Discovering and identifying the puzzling manifestations of immunological disorders can be a complex and formidable task. In today’s fast-paced world, where medical advancements strive to keep up with the ever-evolving nature of these conditions, it becomes crucial for individuals to familiarize themselves with the nuanced indications that could potentially signify an autoimmune disease.
From subtle changes to overt disturbances, the human body often communicates its distress through a range of symptoms that warrant attention and further exploration. However, recognizing and comprehending these signs can be likened to obtaining the keys to deciphering an intricate code, demanding a keen eye and an inquisitive mind.
Within the intricate tapestry of immunological disorders, the symptoms exhibited vary significantly, making it challenging to devise a simplistic roadmap for recognition. This guide endeavors to equip individuals with the knowledge and understanding necessary to navigate this complex terrain, providing insights into the subtle nuances and telltale signs that may indicate the presence of an autoimmune disease.
As we delve into this comprehensive exploration of immune-mediated disorders, it is important to note that no two cases are identical, and symptoms can manifest differently in each person. However, by gaining awareness of the potential clues and being armed with the right information, individuals can become proactive in seeking necessary medical intervention and treatment, thus fostering a higher likelihood of early detection and management of these conditions.
- Understanding Autoimmune Diseases
- The Basics: What Are Autoimmune Diseases?
- How Autoimmune Diseases Affect the Body
- Recognizing the Symptoms
- Key Indicators to Watch Out For
- Various Types of Autoimmune Diseases and Their Symptoms
- Early Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
- Seeking Medical Help and Diagnosis
- When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
- Questions and answers
Understanding Autoimmune Diseases
Acquiring a comprehensive understanding of autoimmune diseases involves exploring the intricate nature of these complex medical conditions. By delving into the underlying mechanisms and processes that occur within the body, one can unravel the enigma behind these diseases.
Autoimmune diseases arise from an aberrant immune response wherein the body’s defense mechanism mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells and tissues. This misguided assault can affect various organs and systems, leading to a wide array of symptoms that differ depending on the specific disease and individual.
Although there are numerous autoimmune diseases, they share common elements in terms of their etiology, pathogenesis, and treatment approaches. Genetic predisposition, environmental factors, and dysregulation of the immune system intertwine to provoke the onset and progression of these conditions.
- Autoimmune diseases can target multiple organs or systems, including the skin, joints, gastrointestinal tract, endocrine glands, and nervous system.
- While some autoimmune diseases exhibit specific symptoms unique to the affected organ or system, others may manifest more general symptoms that are present across multiple diseases.
- The underlying mechanisms of autoimmune diseases involve the production of autoantibodies, immune complex formation, activation of T cells, and chronic inflammation.
- Diagnosing autoimmune diseases can be challenging due to the variability of symptoms, the absence of definitive tests, and the overlap with other medical conditions.
- Treatment for autoimmune diseases typically involves immunosuppressive medications, lifestyle modifications, and managing specific symptoms to improve quality of life.
By comprehending the underlying factors that contribute to autoimmune diseases and recognizing the diverse range of symptoms they can present, individuals can enhance their ability to seek early diagnosis and appropriate management. Understanding these diseases empowers patients, healthcare professionals, and researchers to collaborate in finding effective approaches for prevention, treatment, and ultimately, better outcomes.
The Basics: What Are Autoimmune Diseases?
In this section, we will explore the fundamental aspects of autoimmune diseases, aiming to provide a comprehensive understanding without delving into specific definitions. Autoimmune diseases are conditions wherein the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells and tissues, leading to a broad range of symptoms and complications. These diseases can affect various organs and systems within the body and can manifest differently in each individual.
To better grasp the complexities of autoimmune diseases, it is helpful to think of the immune system as the body’s defense mechanism against foreign invaders such as bacteria or viruses. Under normal circumstances, the immune system can distinguish between these invaders and the body’s own cells. However, in cases of autoimmune diseases, this balance is disrupted, and the immune system begins attacking healthy cells as if they were foreign substances.
The causes of autoimmune diseases are multifactorial and can involve a combination of genetic predisposition, environmental triggers, and dysregulation of the immune system. While the exact mechanisms behind autoimmune diseases are not fully understood, researchers have identified several common factors that may contribute to their development.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| Autoimmune diseases involve the immune system attacking the body’s own cells and tissues. |
| These diseases can affect various organs and systems in the body. |
| The immune system’s balance is disrupted, causing it to mistake healthy cells for foreign substances. |
| Multiple factors, including genetics, environment, and immune system dysfunction, can contribute to the development of autoimmune diseases. |
How Autoimmune Diseases Affect the Body

Autoimmune diseases have a profound impact on the body, causing disruptions in its normal functioning and triggering various adverse reactions. These conditions arise when the body’s immune system, intended to protect against harmful invaders, mistakenly identifies its own healthy cells and tissues as threats. As a result, the immune system launches an attack on these harmless entities, leading to inflammation, tissue damage, and various other symptoms.
When an autoimmune disease affects the body, it can target specific organs or tissues, causing localized damage or affect multiple systems throughout the body, leading to more widespread and systemic effects. Each autoimmune disease is unique in terms of the organs or tissues it impacts, the severity of symptoms, and the course of the disease.
One way autoimmune diseases affect the body is by causing chronic inflammation. Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, but in the case of autoimmune diseases, this response becomes dysregulated. The immune system continuously produces antibodies and inflammatory cells that mistakenly attack healthy cells and tissues, causing persistent inflammation. This chronic inflammation can lead to various symptoms, such as pain, swelling, redness, and heat in the affected areas.
Additionally, autoimmune diseases can disrupt the proper functioning of specific organs or systems. For example, in autoimmune thyroid diseases like Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or Graves’ disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to an underactive or overactive thyroid respectively. This can result in symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, mood swings, and hormonal imbalances.
Autoimmune diseases can also trigger a cascade of immune responses that affect multiple organs or systems simultaneously. Rheumatoid arthritis, for instance, primarily targets the joints but can also cause inflammation in other areas of the body, such as the skin, eyes, lungs, and blood vessels. This can lead to joint pain, stiffness, skin rashes, breathing difficulties, and other systemic symptoms.
Overall, autoimmune diseases can have far-reaching effects on the body, impacting various organs, tissues, and systems. Understanding how these diseases affect the body is crucial for early detection, proper management, and improved quality of life for individuals living with autoimmune conditions.
Recognizing the Symptoms
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Aids-and-autoimmune-diseases-5113376_final-f35eaa36335d4e4d8638ac86fdf16146.jpg)
Identifying and understanding the signs that indicate the presence of autoimmune diseases is crucial for timely diagnosis and effective management of these conditions. By learning to recognize the various indicators that manifest in different individuals, you can take proactive steps towards seeking appropriate healthcare and support.
- Unexplained fatigue or chronic tiredness
- Persistent joint pain or stiffness
- Recurring low-grade fever
- Unusual hair loss or thinning
- Digestive issues such as abdominal pain, bloating, or diarrhea
- Skin abnormalities like rashes, dryness, or sores that won’t heal
- Frequent headaches or migraines
- Swollen glands or lymph nodes
- Muscle weakness or muscle pain
- Changes in weight, either sudden weight loss or gain
- Numbness or tingling sensations in extremities
- Memory problems or difficulty concentrating
It is important to note that these symptoms can vary greatly depending on the specific autoimmune disease and individual factors. Not everyone will experience all of these symptoms, nor will they present themselves in the same intensity or combination. Additionally, some symptoms may mimic those of other health conditions, making diagnosis challenging.
If you notice any persistent or recurring symptoms that are impacting your daily life, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. By sharing your concerns and providing them with a detailed account of your symptoms, you can work together towards finding the underlying cause and developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Remember, early recognition and diagnosis of autoimmune diseases can make a significant difference in managing symptoms and improving overall quality of life. Stay informed and listen to your body’s signals, as being aware of potential indications is the first step towards taking control of your health.
Key Indicators to Watch Out For
In this section, we will explore the important factors to consider when identifying the presence of autoimmune diseases. It is crucial to pay attention to these telltale signs as they can serve as valuable indicators of underlying health conditions. Familiarizing yourself with these key indicators will empower you to recognize potential autoimmune symptoms and seek appropriate medical attention.
- Red Flags: Certain warning signs may point towards the possibility of an autoimmune disease. These indicators often include persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss or gain, recurring fevers, and chronic pain. By carefully monitoring these red flags, you can stay proactive in managing your health.
- Inflammation: Inflammation is a common characteristic of many autoimmune diseases. Symptoms such as joint pain, swelling, redness, or stiffness can suggest an inflammatory response in the body. Recognizing these signs can help you identify potential autoimmune conditions.
- Altered Immune Function: Autoimmune diseases arise from dysregulation of the immune system. Therefore, paying attention to abnormalities in immune function can be crucial in recognizing potential autoimmune symptoms. Factors like frequent infections, susceptibility to allergies, or a history of autoimmune diseases in the family can serve as important cues.
- Organ-Specific Symptoms: Autoimmune diseases can affect specific organs in the body, leading to distinct symptoms. For example, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis may cause fatigue, weight gain, and hair loss, while Crohn’s disease may trigger abdominal pain, diarrhea, and bloody stools. Being aware of organ-specific symptoms can aid in identifying potential autoimmune disorders.
- Fluctuating Symptoms: Autoimmune diseases often exhibit symptoms that come and go or vary in intensity. These fluctuations can make diagnosis challenging. However, recognizing the unpredictability of symptoms can help you keep track of any noticeable patterns and provide important insights to healthcare professionals.
Various Types of Autoimmune Diseases and Their Symptoms
In this section, we will explore the diverse range of autoimmune conditions and their associated symptoms. Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells and tissues, causing inflammation and damage. Each autoimmune disease affects a specific organ or system, leading to a unique set of symptoms.
One common autoimmune disease is rheumatoid arthritis, which primarily affects the joints. People with rheumatoid arthritis may experience symptoms such as joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and difficulty in movement. Another example is multiple sclerosis, an autoimmune disorder that affects the central nervous system. Symptoms of multiple sclerosis may include weakness, numbness, fatigue, difficulty in coordination, and problems with vision.
Lupus, also known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is another autoimmune disease that can affect multiple organs. Common symptoms of lupus include joint pain, rash, fatigue, fever, and sensitivity to light. Type 1 diabetes, an autoimmune condition affecting the pancreas, can lead to symptoms such as frequent urination, increased thirst, unexplained weight loss, and fatigue.
In addition to these examples, there are many other autoimmune diseases with their own distinct symptoms. Some autoimmune disorders primarily affect the skin, resulting in symptoms like rashes, blistering, and hair loss. Others target specific organs such as the thyroid, liver, or kidneys, leading to symptoms related to the dysfunction of these organs.
It is crucial to recognize the symptoms of autoimmune diseases early on, as early detection and treatment can help manage the condition and prevent further damage. If you experience persistent or unexplained symptoms, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Note: This guide provides general information about autoimmune diseases and their symptoms. It is not a substitute for medical advice. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.
Early Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Being aware of the initial indications that may suggest the presence of an autoimmune condition is crucial for early diagnosis and effective management. These early warning signs should not be disregarded, as they can serve as valuable indicators of potential health concerns.
1. Unexplained Fatigue: Persistent exhaustion and feeling tired even after adequate rest can be an early sign of an autoimmune disease. This fatigue may go beyond the usual weariness and often does not improve with rest or sleep.
2. Joint Pain and Stiffness: Frequent joint pain, stiffness, and swelling, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity, can point to an underlying autoimmune issue. It is essential to pay attention to any persistent discomfort or reduced range of motion.
3. Skin Changes: Unusual rashes, redness, or itchiness on the skin may indicate an autoimmune condition. These skin changes can vary in appearance and may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as dryness or sores that take longer to heal.
4. Digestive Issues: Persistent digestive problems, including abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, or constipation, should not be ignored. These symptoms can be early warning signs of an autoimmune disease affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
5. Hair Loss: Experiencing excessive hair loss or thinning could be linked to an autoimmune disorder. Paying attention to changes in hair texture, volume, or sudden bald patches is essential for early detection and appropriate management.
6. Recurrent Infections: Frequent or recurrent infections, such as urinary tract infections, respiratory infections, or yeast infections, can be indicative of an underlying autoimmune condition. These infections may occur more often or take longer to resolve than expected.
7. Muscle Weakness: Noticeable muscle weakness or difficulty in performing daily activities can be an early sign of certain autoimmune diseases affecting the muscles. Paying attention to changes in physical strength and endurance is crucial for timely medical evaluation.
8. Cognitive Impairment: Experiencing ongoing issues with memory, concentration, or changes in cognitive abilities may be linked to an autoimmune disease affecting the brain or central nervous system. These cognitive impairments should be given proper attention and evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Being aware of these early warning signs can empower individuals to seek timely medical advice and follow up on potential autoimmune diseases. Early detection can lead to effective management strategies, improved quality of life, and better long-term outcomes.
Seeking Medical Help and Diagnosis
When faced with potential autoimmune issues, it is essential to seek medical assistance and undergo a proper diagnosis by professionals who specialize in this field. Identifying and understanding the signs and symptoms of autoimmune diseases can be complex, and a thorough examination is crucial to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
The initial step in seeking medical help is to make an appointment with a healthcare provider, such as a primary care physician or an internist. These medical professionals can assess your symptoms, listen to your concerns, and perform a preliminary evaluation. They may take your medical history, conduct a physical examination, and order specific laboratory tests to gather more information about your condition.
Depending on the preliminary findings, your healthcare provider may refer you to a specialist, such as a rheumatologist, dermatologist, endocrinologist, or gastroenterologist. These specialists have extensive knowledge and experience in diagnosing and treating autoimmune diseases and can offer further insight into your condition.
During your consultation with the specialist, they will conduct a more comprehensive evaluation, which may include additional physical exams, imaging tests, or further laboratory investigations. This detailed assessment aims to identify specific biomarkers or abnormalities that can aid in diagnosing your autoimmune condition accurately.
It is essential to provide the healthcare professionals with detailed information about your symptoms, their duration, and any triggers or patterns you may have noticed. This information can help guide the diagnostic process and ensure that all necessary tests are conducted to make an accurate diagnosis.
Receiving a proper diagnosis is essential as it allows for appropriate and timely treatment, which can help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve overall quality of life. Remember, seeking medical help and obtaining a professional diagnosis is the first step towards effectively managing autoimmune diseases.
| If you’re experiencing persistent symptoms that could be related to autoimmune issues, don’t delay in seeking medical assistance. | Remember, an accurate diagnosis requires the expertise of specialists who can perform detailed evaluations. |
| Be open and honest about your symptoms, triggers, and patterns to aid in the diagnostic process. | Proper diagnosis enables timely treatment, symptom management, and improved quality of life. |
When to Consult a Healthcare Professional
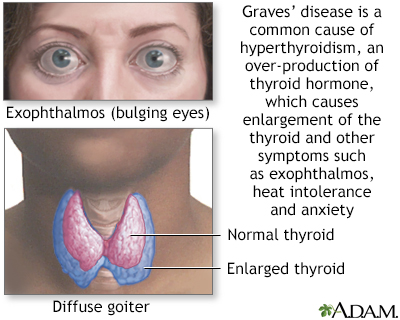
Knowing when to seek medical advice for potential autoimmune diseases is crucial in obtaining a timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Recognizing the signs and symptoms that may indicate an underlying autoimmune condition is an essential step towards getting the help you need.
If you experience persistent or unexplained symptoms such as fatigue, joint pain, chronic inflammation, or recurring infections, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. These symptoms could be indicative of an autoimmune disease and should not be ignored or dismissed.
It is also essential to seek medical attention if you notice a sudden onset or intensification of symptoms, as this could signify an acute flare-up of an underlying autoimmune condition. Additionally, if you have a family history of autoimmune diseases, it is crucial to discuss your concerns with a healthcare professional, as there may be an increased risk for developing similar conditions.
A healthcare professional can conduct a thorough evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, to determine the presence of an autoimmune disease. They can provide expert guidance and advice, helping you navigate the complexities of autoimmune conditions, and develop a personalized treatment plan to manage and alleviate your symptoms.
Remember, early detection and intervention are key in effectively managing autoimmune diseases. Do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional if you suspect you may be experiencing symptoms associated with these conditions.
Seeking medical advice promptly can make a significant difference in improving your quality of life and overall well-being.
Questions and answers
What are autoimmune diseases?
Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own cells, tissues, and organs. This can lead to various symptoms and health complications.
What are some common symptoms of autoimmune diseases?
Common symptoms of autoimmune diseases include fatigue, joint pain, muscle weakness, rashes, fever, hair loss, and unexplained weight changes. However, the specific symptoms can vary depending on the type of autoimmune disease.
How can I recognize if I have an autoimmune disease?
If you experience persistent and unexplained symptoms such as chronic pain, inflammation, and fatigue, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. They will evaluate your medical history, conduct physical examinations, and order appropriate tests to determine if you have an autoimmune disease.
Are autoimmune diseases hereditary?
There is evidence suggesting that certain autoimmune diseases have a genetic component, meaning they can run in families. However, having a family history of autoimmune disease does not necessarily mean you will develop the same condition, as other factors like environmental triggers also play a role.
Can stress aggravate the symptoms of autoimmune diseases?
Yes, stress can worsen the symptoms of autoimmune diseases. Stress can lead to increased inflammation and disrupt the immune system, which can trigger flare-ups and intensify existing symptoms. Therefore, managing stress through relaxation techniques and lifestyle changes is important for individuals with autoimmune diseases.
Can you explain what autoimmune diseases are?
Autoimmune diseases are disorders in which the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys healthy body tissues. The immune system is supposed to protect the body from harmful substances, but in autoimmune diseases, it cannot differentiate between healthy cells and harmful invaders.
What are some common symptoms of autoimmune diseases?
The common symptoms of autoimmune diseases vary depending on the specific disease but can include fatigue, joint pain, muscle weakness, fever, and inflammation. Other symptoms may include skin rashes, hair loss, digestive problems, and organ-specific symptoms.
How are autoimmune diseases diagnosed?
Diagnosing autoimmune diseases can be challenging as many symptoms are common to multiple diseases. It often involves a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examinations, blood tests, and possibly further testing like imaging studies or biopsies.
Are there any treatments available for autoimmune diseases?
Yes, there are treatments available for autoimmune diseases. The treatment options vary depending on the specific disease and its severity, but they commonly involve medications to suppress the immune system, relieve symptoms, and manage complications. Additionally, lifestyle changes and alternative therapies may also be recommended.
Can autoimmune diseases be cured?
Currently, most autoimmune diseases cannot be cured completely. However, with proper treatment and management, many people with autoimmune diseases can experience significant improvements in their symptoms and quality of life. The goal of treatment is often to suppress the immune response, reduce inflammation, and prevent further damage to organs or tissues.