In today’s fast-paced society, stress has become an inevitable part of our lives. It creeps into our daily routines, affecting us both mentally and physically. While most of us are familiar with the concept of stress, it is important to delve deeper into understanding its underlying mechanisms, particularly the role of cortisol – a hormone that plays a significant role in our body’s response to stress.
Cortisol, often referred to as the body’s stress hormone, is a natural hormone produced by the adrenal glands. It acts as a powerful messenger within our bodies, influencing various physiological functions and playing a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis – the internal balance necessary for overall well-being. This remarkable hormone impacts a wide range of bodily systems, including metabolism, immune function, sleep patterns, and even emotional responses.
While cortisol is essential for our survival and adaptation to stressful situations, prolonged exposure to high levels of this hormone can have detrimental effects on our health. Chronic stress leads to a constant release of cortisol, which can disrupt the delicate balance in our body and contribute to a multitude of health issues. Understanding the intricate relationship between cortisol and our overall well-being is vital in order to effectively manage stress and maintain a healthy lifestyle.
- Understanding Cortisol: The Role of the Stress Hormone in Health
- The Basics: What is Cortisol and How Does It Affect the Body?
- Functions of Cortisol in the Body
- Effects of Cortisol on Physical Health
- The Connection Between Cortisol and Mental Well-being
- Cortisol and Stress: Impact on Mental Health
- The Connection Between Cortisol and Anxiety
- Cortisol’s Impact on Overall Physical Health
- Cortisol and Weight Gain
- Cortisol and the Immune System
- Questions and answers
Understanding Cortisol: The Role of the Stress Hormone in Health
In this section, we will delve into the significant influence of cortisol, the hormone associated with stress, on our overall well-being, exploring its role in determining our physical and mental health.
First and foremost, cortisol plays a vital role in our body’s response to stress, helping us adapt and cope with challenging situations. It regulates a wide range of physiological processes, including metabolism, immune system function, and blood pressure, among others.
- Cortisol impacts our energy levels and can affect our ability to maintain a healthy weight.
- It is intricately involved in the regulation of our sleep-wake cycle, influencing both the quantity and quality of our rest.
- The hormone also plays a crucial role in modulating inflammation and immune responses, affecting our overall resistance to infections.
- Furthermore, cortisol interacts with other hormones in our body, such as insulin, impacting our blood sugar levels and potentially contributing to the development of conditions like diabetes.
- In addition, cortisol exerts influence on our mood and cognitive function, as excessive levels or chronic stress can lead to anxiety, depression, and impaired memory.
It is important to note that while cortisol is crucial for our survival and adaptation to acute stress, prolonged exposure to elevated levels can have detrimental effects on our health. Chronic stress and continuously elevated cortisol levels have been linked to various conditions, including cardiovascular disease, obesity, immune system dysregulation, and mental health disorders.
Understanding the role of cortisol in our overall health is critical for maintaining a balanced lifestyle and effectively managing stress. By implementing strategies to promote relaxation, engage in regular physical activity, adopt healthy sleep habits, and cultivate positive coping mechanisms, we can strive to keep our cortisol levels in check, fostering optimal well-being.
The Basics: What is Cortisol and How Does It Affect the Body?

In this section, we will delve into the fundamental concept of cortisol and gain insights into its profound influence on the human body. Cortisol, often referred to as the body’s primary stress hormone, plays a crucial role in a wide array of physiological processes. It serves as an essential messenger that helps regulate various bodily functions and maintain a delicate balance. Understanding the impact of cortisol can provide valuable insights into the intricate workings of our complex biological systems.
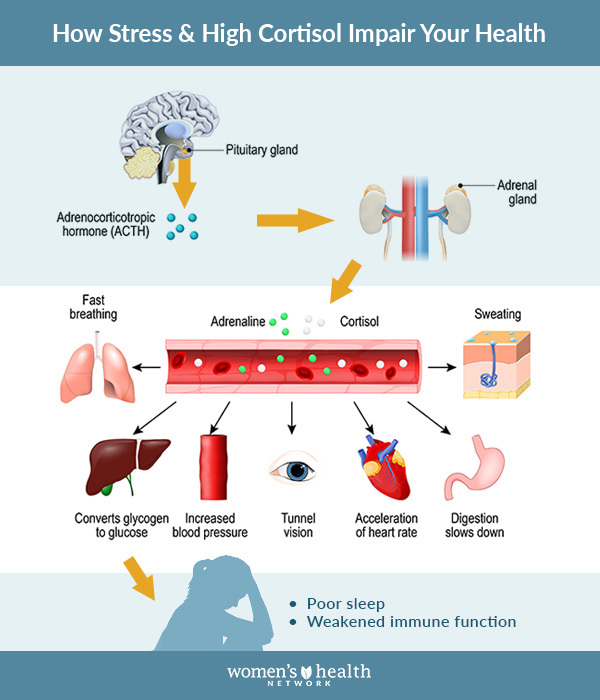
Cortisol – a hormone produced by the adrenal glands, nestled atop each kidney – plays a significant role in mobilizing our body’s resources to respond to internal and external stressors. It acts as a master regulator, influencing metabolism, immune responses, inflammation levels, and the sleep-wake cycle. Additionally, cortisol helps regulate blood pressure and blood sugar levels, aiding in the body’s ability to adapt to challenges and maintain overall homeostasis.
When the body encounters a stressful situation, whether it be physical, psychological, or emotional, cortisol levels swiftly rise to meet the demands. This surge in cortisol helps prepare the body to navigate the stressful event effectively. However, prolonged or excessive cortisol production can lead to detrimental effects on the body’s various systems. Chronic stress and consistently elevated cortisol levels have been linked to a range of health issues, including impaired cognitive function, weakened immune response, increased susceptibility to weight gain, and cardiovascular problems.
It is crucial to recognize the intricate interplay between cortisol and overall health. By understanding how cortisol affects the body, we lay the foundation for exploring strategies to manage stress effectively and maintain a balanced, optimal state of well-being.
Functions of Cortisol in the Body
Cortisol, a vital hormone in the human body, plays a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions and promoting overall well-being. It is involved in numerous physiological processes and helps regulate key systems within the body.
One of cortisol’s primary functions is its role in the body’s stress response. In times of stress, cortisol levels rise, preparing the body for fight-or-flight responses. This hormone helps mobilize energy reserves, increases heart rate and blood pressure, and enhances mental alertness and focus. Furthermore, cortisol aids in suppressing non-essential functions during stress, such as digestion and growth, redirecting energy towards immediate survival needs.
Cortisol also actively participates in regulating the immune system. It has anti-inflammatory properties and works to suppress immune responses to prevent excessive inflammation. Additionally, cortisol plays a vital role in modulating immune cell activity and dampening immune reactions, which helps maintain immune balance and prevent autoimmune diseases. It is a key factor in the body’s response to infection, injury, or other immune challenges.
Another important function of cortisol is its role in metabolism and energy regulation. It promotes the breakdown of stored glycogen in the liver, releasing glucose into the bloodstream for use as an immediate energy source. Additionally, cortisol stimulates the breakdown of fats and proteins, provides energy substrates during prolonged fasting or starvation, and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels. It also plays a role in regulating the body’s sensitivity to insulin, which is essential for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels.
Besides its direct impact on stress, immune responses, and metabolism, cortisol also supports proper cardiovascular function. It helps regulate blood pressure by increasing the sensitivity of blood vessels to constrictive signals, leading to vasoconstriction and increased blood pressure. Cortisol also plays a role in maintaining fluid balance and electrolyte levels in the body.
In summary, cortisol is a versatile hormone with various functions in the body, including its involvement in stress response, immune regulation, metabolism, and cardiovascular function. Understanding the diverse roles of cortisol is crucial for comprehending its impact on overall health and well-being.
Effects of Cortisol on Physical Health
Cortisol, a naturally occurring hormone in the body, has a profound impact on various aspects of physical health. This hormone, commonly associated with stress, plays a crucial role in regulating several bodily functions, including metabolism, immune response, and inflammation. Understanding the effects of cortisol on physical health can provide valuable insight into the relationship between stress and overall well-being.
| Effects of Cortisol on Physical Health | |
|---|---|
| Metabolism | Cortisol influences the breakdown of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats, contributing to changes in body composition. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to increased appetite, weight gain, and redistribution of fat, particularly around the abdomen. |
| Immune Response | While cortisol plays a crucial role in suppressing inflammation during short-term stress, chronic stress can dysregulate the immune system, leading to an increased susceptibility to infections, delayed wound healing, and autoimmune disorders. |
| Inflammation | Chronic elevation of cortisol levels can promote chronic inflammation in the body, which has been linked to various health conditions, including cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. |
| Bone Health | Prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol can impair bone formation and increase the risk of osteoporosis, leading to weakened bones and an increased susceptibility to fractures. |
| Cardiovascular Health | Increased cortisol levels can contribute to elevated blood pressure, impaired blood sugar regulation, and abnormal lipid profiles, all of which are risk factors for cardiovascular disease. |
| Sexual and Reproductive Health | Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels can disrupt hormonal balance, leading to menstrual irregularities, decreased fertility, and reduced libido in both men and women. |
By understanding the effects of cortisol on physical health, individuals can take steps to manage their stress levels effectively and mitigate the potential negative impact on overall well-being. Techniques such as stress reduction strategies, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and mindfulness practices can help regulate cortisol levels and promote optimal physical health.
The Connection Between Cortisol and Mental Well-being

A correlation exists between the stress hormone cortisol and one’s mental well-being. Studies have revealed a complex interplay between cortisol, also referred to as the fight-or-flight hormone, and various aspects of mental health. While stress is often perceived as detrimental to both physical and mental health, understanding the specific impact of cortisol on mental well-being sheds light on its role in the body’s response to stress.
Increasing evidence suggests that imbalances in cortisol levels can have profound effects on mental health. Cortisol is secreted by the adrenal glands in response to stress, and its function is crucial for maintaining homeostasis. However, sustained high levels of cortisol can negatively impact the brain’s structures and functions, leading to various mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression.
Moreover, cortisol levels can fluctuate throughout the day, influencing our emotional states and cognitive abilities. Elevated cortisol levels can impair memory and concentration, affecting productivity and overall cognitive performance. Additionally, imbalances in cortisol levels have been associated with mood disorders, leading to emotional dysregulation and increased vulnerability to stress.
Understanding the intricate relationship between cortisol and mental well-being is essential in promoting mental health and developing effective interventions. By recognizing the impact of cortisol on brain structure and function, healthcare professionals can devise strategies to regulate cortisol levels and mitigate the negative effects on mental health. Furthermore, individuals can incorporate stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and relaxation exercises, to reduce cortisol levels and support their overall mental well-being.
Cortisol and Stress: Impact on Mental Health
In this section, we will explore the profound influence that cortisol and stress have on our mental well-being. Excessive levels of cortisol, the stress hormone, can have detrimental effects on our mental health, affecting various aspects of cognition, emotions, and overall psychological functioning.
The Role of Cortisol: Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, is a natural hormone produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress. It helps regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism, immune response, and the sleep-wake cycle. While cortisol is essential for our survival, prolonged and excessive levels can have negative consequences on our mental health.
Effects on Cognitive Function: Elevated cortisol levels can impair cognitive abilities such as memory, attention, and decision-making. Chronic stress and cortisol dysregulation have been linked to difficulties in concentration, reduced mental clarity, and decreased problem-solving skills. Additionally, high levels of cortisol have been associated with a higher risk of developing age-related cognitive decline and disorders like Alzheimer’s disease.
Emotional Well-being: Cortisol plays a crucial role in regulating emotions and can impact our emotional well-being. Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels have been linked to an increased risk of developing mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. Furthermore, prolonged exposure to stress can lead to emotional dysregulation, irritability, and a decreased ability to cope with everyday challenges.
Psychological Functioning: The impact of cortisol on mental health extends beyond cognition and emotions. Excessive cortisol production can disrupt the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, affecting mood regulation and contributing to the development of mental health disorders. Furthermore, cortisol dysregulation has been associated with heightened sensitivity to stress, leading to a vicious cycle of chronic stress and worsened mental well-being.
Managing Cortisol and Stress: Understanding the impact of cortisol on mental health highlights the importance of stress management techniques. Regular exercise, mindfulness practices, adequate sleep, and seeking social support are all effective strategies for reducing cortisol levels and promoting mental well-being. Additionally, therapy and medication may be beneficial for individuals experiencing chronic stress and its impact on mental health.
It is crucial to prioritize our mental health by recognizing the interplay of cortisol and stress on our overall well-being. By actively managing stress levels and implementing healthy coping mechanisms, we can safeguard our mental health and cultivate a better quality of life.
The Connection Between Cortisol and Anxiety

When it comes to the link between cortisol and anxiety, it is essential to explore the intricate relationship between these two factors. Cortisol, also known as the stress hormone, plays a crucial role in our body’s response to stressful situations. Anxiety, on the other hand, is a complex mental health condition characterized by excessive worrying, fear, and restlessness. Understanding how cortisol levels can affect anxiety levels is key in comprehending the impact of stress on our overall well-being.
A growing body of research suggests that elevated cortisol levels can contribute to the development and exacerbation of anxiety disorders. When we experience stress, our bodies release cortisol, which triggers a range of physiological responses to help us cope with the perceived threat. However, chronic stress or persistent activation of the stress response can lead to prolonged elevation of cortisol levels, resulting in an imbalance in the body’s stress regulation system.
This dysregulation of cortisol can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders. High cortisol levels have been linked to increased anxiety symptoms, such as excessive worry, irritability, and difficulty concentrating. Additionally, cortisol can interfere with the production and function of neurotransmitters involved in mood regulation, further exacerbating anxiety symptoms. Understanding the intricate relationship between cortisol and anxiety is crucial for developing effective strategies to manage and alleviate anxiety symptoms.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| – Cortisol, the stress hormone, is closely associated with anxiety. |
| – Elevated cortisol levels can contribute to the development and exacerbation of anxiety disorders. |
| – Chronic stress and dysregulation of cortisol can lead to increased anxiety symptoms. |
| – Understanding the relationship between cortisol and anxiety is essential for effective anxiety management. |
Cortisol’s Impact on Overall Physical Health
Cortisol, the hormone produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress, plays a significant role in our physical well-being. It affects various aspects of our body and its functioning, influencing our overall health and vitality.
When cortisol levels are elevated for extended periods due to chronic stress, it can have detrimental effects on our physical health. Increased cortisol levels have been associated with a weakened immune system, making us more susceptible to infections and diseases.
Cortisol also plays a role in metabolism, specifically in regulating blood sugar levels. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to imbalances in blood sugar, potentially contributing to the development of conditions such as diabetes. Additionally, cortisol promotes the storage of fat, particularly around the abdomen, which can increase the risk of obesity and related health issues.
Furthermore, cortisol influences cardiovascular health by contributing to high blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Prolonged exposure to elevated cortisol levels can lead to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
The impact of cortisol on physical health extends to bone health as well. When cortisol levels are consistently high, it can lead to a decrease in bone density, making individuals more susceptible to osteoporosis and fractures.
Moreover, cortisol affects the reproductive system, influencing fertility and the regulation of reproductive hormones. Chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels have been associated with menstrual irregularities, decreased libido, and even infertility.
In conclusion, cortisol’s impact on overall physical health is undeniable. Chronic stress and elevated levels of cortisol can have detrimental effects on the immune system, metabolism, cardiovascular health, bone health, and reproductive system. Understanding and effectively managing cortisol levels is crucial for maintaining optimal physical well-being.
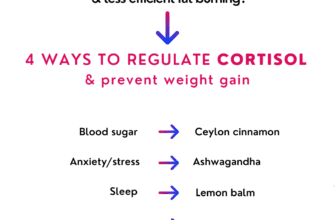
Cortisol and Weight Gain
Understanding the connection between cortisol and weight gain unveils the profound impact that this stress hormone can have on the body’s overall composition. Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, is a vital component of the body’s natural stress response system. It plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological functions and maintaining homeostasis.
Research has shown that chronic stress and elevated cortisol levels can lead to weight gain, particularly in the abdominal area. When the body is under constant stress, cortisol is released in high amounts, which can disrupt normal metabolic processes. This disruption can result in increased appetite, cravings for sugary and fatty foods, and a decreased ability to burn calories efficiently.
Additionally, the presence of excess cortisol in the body can promote the storage of fat, especially visceral fat. Visceral fat is the dangerous type of fat that surrounds organs and is associated with an increased risk of various health conditions, such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Furthermore, cortisol can interfere with the body’s ability to break down stored fat, leading to further weight gain.
However, it is important to note that the relationship between cortisol and weight gain is complex and multifaceted. While high cortisol levels may contribute to weight gain in some individuals, others may experience weight loss or no significant changes. Factors such as genetics, lifestyle habits, and overall health can influence how cortisol affects weight regulation.
To mitigate the potential negative impact of cortisol on weight gain, it is essential to adopt healthy stress management techniques. Engaging in regular physical activity, practicing relaxation exercises like meditation or yoga, and prioritizing sleep can help regulate cortisol levels and promote a healthy weight. It is also crucial to maintain a balanced diet, focusing on nutrient-dense foods and avoiding excessive consumption of sugar and processed foods.
The relationship between cortisol and weight gain serves as a reminder of the intricate connection between stress, hormones, and overall health. By better understanding the role of cortisol in weight regulation, individuals can take proactive measures to support their well-being and maintain a healthy weight.
Cortisol and the Immune System
Cortisol plays a crucial role in the intricate relationship between our body’s stress response and the immune system. This section explores the profound impact of cortisol on our immune response and overall well-being.
Modulation of Immune Function: Cortisol, often referred to as the stress hormone, exerts significant influence on the immune system. It suppresses certain aspects of immune function, including inflammation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. At the same time, cortisol enhances other immune responses, such as the production of anti-inflammatory compounds and the activation of regulatory immune cells.
Stress-Induced Immune Suppression: Excessive or prolonged stress can disrupt the delicate balance of cortisol and immune system interactions. Under conditions of chronic stress, elevated cortisol levels can lead to immune suppression. This weakened immune response can make individuals more susceptible to infections, delay wound healing, and reduce resistance to certain diseases.
Autoimmune Disorders: In some cases, dysregulation of cortisol and immune function can contribute to the development or exacerbation of autoimmune disorders. Immune cells may mistakenly attack the body’s own tissues, causing chronic inflammation and damage. The impact of cortisol on the immune system is particularly relevant in autoimmune conditions, where immune activity needs to be carefully balanced.
Psychoneuroimmunology: The emerging field of psychoneuroimmunology explores the complex interplay between psychological factors, the nervous system, and the immune system. Cortisol serves as an important mediator in this connection, with stress and emotional states influencing immune responses through cortisol’s regulatory effects.
Optimizing Cortisol-Immune Balance: Understanding the relationship between cortisol and the immune system can provide insights into strategies for promoting overall health. Maintaining a healthy stress response and managing chronic stress can help prevent immune suppression and support immune function. Lifestyle factors such as sleep, exercise, and relaxation techniques can also play a role in optimizing cortisol-immune balance.
In conclusion, cortisol plays a multifaceted role in shaping immune responses. It can both dampen and enhance immune function, depending on the context and duration of stress. By understanding the intricate connections between cortisol and the immune system, we can strive to maintain a healthy cortisol-immune balance for improved well-being.
Questions and answers
What is cortisol and how does it affect my overall health?
Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands that helps regulate metabolism, immune responses, and stress levels. While it plays an important role in the body, prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol due to chronic stress can lead to various health problems such as weight gain, weakened immune system, and increased risk of heart disease.
How does cortisol impact my weight?
Cortisol can contribute to weight gain when its levels are consistently high. When you’re stressed, cortisol triggers cravings for high-calorie foods, which can lead to overeating and weight gain, particularly around the abdominal area. Moreover, cortisol also promotes the storage of fat, especially visceral fat, which is associated with various health risks.
Can cortisol affect my sleep patterns?
Yes, cortisol can affect your sleep patterns. Normally, cortisol levels decrease in the evening, allowing you to relax and fall asleep. However, chronic stress can disrupt this natural rhythm, causing increased cortisol levels at night, which can make it harder to fall asleep or stay asleep. This can result in decreased sleep quality and leave you feeling tired and fatigued during the day.
Is cortisol always bad for my health?
No, cortisol is not always bad for your health. In fact, it is necessary for our bodies to function properly. Cortisol helps regulate blood pressure, reduce inflammation, and manage stress. The key is maintaining a balance and allowing cortisol levels to return to normal after a stressor has been resolved. It is the prolonged exposure to high levels of cortisol due to chronic stress that can have negative effects on overall health.
Are there ways to naturally lower cortisol levels?
Yes, there are several natural ways to lower cortisol levels. These include practicing stress-management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and yoga. Regular exercise, getting enough sleep, and maintaining a healthy diet can also help regulate cortisol levels. Additionally, certain herbs and supplements like ashwagandha and omega-3 fatty acids have been shown to have cortisol-lowering effects.
What is cortisol and how does it impact overall health?
Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands in response to stress. It plays a crucial role in the body’s response to stress, regulating metabolism, immune system, and blood pressure. However, excessive levels of cortisol can have negative effects on overall health, including increased risk of weight gain, compromised immune system, and mental health issues.
How does chronic stress affect cortisol levels?
Chronic stress can significantly impact cortisol levels in the body. Prolonged periods of stress can lead to continuously elevated cortisol levels, which can disrupt the body’s natural balance. This can result in a variety of health issues, including weakened immune system, fatigue, weight gain, and mood disorders.
Can cortisol levels be measured through blood tests?
Yes, cortisol levels can be measured through blood tests. A blood test is a common method used by healthcare professionals to assess cortisol levels and identify any potential imbalances. It can provide valuable information about an individual’s stress response and overall health.
What are some natural ways to reduce cortisol levels?
There are several natural ways to reduce cortisol levels. Engaging in regular exercise, practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga, getting enough sleep, and maintaining a healthy diet are all effective methods. Additionally, reducing stressors in one’s life and seeking support from loved ones can help lower cortisol levels.
Can cortisol levels impact weight gain?
Yes, cortisol levels can impact weight gain. Elevated cortisol levels can lead to increased appetite, particularly for unhealthy, high-calorie foods. Additionally, cortisol can promote the storage of fat, particularly in the abdominal area. Therefore, excessive levels of cortisol can contribute to weight gain and difficulty in losing weight.