In today’s fast-paced and demanding world, stress has become an unwelcome companion for many. It permeates our daily lives, affecting our physical and mental well-being in ways we may not even realize. At the forefront of this intricate interaction lies a crucial hormone known as cortisol, which plays a pivotal role in our body’s response to stress.
Understanding the delicate balance of cortisol levels and how it can be disrupted is essential in comprehending the wide-ranging effects stress can have on our health. Stress-induced hormonal fluctuations can lead to a cascade of physiological and psychological consequences, ranging from disrupted sleep and mood swings to weight gain and compromised immune function.
It is like a seesaw, with cortisol acting as the fulcrum. When stress triggers the body’s fight-or-flight response, cortisol levels surge, enabling us to react quickly to potential threats. This temporary surge can be beneficial, but an imbalance in cortisol levels can overburden the body, creating a multitude of health issues.
Therefore, it becomes imperative to delve into the mechanisms behind cortisol fluctuations, their implications, and strategies to manage stress effectively, thereby restoring harmony to our hormonal equilibrium. By examining the intricate relationship between stress and cortisol, we can gain valuable insights into the impact of chronic stress on our well-being and discover targeted techniques to regain control over our overall health.
- Cortisol Imbalance: Unraveling the Effects of Stress-induced Hormonal Fluctuations
- Understanding the Role of Cortisol in the Body
- Exploring the Function of Cortisol in Stress Response
- The Impact of Excessive Cortisol Levels on Health
- Identifying Symptoms of Cortisol Imbalance
- Recognizing Physical Manifestations of Hormonal Fluctuations
- Unveiling the Emotional and Mental Signs of Cortisol Imbalance
- Effective Strategies for Managing Cortisol Levels
- Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Changes to Regulate Cortisol
- Questions and answers
Cortisol Imbalance: Unraveling the Effects of Stress-induced Hormonal Fluctuations
In this section, we delve into the intricate web of effects that arise from hormonal fluctuations induced by stress. By exploring the consequences of these physiological shifts, we aim to shed light on the underlying mechanisms that can disrupt our well-being and overall health.
Stressful situations can trigger a cascade of hormonal responses within our bodies, leading to significant changes in our internal equilibrium. These fluctuations can impact various aspects of our mental and physical health, influencing our mood, sleep patterns, energy levels, and even cognitive function.
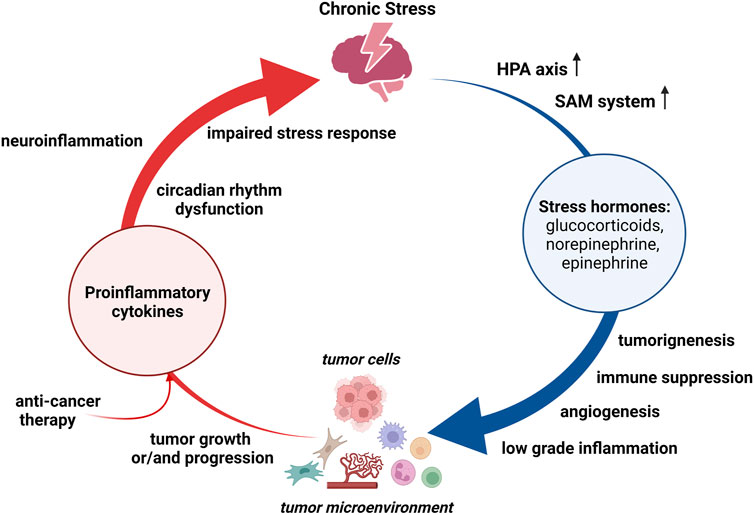
Unraveling the effects of stress-induced hormonal imbalances reveals a complex interplay between different systems in our body. Our body’s natural response to stress involves the activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, a crucial regulatory pathway that controls the release of stress hormones. This intricate system can become dysregulated under chronic stress, resulting in an imbalance in cortisol production.
Excess cortisol, commonly referred to as the stress hormone, can exert detrimental effects on various physiological processes. It can disrupt the functioning of our immune system, increase blood pressure, impair cognitive performance, and contribute to the development of mood disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Conversely, inadequate cortisol levels can also have significant repercussions. Insufficient cortisol can lead to fatigue, low energy levels, and even adrenal insufficiency, a condition characterized by the inability of the adrenal glands to produce adequate amounts of cortisol. This imbalance can further impact our overall well-being and hinder our ability to cope with stress effectively.
Understanding the effects of stress-induced hormonal fluctuations is crucial in developing strategies to mitigate their negative impact. By recognizing the intricate relationship between stress, cortisol, and our overall health, we can explore various approaches to restore hormone balance and promote well-being. Through lifestyle modifications, stress management techniques, and medical interventions if necessary, we can strive to regain equilibrium and optimize our physiological and psychological health.
Understanding the Role of Cortisol in the Body
Exploring the intricate workings of the human body, one cannot overlook the significant role played by cortisol. This vital hormone, secreted by the adrenal glands, regulates a wide range of physiological processes, ensuring the body’s proper functioning in various situations.
Regulator: Cortisol serves as a key regulator, orchestrating the body’s response to both internal and external stressors. It helps maintain a delicate balance, ensuring that essential metabolic functions continue uninterrupted while adapting to changing conditions.
Stress Response: In times of stress, cortisol enables the body to react swiftly and effectively. It mobilizes energy reserves, heightens sensory perception, and sharpens focus, preparing the individual for fight-or-flight situations.
Immune Support: Beyond its stress response function, cortisol also plays a vital role in modulating the immune system. Recognized as an anti-inflammatory agent, cortisol facilitates the body’s defenses against harmful pathogens and aids in the healing process.
Metabolic Balance: Cortisol profoundly influences energy metabolism. It regulates blood sugar levels, ensuring a constant supply of glucose, the body’s primary fuel source. Additionally, cortisol aids in fat, protein, and carbohydrate metabolism, participating in the intricate dance of energy regulation.
Circadian Rhythm: Cortisol levels follow a natural pattern dictated by the body’s internal clock. It peaks in the early morning, providing an energy boost to start the day, and gradually declines throughout the day, preparing the body for restful sleep at night.
Understanding the multifaceted role of cortisol in the body is essential for comprehending the implications of any hormonal imbalances that may arise. By exploring and unraveling this intricate web, we can gain valuable insights into the complex mechanisms governing our physiological responses to stress.
Exploring the Function of Cortisol in Stress Response
Delving into the intricate mechanisms of the human stress response, we uncover the crucial role played by a hormone closely associated with the body’s reaction to stress. This hormone, which we will refer to as the stress hormone, is a key player in orchestrating the body’s response to challenging situations.
- Understanding the stress hormone’s role
- Examining its impact on physiological processes
- Exploring its effect on cognitive and emotional functions
The stress hormone, being a vital part of the body’s stress response, affects a wide range of physiological processes. Its influence on the cardiovascular system, for example, can result in increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure, priming the body for a quick response. Moreover, this hormone also impacts immune function, which helps bolster our defenses in the face of potential threats.
Beyond its effect on the body’s physical responses to stress, the stress hormone also plays a significant role in cognitive and emotional functioning. Studies have shown that elevated levels of this hormone can lead to impairments in memory and attention, as well as influencing our emotional state and regulating our responses to stressors. By better understanding these effects, we can develop strategies to cope with stress more effectively and maintain a healthy balance.
As we dive deeper into the exploration of cortisol’s function in stress response, we gain valuable insights into the intricate workings of our body. By comprehending its impact on various systems and its role in shaping our cognitive and emotional responses, we can pave the way for developing effective strategies to manage stress-induced hormonal fluctuations.
The Impact of Excessive Cortisol Levels on Health
When the body’s stress response becomes disrupted, it can lead to an overproduction of a certain hormone. This hormone, known for its role in regulating various bodily functions, can have negative effects on overall health when present in excessive amounts. The consequences of elevated levels of this hormone can manifest in a range of physical and mental health issues.
Physiological Effects
Excessive levels of this hormone can disturb the delicate balance within the body, leading to disturbances in the functioning of various systems. It can adversely affect the cardiovascular system, adversely impacting heart health and increasing the risk of hypertension. Immune system impairment is another consequence, making individuals more susceptible to infections and impairing their ability to recover from illnesses.
Mental and Emotional Impact
Elevated levels of this hormone can also have profound effects on mental and emotional well-being. It can contribute to increased anxiety, depression, and mood swings, making it challenging to maintain stable emotional states. Cognitive functions such as concentration and memory may also be compromised, impacting daily performance and overall productivity.
Metabolic Disturbances
Excessive levels of this hormone can disrupt the body’s metabolic processes, leading to weight gain, particularly in the abdominal region. It can interfere with insulin production and contribute to the development of insulin resistance, increasing the risk of diabetes. Additionally, it can affect appetite and cravings, leading to unhealthy eating habits and further compounding the metabolic disturbances.
Sleep Disorders
One of the consequences of elevated levels of this hormone is disrupted sleep patterns. It can lead to difficulties falling asleep and staying asleep, resulting in chronic insomnia. The lack of quality sleep can further contribute to other health issues and exacerbate the impact of stress on both physical and mental well-being.
In order to mitigate the detrimental effects of excessive levels of this hormone, it is crucial to address and manage stress levels effectively. Implementing stress-reduction techniques, such as exercise, meditation, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, can help restore the balance and promote overall well-being.
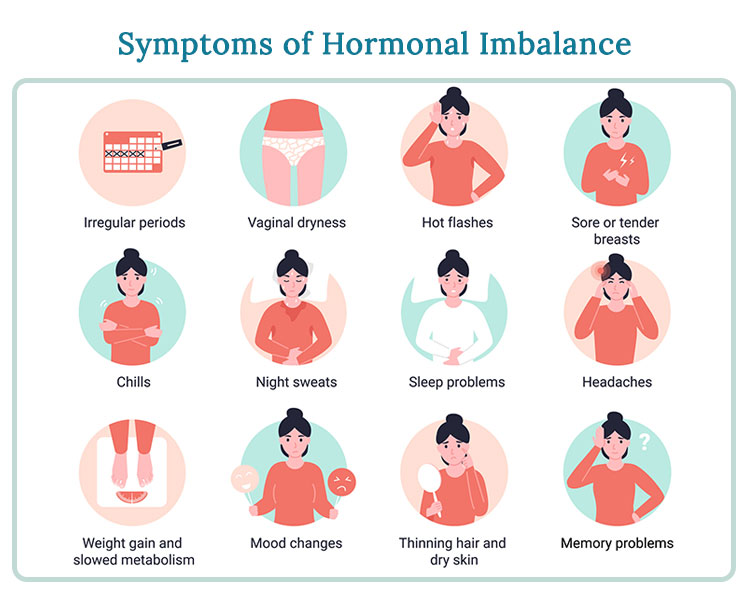
Identifying Symptoms of Cortisol Imbalance
In this section, we will explore the signs and indications that can help identify a potential imbalance in the hormone responsible for the body’s response to stress and inflammation. By recognizing these symptoms, individuals can take proactive measures to address their cortisol levels and promote overall well-being.
| Signs and Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Unexplained Weight Changes | Fluctuations in weight that cannot be attributed to diet or exercise may indicate an imbalance in cortisol levels. This could manifest as weight gain or sudden weight loss. |
| Changes in Sleep Patterns | Insomnia or restless sleep may signal cortisol irregularity. Conversely, excessive fatigue or a constant need for sleep can also be a result of hormonal imbalance. |
| Mood Swings and Irritability | Unexplained mood shifts, increased irritability, or heightened anxiety may indicate cortisol imbalance. Individuals may experience heightened emotions or have difficulty managing stress effectively. |
| Digestive Issues | Problems like bloating, indigestion, or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) that persist without any apparent cause might be linked to cortisol disruption. |
| Changes in Skin Texture | Dryness, acne breakouts, or thinning of the skin could be manifestations of cortisol imbalance. Skin may appear dull, lackluster, or prone to excessive oiliness. |
| Decreased Libido | A decrease in sexual desire or performance may be related to cortisol dysfunction. Hormonal imbalances can affect both men and women in this aspect. |
| Memory and Cognitive Problems | Cortisol imbalance may also impact cognitive abilities such as memory, focus, and concentration. Individuals may experience difficulty retaining information or making decisions. |
It is important to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to cortisol imbalance and could be attributed to other factors. Consulting a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and appropriate diagnosis is crucial in determining the underlying cause and formulating an effective treatment plan.
Recognizing Physical Manifestations of Hormonal Fluctuations
In this section, we will explore the various physical signs and symptoms that can be indicative of hormonal fluctuations in the body. It is important to be able to recognize these manifestations as they can often provide valuable insights into the overall hormonal balance and potential stress levels.
Physical changes
One of the key indicators of hormonal fluctuations can be observed through physical changes in the body. These changes may vary from person to person and can include alterations in weight, appetite, and energy levels. Additionally, individuals may experience changes in their skin, hair, and nails, as well as inflammation or bloating in certain areas.
Affective and cognitive symptoms
Hormonal imbalances can also manifest through affective and cognitive symptoms. This may include mood swings, irritability, anxiety, or even depression. Cognitive symptoms such as difficulty concentrating, memory problems, or a decrease in cognitive functioning may also be present.
Menstrual irregularities
In women, hormonal fluctuations can often be observed through menstrual irregularities. This may include changes in the length, intensity, or regularity of menstrual cycles. Symptoms such as heavy or prolonged periods, irregular ovulation, or even the absence of menstruation altogether can indicate hormonal imbalances.
Sleep disturbances
Another common manifestation of hormonal fluctuations is sleep disturbances. This can range from insomnia or difficulty falling asleep to excessive sleepiness or frequent waking up during the night. Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to disturbances in sleep patterns.
Physical discomfort and pain
Hormonal fluctuations can also contribute to physical discomfort and pain in various parts of the body. This may include muscle aches, joint pain, headaches, or even gastrointestinal issues. These manifestations can significantly impact one’s overall well-being and quality of life.
Recognizing the physical manifestations of hormonal fluctuations is crucial for addressing and managing potential cortisol imbalances. By understanding these signs and symptoms, individuals can take proactive steps towards achieving hormonal balance and enhancing their overall health and well-being.
Unveiling the Emotional and Mental Signs of Cortisol Imbalance
In this section, we explore the various emotional and mental indicators that may hint at an underlying cortisol imbalance. While not directly mentioning the hormone or its fluctuation, these signs offer valuable insights into the potential presence of a hormonal disturbance resulting from stress.
One potential manifestation of cortisol imbalance is the experience of heightened anxiety or constant worry. Individuals may find themselves feeling excessively on edge, struggling to relax, or experiencing a sense of impending doom without a clear trigger. This emotional state, often accompanied by racing thoughts or an inability to control one’s worries, can be indicative of cortisol disruptions.
Depression, another emotional sign often linked to cortisol imbalance, presents itself as consistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or a loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities. Individuals may experience a lack of motivation or energy, difficulty concentrating, and changes in appetite or sleep patterns. These emotional changes can be closely tied to hormonal fluctuations caused by chronic stress.
Additionally, individuals with cortisol imbalances may notice a decrease in their ability to cope with everyday stressors. They may find themselves feeling overwhelmed or easily overwhelmed by even minor challenges. This emotional sensitivity, coupled with an increased irritability or agitation, can often be attributed to an imbalance in stress hormones.
Another hallmark of cortisol imbalance is difficulty in maintaining a positive outlook or a general sense of well-being. Individuals may find themselves constantly in negative thought patterns, struggling to find joy or contentment in their daily lives. This emotional state, often accompanied by a lack of enthusiasm or a loss of interest in social interactions, can be indicative of hormonal disruptions caused by chronic stress.
It is important to note that while emotional and mental signs can indicate a potential cortisol imbalance, further evaluation and consultation with healthcare professionals are necessary for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Effective Strategies for Managing Cortisol Levels
In this section, we will explore practical methods and techniques that can be helpful in maintaining healthy cortisol levels. By implementing these strategies, individuals can enhance their overall well-being and reduce the impact of stress on their hormonal balance.
| 1. Stress Reduction Techniques |
| Implementing effective stress reduction techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies, can play a significant role in managing cortisol levels. These activities promote relaxation and can help reduce the production of stress hormones. |
| 2. Regular Exercise |
| Engaging in regular physical activity is not only beneficial for overall health but can also help regulate cortisol levels. Exercise stimulates the production of endorphins, which are known to elevate mood and decrease stress levels. |
| 3. Balanced Diet |
| A well-balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing cortisol levels. Consuming foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, and incorporating sources of lean protein can help stabilize cortisol production and support a healthy hormonal balance. |
| 4. Quality Sleep |
| Adequate and quality sleep is essential for maintaining stable cortisol levels. Creating a relaxing bedtime routine and ensuring a comfortable sleep environment can promote restful sleep and reduce the impact of stress on hormone regulation. |
| 5. Social Support |
| Building and nurturing strong social connections can provide a valuable support system in managing cortisol levels. Surrounding oneself with empathetic and understanding individuals can help alleviate stress and contribute to a healthier hormonal balance. |
By implementing these strategies and customizing them to individual needs, individuals can effectively manage cortisol levels, promoting overall well-being and reducing the negative impact of stress-induced hormonal fluctuations.
Natural Remedies and Lifestyle Changes to Regulate Cortisol

The section below explores various natural remedies and lifestyle adjustments that can help in managing and regulating the levels of cortisol in your body. These techniques aim to restore balance, enhance well-being, and mitigate the negative effects of stress-induced hormonal fluctuations.
- 1. Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): Incorporating mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep breathing exercises, into your daily routine can aid in stress reduction and promote hormonal balance.
- 2. Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity, such as cardiovascular exercises, strength training, or yoga, can reduce stress levels and promote the release of endorphins, which contribute to a sense of well-being.
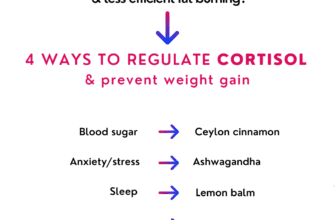
- 3. Herbal Supplements: Certain herbs, like ashwagandha, rhodiola, and holy basil, have been found to regulate cortisol levels and alleviate stress. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating any herbal supplements into your routine.
- 4. Adequate Sleep: Establishing a consistent sleep schedule and getting enough restful sleep can enhance your body’s ability to handle stress and maintain hormonal balance.
- 5. Balanced Nutrition: Consuming a well-rounded diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support overall health and help regulate cortisol levels.
- 6. Stress Management Techniques: Utilizing stress management techniques such as journaling, engaging in hobbies or activities you enjoy, practicing relaxation exercises, or seeking support from friends or a therapist, can aid in stress reduction and cortisol regulation.
- 7. Social Support: Cultivating and maintaining strong social connections can provide emotional support, improve resilience to stress, and positively influence hormonal balance.
By incorporating these natural remedies and lifestyle changes into your routine, you can take proactive steps towards managing cortisol levels and promoting hormonal equilibrium. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.
Questions and answers
How does stress affect cortisol levels?
Stress triggers the release of cortisol from the adrenal glands. Chronic stress can lead to an imbalance in cortisol levels, with prolonged high levels or chronically low levels.
What are the symptoms of cortisol imbalance?
The symptoms of cortisol imbalance can vary, but common signs include fatigue, weight gain or loss, mood swings, sleep disturbances, decreased libido, and weakened immune system.
Can cortisol imbalance affect mental health?
Yes, cortisol imbalance can negatively impact mental health. High cortisol levels are associated with anxiety and depression, while chronically low cortisol levels may lead to feelings of low energy and motivation.
Are there any natural ways to manage cortisol imbalance?
Yes, there are natural ways to manage cortisol imbalance. These include practicing stress-reducing techniques such as meditation and yoga, getting regular exercise, maintaining a healthy diet, and ensuring adequate sleep.
When should I seek medical help for cortisol imbalance?
If you suspect you have a cortisol imbalance and are experiencing persistent symptoms such as weight fluctuations, extreme fatigue, or mood changes, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What is cortisol imbalance?
Cortisol imbalance refers to an abnormal level of cortisol hormone in the body. Cortisol is a stress hormone that is released by the adrenal glands in response to stress. An imbalance occurs when cortisol levels are either too high or too low, disrupting the body’s normal functioning.
What causes cortisol imbalance?
Cortisol imbalance can be caused by various factors, such as chronic stress, certain medications, hormonal disorders, and medical conditions like Cushing’s syndrome or Addison’s disease. Lifestyle factors like poor diet, lack of exercise, and inadequate sleep can also contribute to cortisol imbalance.
What are the symptoms of cortisol imbalance?
The symptoms of cortisol imbalance can vary, but common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain or weight loss, mood swings, anxiety, depression, sleep disturbances, digestive problems, and difficulty concentrating. These symptoms can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life.
How can cortisol imbalance be diagnosed?
Cortisol imbalance can be diagnosed through various methods. A healthcare provider may conduct a physical examination, review medical history, and perform blood tests to measure cortisol levels. Additional tests, such as the dexamethasone suppression test or ACTH stimulation test, may be ordered to further evaluate cortisol production and regulation.
What are the treatment options for cortisol imbalance?
The treatment for cortisol imbalance depends on the underlying cause. Lifestyle modifications such as stress management techniques, regular exercise, and a balanced diet can help regulate cortisol levels. In some cases, medications or hormone replacement therapy may be prescribed. It is important to work closely with a healthcare professional to develop an individualized treatment plan.