems associated with fluctuations in cortisol levels.
When cortisol levels become imbalanced, individuals may experience various cognitive impairments, such as difficulties with attention, concentration, and executive functioning. These functions are essential for tasks that require decision-making, problem-solving, and planning. Furthermore, memory problems can also arise, affecting both short-term and long-term memory processes. It is crucial to understand the underlying causes and symptoms of cognitive impairments and memory problems to seek appropriate treatment and support.
The impact of cortisol imbalance on cognitive function:
Cortisol is a hormone secreted by the adrenal glands in response to stress. While cortisol is vital for the body’s stress response, chronic high or low levels can disrupt the delicate balance necessary for optimal cognitive function. Elevated cortisol levels can impair memory formation and retrieval, making it difficult to remember recent events or recall previously learned information.
Symptoms of cognitive impairment and memory problems:
Individuals experiencing cognitive impairment and memory problems may exhibit signs such as forgetfulness, difficulty concentrating, struggling to learn new information, and experiencing cognitive fatigue. These symptoms can significantly impact daily activities, work performance, and overall quality of life.
Treatment options and management strategies:
Addressing cortisol imbalances through a comprehensive treatment approach is vital in managing cognitive impairment and memory problems. Treatment options may include stress management techniques, lifestyle modifications, cognitive rehabilitation programs, and medication when necessary. It is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized treatment plan tailored to address the specific needs of each individual.
In conclusion, cognitive impairments, and memory problems can be significant consequences of cortisol imbalances. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential in providing appropriate support and improving overall cognitive functioning and quality of life.
Exploring Treatment Options
In this section, we will delve into various approaches and techniques available for addressing the disruption in cortisol levels, which can have profound effects on an individual’s psychological well-being. By exploring different treatments, we can gain a better understanding of the potential remedies and interventions that can help alleviate the symptoms associated with imbalances in cortisol levels.
1. Therapeutic Interventions: One approach to addressing cortisol imbalances is through therapeutic interventions. These interventions aim to provide individuals with a safe and supportive environment to explore and understand the underlying causes contributing to their cortisol imbalance. Therapists may use techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which focuses on identifying and modifying negative thought patterns and behaviors that may contribute to cortisol imbalances.
2. Medication: Another potential treatment option for cortisol imbalances is the use of medication. Psychiatrists may prescribe certain medications that can help regulate cortisol levels and alleviate associated mental health symptoms. Medications such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety medications may be used to target specific symptoms related to imbalances in cortisol levels.
3. Lifestyle Changes: Making certain lifestyle modifications can also play a role in managing cortisol imbalances. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation or yoga, and adopting a healthy diet can all help regulate cortisol levels naturally. These lifestyle changes can have a positive impact on an individual’s mental health and overall well-being.
4. Supportive Networks: Building a strong support system and surrounding oneself with understanding and empathetic individuals can be immensely beneficial in managing cortisol imbalances. Connecting with support groups or seeking out therapy groups can provide opportunities for individuals to share their experiences, learn from others, and gain additional tools for coping with the challenges associated with cortisol imbalances.
In conclusion, exploring the various treatment options available can shed light on effective ways to address cortisol imbalances and improve mental health outcomes. It is important for individuals experiencing these imbalances to seek professional help and work with healthcare providers to determine the most suitable treatment plan tailored to their unique needs.
Questions and answers
What is cortisol imbalance and how does it affect mental health?
Cortisol imbalance refers to an abnormal level of cortisol hormone in the body. Cortisol is a hormone released by the adrenal glands in response to stress. When cortisol levels are imbalanced, it can have a significant impact on mental health, leading to conditions such as anxiety, depression, and mood disorders.
What are the main causes of cortisol imbalance?
There are various factors that can cause a cortisol imbalance, including chronic stress, certain medications, hormonal disorders, and underlying health conditions such as Cushing’s syndrome or Addison’s disease. Additionally, poor sleep patterns, unhealthy lifestyle choices, and excessive caffeine or alcohol intake can also contribute to cortisol imbalance.
What are the common symptoms of cortisol imbalance?
The symptoms of cortisol imbalance can vary, but commonly include persistent fatigue, insomnia or poor sleep quality, weight gain or difficulty losing weight, increased anxiety or irritability, depression, difficulty concentrating, and weakened immune system.
What are the treatment options for cortisol imbalance?
Treatment options for cortisol imbalance depend on the underlying cause. Lifestyle modifications such as stress management techniques, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy diet can help in balancing cortisol levels. Additionally, therapy, medication, and hormonal replacement therapy may be recommended by healthcare professionals based on individual circumstances.
How can cortisol imbalance be diagnosed?
To diagnose cortisol imbalance, healthcare professionals often perform a series of tests including blood tests, saliva tests, or urine tests to measure cortisol levels at different times of the day. Imaging tests may also be conducted to identify any underlying health conditions that might be causing the imbalance.
What is cortisol imbalance and how does it impact mental health?
Cortisol imbalance refers to an abnormal level of cortisol, which is a hormone released by the adrenal glands in response to stress. This imbalance can have a significant impact on mental health as it can lead to anxiety, depression, and mood disorders.
What are the causes of cortisol imbalance?
Several factors can contribute to cortisol imbalance, including chronic stress, lack of sleep, certain medical conditions like Cushing’s syndrome or Addison’s disease, and long-term use of corticosteroid medications.
What are the common symptoms of cortisol imbalance?
The symptoms of cortisol imbalance can vary, but common signs include persistent fatigue, weight gain, difficulty sleeping, irritability, low libido, difficulty concentrating, and frequent infections.
Are there any effective treatment options for cortisol imbalance?
Yes, there are various treatment options available. These include stress management techniques like meditation and exercise, therapy, medications to regulate cortisol levels, and lifestyle changes such as getting enough sleep and maintaining a healthy diet.
Can cortisol imbalance be prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent cortisol imbalance entirely, there are steps individuals can take to manage stress effectively, maintain a balanced lifestyle, get regular exercise, practice relaxation techniques, and seek help when needed to minimize the risk of cortisol imbalance and its impact on mental health.










