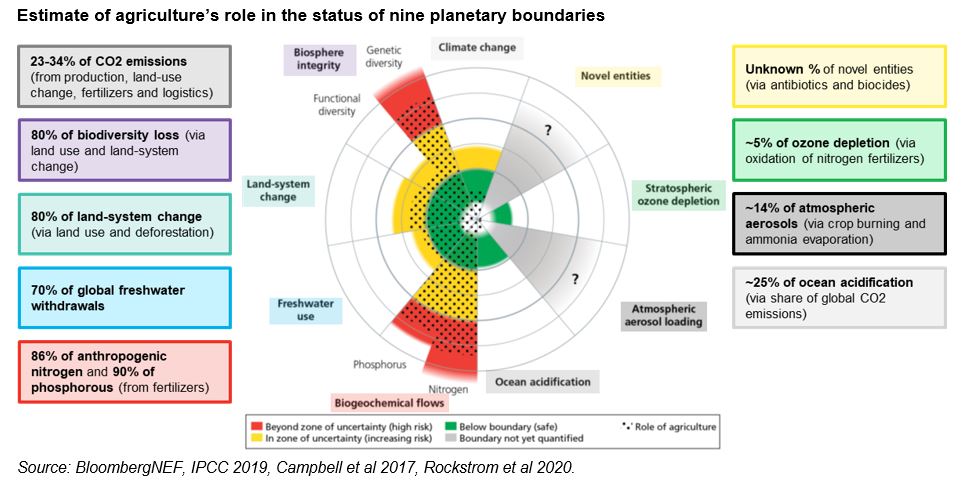
In today’s ever-evolving world, the agricultural sector has witnessed a profound shift towards a more sustainable and environmentally conscious system. This movement, often referred to as an unprecedented transformation, has significantly reshaped the way food is produced, distributed, and consumed. By employing innovative methods and practices, a new era has dawned upon us, one where the cultivation of crops and the rearing of livestock no longer strive solely for profit, but also for the preservation of our planet’s delicate ecosystems.
Within this epoch of change, the food industry is experiencing a paradigm shift that is fundamentally altering its very core. Sustainability and ecological preservation are now at the forefront, with agricultural practices adapting to mitigate the adverse impact on soil quality, water resources, and biodiversity. Gone are the days when large-scale industrial farming disregarded the consequences of conventional techniques, giving rise to environmental degradation and diminishing yields.
Revolutionize Your Health & Lifestyle!
Dive into the world of Ketogenic Diet. Learn how to lose weight effectively while enjoying your meals. It's not just a diet; it's a lifestyle change.
Learn MoreEmbracing this green revolution entails a harmony of diverse strategies, encompassing organic and regenerative agriculture, precision farming, agroforestry, and sustainable livestock management. The implementation of these approaches ensures the adoption of ecologically sound practices, minimizing the use of chemical inputs, reducing land degradation, and promoting wildlife conservation. The key lies in cultivating crops that are resilient to climatic variations, maximizing resource efficiency, and nurturing a symbiotic relationship between nature and farming.
- The Impact of Sustainable Agriculture on the Food Industry
- Increasing Efficiency and Productivity
- Reducing Environmental Footprint
- Promoting Organic Farming
- Implementing Precision Agriculture
- Adopting Sustainable Irrigation Methods
- Encouraging Agroforestry and Crop Rotation
- Enhancing Food Security
- The Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
- Precision Farming and Smart Irrigation
- Genetic Engineering for Resistance and Yield
- Sustainable Packaging and Waste Reduction
- Challenges and Future Prospects in Sustainable Agriculture
- Questions and answers
The Impact of Sustainable Agriculture on the Food Industry
Sustainable agriculture has significantly influenced the landscape of the food sector, bringing about a series of notable changes and advancements. This section explores the wide-ranging effects of adopting sustainable practices in agriculture on the food industry. By implementing sustainable methods, businesses and farmers are able to foster positive ecological outcomes while simultaneously improving the quality, availability, and safety of food products. Let us delve into the transformative impact sustainable agriculture has on various aspects of the food industry.
| Enhanced Environmental Stewardship | Resilient Food Supply Chains | Innovation and Technological Advancements |
|---|---|---|
| Sustainable agriculture fosters harmonious relationships with the environment, mitigating the negative impact on soil, water, and air quality. By utilizing organic and natural farming techniques, the industry reduces the need for harmful chemical inputs, preserving biodiversity and ecosystem health. | Adopting sustainable practices in agriculture ensures the resilience of food supply chains by minimizing the risk of crop failure and reducing dependence on external factors. This increased resilience enables a more stable and secure food system, capable of withstanding environmental and socio-economic shocks. | Sustainable agriculture drives innovation and technology adoption in the food industry. From precision farming and automation to climate-smart technologies, sustainable practices encourage the development of efficient and sustainable methods of production, improving productivity and profitability. |
| Improved Food Quality | Healthier Consumer Choices | Positive Economic Impacts |
| Sustainable agriculture prioritizes the production of high-quality food products, free from synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms. By focusing on natural and organic approaches, the industry ensures the provision of nutritious and delicious food options for consumers. | The rise of sustainable agriculture promotes healthier consumer choices. As people become more conscious of the environmental and health impacts of their dietary choices, sustainable food options gain traction. This shift towards sustainable and organic products contributes to improved public health and well-being. | Sustainable agriculture has positive economic implications for the food industry. By adopting sustainable practices, businesses can reduce production costs in the long run, improve resource efficiency, and enhance market competitiveness. Additionally, the global demand for sustainably produced food presents opportunities for growth and market expansion. |
Overall, the impact of sustainable agriculture on the food industry is vast and multifaceted. Its positive effects on environmental stewardship, food quality, consumer choices, and economic viability are crucial in establishing a more sustainable and resilient food system for the future.
Increasing Efficiency and Productivity
Enhancing operational effectiveness and improving output levels are fundamental goals in the pursuit of sustainable agriculture. By implementing innovative practices and employing cutting-edge technologies, the food industry can maximize efficiency and productivity.
One key aspect of increasing efficiency lies in optimizing resource management. By utilizing advanced techniques in water and nutrient management, agricultural enterprises can ensure that essential inputs are utilized in the most effective and sustainable manner. This includes implementing precision irrigation systems that deliver water directly to plant roots, reducing water waste and improving crop health. Additionally, the use of precision fertilization techniques enables farmers to deliver nutrients directly to plants, minimizing nutrient loss and optimizing uptake.
Adopting modern technology also plays a crucial role in boosting efficiency and productivity. The integration of data-driven decision-making processes allows farmers to make informed choices based on real-time information. By utilizing Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors, farms can collect data on soil moisture, temperature, and crop growth, enabling farmers to make timely adjustments and optimize productivity. Additionally, the use of automation in tasks such as planting, harvesting, and monitoring can significantly reduce labor requirements, allowing farmers to allocate resources more efficiently.
Collaboration and knowledge sharing are essential components in increasing efficiency and productivity within the food industry. Farmers can benefit from joining cooperative organizations that promote information exchange, learning from each other’s experiences, and adopting best practices. Additionally, partnerships between agricultural research institutions, government agencies, and private enterprises can foster innovation and support the development of new technologies and methods that increase productivity and sustainability.
In conclusion, improving efficiency and productivity within the food industry is crucial for transforming it towards sustainable agriculture. By optimizing resource management, embracing technology, and promoting collaboration, the industry can achieve a more sustainable future while meeting the growing demand for food.
| Benefits of Increasing Efficiency and Productivity | Challenges |
|---|---|
| – Higher crop yields | – Initial investment costs |
| – Reduced resource consumption | – Adoption of new practices |
| – Improved profitability | – Technological infrastructure |
| – Enhanced sustainability | – Knowledge and information gaps |
Reducing Environmental Footprint
In this section, we will explore the measures and strategies aimed at minimizing the ecological impact of agricultural practices. By adopting sustainable methods and techniques, we can reduce our environmental footprint, ensuring a healthier future for both the planet and our food production systems. Let us delve into the key approaches to achieve this goal.
Promoting Organic Farming
- Encouraging organic farming practices can significantly contribute to reducing the environmental footprint of the food industry.
- Emphasizing organic processes that avoid synthetic chemicals and genetically modified organisms.
- Highlighting the benefits of organic farming in terms of soil fertility, biodiversity preservation, and minimizing water pollution.
- Supporting organic certification programs to ensure transparency and trust for consumers.
Implementing Precision Agriculture
- Deploying precision agriculture techniques can optimize resource utilization while minimizing waste.
- Utilizing advanced technologies such as GPS, sensors, and drones to precisely monitor and manage soil nutrition, water usage, and pest control.
- Reducing excessive and unnecessary application of fertilizers and pesticides through targeted interventions.
- Improving farm management practices by incorporating real-time data analysis for informed decision-making.
Adopting Sustainable Irrigation Methods
- Promoting the use of efficient irrigation systems, such as drip irrigation and micro-sprinklers, to reduce water waste.
- Encouraging water conservation practices, such as rainwater harvesting and recycling, to minimize the strain on freshwater resources.
- Implementing smart irrigation technologies that optimize water usage based on weather conditions and plant needs.
- Educating farmers on proper irrigation scheduling and water management techniques to prevent over-irrigation and waterlogging.
Encouraging Agroforestry and Crop Rotation
- Promoting agroforestry systems that integrate trees, crops, and livestock to enhance soil quality, carbon sequestration, and wildlife habitat.
- Advocating for crop rotation practices that diversify plant species, minimize pest and disease pressures, and improve soil fertility.
- Raising awareness about the multiple benefits of agroforestry and crop rotation, including erosion control, enhanced pollination, and reduced reliance on chemical inputs.
- Supporting research and education programs focused on exploring innovative agroforestry and crop rotation techniques.
By implementing these strategies and promoting sustainable agricultural practices, we can significantly reduce the negative environmental impact of the food industry. Through collective efforts, we can pave the way for a greener, more resilient, and sustainable future.
Enhancing Food Security
In this section, we explore the pivotal aspect of bolstering the availability and access to sustenance, instigating a sense of permanence, and ensuring a stable supply of nourishment. By focusing on this paramount concern, we scrutinize the overarching effort to fortify the reliability and resilience of the agricultural system, encompassing a broad array of strategies to guarantee ample sustenance for all.
To augment food security, it is imperative to implement measures that promote self-sufficiency and mitigate the vulnerability posed by external factors. This entails enhancing agricultural productivity through judicious resource management and the adoption of innovative practices. By nurturing and expanding local agricultural production, communities can cultivate a resilient foundation that lessens reliance on imports and empowers self-reliance.
Furthermore, diversifying agricultural practices and championing the cultivation of a multifarious range of crops strengthens food security. By reducing dependence on a limited number of staple foods, communities can counteract the risks associated with crop failures and susceptible ecosystems. Encouraging the cultivation of traditional and lesser-known crops helps to unlock new sources of sustenance and foster a more robust and adaptable food system.
In addition to promoting sustainable agricultural practices, it is vital to foster effective storage and distribution systems that prevent post-harvest losses and ensure equitable access to food resources. By investing in improved storage facilities and transportation infrastructure, communities can minimize wastage and guarantee the availability of food throughout the year, even during times of crisis or disruption.
Addressing food security also involves empowering vulnerable communities and enhancing their capacity to adapt and withstand the challenges posed by climate change and other environmental factors. By providing access to education, resources, and support, communities can develop the necessary skills and knowledge to diversify their livelihoods and build resilience to ensure sustained access to food.
The Role of Technology in Sustainable Agriculture
In today’s rapidly changing world, technology plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable agriculture. The use of innovative tools and techniques has revolutionized the way we produce, process, and distribute food, ensuring its availability and quality, while preserving our natural resources for future generations.
One key aspect of technology’s role in sustainable agriculture is its ability to enhance efficiency and productivity. Through advanced machinery, precision farming techniques, and data-driven decision-making, farmers can optimize resource allocation, reduce waste, and increase yields. These technologies enable them to monitor soil health, water usage, and crop growth patterns, allowing for targeted interventions and improved resource management.
Additionally, technology enables the adoption of sustainable practices such as organic farming and integrated pest management. With the help of digital platforms and mobile applications, farmers can access information on sustainable farming methods, pest and disease control measures, and environmentally friendly alternatives to chemical inputs. This knowledge empowers farmers to make informed choices that minimize environmental impact while ensuring profitable agricultural production.
Furthermore, technology facilitates effective supply chain management, enabling farmers to connect directly with consumers and reduce the reliance on intermediaries. Online platforms and e-commerce solutions connect producers and consumers, promoting transparency, traceability, and fair pricing. This direct link between farmers and consumers fosters a closer relationship, encourages support for local agriculture, and reduces the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation.
The role of technology in sustainable agriculture extends beyond the farm gate. It encompasses innovations in food processing, packaging, and distribution, ensuring the efficient use of resources, reducing food waste, and promoting sustainable consumption. Advanced processing techniques, such as cold chain management and value-addition technologies, enhance food safety, quality, and shelf life, while minimizing losses due to spoilage and contamination.
In conclusion, technology plays a pivotal role in realizing the vision of sustainable agriculture. By harnessing its potential, we can address the challenges facing the food industry and pave the way for a future where food production is environmentally friendly, socially responsible, and economically viable. Embracing technological advancements empowers farmers, enhances productivity, and promotes sustainable practices, ultimately contributing to a greener and more resilient food system.
Precision Farming and Smart Irrigation
Precision farming and smart irrigation are innovative practices that are revolutionizing the agricultural landscape by utilizing advanced technologies to optimize crop production and water usage. These techniques harness the power of data analytics, automation, and sensor technologies to enable farmers to make precise decisions and conserve resources effectively.
Genetic Engineering for Resistance and Yield
In this section, we will explore the role of genetic engineering in developing crop varieties that are able to withstand various challenges and offer higher productivity. By utilizing advanced techniques in genetics, scientists have been able to enhance resistance to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses, while also improving the overall yield of crops without compromising sustainability.
Genetic engineering allows for the targeted manipulation of an organism’s genetic material, enabling researchers to introduce beneficial traits into crops. Through the identification and modification of specific genes responsible for resistance and yield, scientists can enhance the plant’s ability to fend off pests and diseases, as well as adapt to harsh environmental conditions.
By incorporating genes from naturally resistant plant species or introducing genes that produce proteins toxic to specific pests, genetically engineered crops can effectively defend themselves against insect damage and reduce the reliance on chemical pesticides. This approach not only improves the overall health of the crop, but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with pesticide use.
In addition, genetic engineering can improve the yield potential of crops by modifying genes associated with traits such as plant size, root architecture, and photosynthesis efficiency. By enhancing these traits, crops can utilize resources more effectively, leading to increased productivity and a reduced environmental footprint.
It is important to note that genetic engineering is just one tool in the broader toolkit of sustainable agriculture. When implemented responsibly and in combination with other sustainable practices, such as crop rotation, integrated pest management, and soil conservation, genetic engineering can contribute to achieving food security and environmental sustainability in the face of global challenges.
Sustainable Packaging and Waste Reduction
In today’s era of environmentally-conscious practices and the pursuit of sustainable development, the focus is increasingly shifting towards the food industry’s packaging and waste management. This section explores the significance of sustainable packaging and waste reduction as integral parts of the ongoing transformation.
The concept of sustainable packaging entails the use of materials and design strategies that minimize environmental impacts throughout a product’s entire lifecycle. This approach emphasizes the utilization of renewable and recyclable resources, the reduction of materials required for packaging, and the adoption of eco-friendly manufacturing processes. By implementing sustainable packaging practices, the food industry can contribute to the conservation of natural resources and mitigate the generation of non-biodegradable waste.
Moreover, waste reduction plays a crucial role in promoting sustainability in the food industry. By minimizing the amount of waste generated through various stages of production, distribution, and consumption, substantial environmental benefits can be realized. This encompasses strategies like composting organic waste, implementing efficient recycling programs, and encouraging responsible consumer behavior through awareness campaigns. Achieving waste reduction not only decreases the industry’s ecological footprint but also presents potential cost savings and operational efficiency improvements.
Furthermore, the implementation of sustainable packaging and waste reduction practices can provide numerous advantages to businesses operating in the food industry. Alongside their environmental benefits, these practices can enhance brand reputation, attract environmentally conscious consumers, and foster a positive image of corporate social responsibility. Additionally, as governments and regulatory bodies increasingly prioritize sustainability, adhering to sustainable packaging requirements and waste reduction goals can preemptively position food businesses for compliance and future market success.
In conclusion, sustainable packaging and waste reduction are fundamental considerations within the transformation of the food industry towards sustainable agriculture. By adopting these practices, businesses can contribute to environmental preservation, gain a competitive edge, and actively participate in shaping a more sustainable and responsible future.
Challenges and Future Prospects in Sustainable Agriculture

Achieving sustainability in agriculture presents numerous obstacles and promising prospects for the future. This section delves into the difficulties faced by sustainable agriculture practices and outlines potential opportunities for advancement in the industry.
1. Resource Management: One of the foremost challenges in sustainable agriculture lies in the proper management of limited resources. Developing efficient irrigation systems, utilizing precision farming techniques, and implementing advanced technology can aid in maximizing the use of water, energy, and fertilizers while minimizing waste.
2. Biodiversity Conservation: The preservation and promotion of biodiversity play a critical role in sustainable agriculture. Encouraging crop rotation, promoting natural pest control methods, and fostering the protection of habitats and native species enhance the resilience of agricultural ecosystems.
3. Climate Change Mitigation: Climate change poses significant threats to agricultural productivity. Embracing climate-smart practices, such as utilizing climate-resistant crop varieties, implementing agroforestry techniques, and sequestering carbon in soils, can help mitigate the adverse effects of climate change on food production.
4. Community Engagement: Ensuring the engagement and participation of local communities in sustainable agricultural practices is crucial for long-term success. Promoting knowledge sharing, supporting small-scale farmers, and fostering partnerships between different stakeholders can enhance the implementation and acceptance of sustainable farming methods.
5. Economic Viability: Sustainable agriculture should also be economically viable to incentivize its widespread adoption. Developing markets for organic and sustainably produced crops, providing financial support for farmers transitioning to sustainable practices, and implementing fair trade policies can contribute to the economic sustainability of the industry.
Despite the challenges, there are promising future prospects in sustainable agriculture:
- The advancement of precision agriculture and the use of technologies like drones and sensors can enhance resource efficiency and productivity.
- Integration of agroecology principles into mainstream farming practices can promote biodiversity conservation and improve soil health.
- Investment in research and development can lead to the discovery of innovative solutions for sustainable pest and disease management.
- Supporting agroforestry systems that combine crop production with tree cultivation can contribute to climate change mitigation and diversify income streams for farmers.
- Promoting sustainable farming practices in urban areas through initiatives like rooftop gardens and vertical farming can enhance food security and reduce the environmental footprint of food production.
By addressing these challenges and capitalizing on the prospects for the future, sustainable agriculture holds the potential to revolutionize the food industry and contribute to a greener and more resilient future.
Questions and answers
What is the Green Revolution and how does it relate to sustainable agriculture?
The Green Revolution refers to a period in the 20th century when agricultural practices and technologies were developed to increase crop yields. It relates to sustainable agriculture because it focuses on using methods that have less impact on the environment and promote long-term sustainability.
What are some examples of sustainable agriculture practices?
Some examples of sustainable agriculture practices include crop rotation, organic farming, conservation tillage, agroforestry, and the use of natural fertilizers and pest management techniques. These methods aim to minimize environmental harm, promote soil health, and preserve biodiversity.
How does sustainable agriculture contribute to food security?
Sustainable agriculture contributes to food security by ensuring the availability of nutritious and affordable food in the long run. It promotes resilient farming systems that can withstand climate change, reduces dependence on synthetic inputs, and protects natural resources essential for food production.
What are the main challenges to implementing sustainable agriculture on a large scale?
The main challenges to implementing sustainable agriculture on a large scale include the resistance to change from conventional farming methods, the need for education and training of farmers, the upfront costs of transitioning to sustainable practices, and the need for supportive policies and market incentives.
What is the role of technology in promoting sustainable agriculture?
Technology plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable agriculture. It enables the development and use of precision farming techniques, such as remote sensing, data analytics, and automation, which can optimize resource use, improve crop management, and reduce environmental impact.
What is the Green Revolution?
The Green Revolution refers to a period of significant advancements in agricultural practices that began in the 1940s and aimed to increase food production worldwide, particularly in developing countries.
How has sustainable agriculture transformed the food industry?
Sustainable agriculture has transformed the food industry by promoting environmentally friendly practices, such as organic farming, reducing the use of chemical inputs, and adopting techniques that conserve water and soil, resulting in healthier food products and reduced impact on the environment.
What are some benefits of sustainable agriculture?
Sustainable agriculture has numerous benefits, including improved soil quality, increased biodiversity, preservation of natural resources, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and healthier and safer food for consumers.
How does the Green Revolution contribute to food security?
The Green Revolution contributes to food security by introducing high-yielding crop varieties, increasing agricultural productivity, and ensuring a constant supply of food to meet the growing demands of the global population.
What are the challenges faced in implementing sustainable agriculture?
Implementing sustainable agriculture faces challenges such as resistance to change from conventional farming practices, lack of awareness and education among farmers, limited financial resources, and the need for policy support and incentives to encourage widespread adoption of sustainable methods.