Begin a journey of understanding and discover the intricacies and workings of one of the most popular and effective diets – the Atkins Diet. Delve into the mechanisms and science behind this renowned nutritional approach to weight loss while unraveling its numerous health benefits.
Embark on a voyage of enhanced well-being as you uncover the secrets to achieving optimal health through the power of the Atkins Diet. Gain a deeper comprehension of its mechanism and witness firsthand how this revolutionary eating plan focuses on a low-carbohydrate, high-fat approach to transform your body and health.
Discover the wonders of this groundbreaking dietary regimen as it empowers you to achieve your weight loss goals through a unique metabolic process. Dive into the intricacies of the Atkins Diet and grasp how it influences your body to burn fat for fuel, resulting in accelerated weight loss and improved overall health.
Unearth the therapeutic benefits of the Atkins Diet as it not only aids in shedding those extra pounds but also offers a multitude of health advantages. Explore how this nutritional approach can help regulate blood sugar levels, enhance cardiovascular health, and combat metabolic disorders, all while improving energy levels and mental clarity.
The Atkins Diet: Unveiling Its Mechanism and Exploring the importance to Health

Embarking on a journey to understand the scientific mechanism underpinning the Atkins Diet offers profound insights into the dietary plan’s effectiveness and its potential health benefits. This section brings to light the intricate workings of the Atkins Diet, highlighting its impact on the body and the positive outcomes it can yield.
The Atkins Diet promotes a low-carbohydrate approach to nutrition, a departure from conventional dietary norms. By limiting the intake of carbohydrates, the body transitions into a state of ketosis, wherein it primarily relies on stored fat for fuel, resulting in weight loss. Additionally, this process offers metabolic advantages, such as improved insulin sensitivity and the reduction of triglyceride levels, ultimately enhancing overall health.
- Enhanced weight loss: By restricting carbohydrate intake, the Atkins Diet enables the body to rapidly deplete its glycogen stores, shifting its energy source to stored fat. This metabolic state facilitates significant weight loss, making it an attractive dietary option for individuals seeking to shed excess pounds.
- Improved insulin sensitivity: Carbohydrates stimulate the secretion of insulin in the body. However, excessive and frequent consumption of carbohydrates can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. By limiting carbohydrate intake, the Atkins Diet helps enhance insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of developing diabetes.
- Reduced triglyceride levels: High levels of triglycerides in the bloodstream can contribute to cardiovascular diseases. The Atkins Diet’s low-carbohydrate approach aids in the reduction of triglyceride levels, promoting heart health and potentially preventing heart-related complications.
Exploring the science behind the Atkins Diet reveals its efficacy in promoting weight loss, improving insulin sensitivity, and reducing triglyceride levels. By embracing this low-carbohydrate dietary plan, individuals can pave the way to a healthier lifestyle and enhance their overall well-being.
Overview

In this section, we will provide an overview of the fundamental principles and concepts related to the Atkins diet. The objective is to gain a comprehensive understanding of how this dietary approach functions and the potential health benefits it offers.
Firstly, we will explore the core principles that underpin the Atkins diet, focusing on the primary mechanism behind its effectiveness. We will delve into the concept of carbohydrate restriction and how it affects the body’s metabolism, encouraging the utilization of stored fat for energy production.
Additionally, we will examine the various phases of the Atkins diet, highlighting the specific dietary guidelines and food choices prescribed in each stage. By doing so, we aim to provide a clear roadmap for individuals considering or already following this dietary approach.
Furthermore, we will discuss the potential health benefits associated with the Atkins diet. We will explore how it may aid in weight loss, improve blood sugar control, and positively impact cardiovascular health. Additionally, we will address potential concerns and controversies surrounding the diet, ensuring a balanced and informed perspective.
Through this comprehensive overview, readers will gain a solid understanding of the Atkins diet, its mechanism, and the potential health benefits it may provide. Armed with this knowledge, individuals can make informed decisions about whether this dietary approach aligns with their personal goals and health requirements.
History and Development
In this section, we will take a closer look at the historical background and evolution of the popular eating plan known as the Atkins Diet. From its inception to the present day, we will explore the milestones and developments that have shaped and refined this dietary approach.
To truly grasp the context surrounding the Atkins Diet, we must delve into its origins. This dietary regimen emerged as a response to conventional wisdom on weight loss and nutrition, challenging traditional beliefs and advocating for a different approach.
Over time, the Atkins Diet has undergone several modifications and refinements, adapting to scientific research and incorporating new findings. Through continuous experimentation and advancements, the diet has evolved into the comprehensive program we know today.
Throughout its journey, the Atkins Diet has faced criticism and controversy, yet it has remained a popular choice for individuals seeking weight loss and improved health. The diet’s development has been shaped by not only scientific discoveries, but also public opinion and cultural shifts.
This section aims to provide an insightful overview of the history and development of the Atkins Diet, shedding light on the factors that have contributed to its growth and the impact it has had on the field of nutrition and health.
Principles and Philosophy
The core principles and underlying philosophy of the Atkins diet delve into the fundamental concepts and beliefs that form its basis. This section aims to provide an overview of the guiding principles and the philosophy that this dietary approach relies upon.
At the heart of the Atkins diet lies a deep understanding of human metabolism and the intricate connection between nutrition and our overall health. By emphasizing the significance of macronutrients and their impact on our body’s energy production, the Atkins diet seeks to optimize our dietary choices for optimal well-being.
Central to the Atkins philosophy is the notion of reducing carbohydrate intake to induce a metabolic state known as ketosis. Through this dietary approach, the body switches from relying primarily on carbohydrates for energy to utilizing stored fat as its primary fuel source. This shift in metabolism is believed to not only aid in weight loss but also bring about other potential health benefits.
Furthermore, the principles of the Atkins diet stress the importance of consuming high-quality proteins and fats, while minimizing the intake of processed and refined carbohydrates. This approach acknowledges the role of nutrient-dense foods in supporting satiety, maintaining blood sugar levels, and promoting overall health and vitality.
Moreover, the Atkins diet affirms the significance of individual variation and personalized approaches to nutrition. It recognizes that each person’s specific metabolic needs and dietary preferences should be considered when tailoring an effective eating plan. By acknowledging the uniqueness of each individual, the Atkins diet promotes flexibility and the ability to adapt the dietary approach to suit personal needs and goals.
In essence, the principles and philosophy underlying the Atkins diet revolve around understanding how our body metabolizes different nutrients, particularly carbohydrates, and harnessing this knowledge to optimize our eating habits for improved health and well-being.
Mechanism of the Atkins Diet

The Atkins Diet operates on a unique and intricate bodily mechanism that promotes weight loss and other health benefits. By adopting a low-carbohydrate, high-protein eating plan, the body is induced into a metabolic state known as ketosis. During ketosis, the body primarily relies on stored fat for energy instead of carbohydrates. This metabolic shift leads to an increased burning of fat, resulting in weight loss.
Furthermore, the Atkins Diet promotes stable blood sugar levels and insulin levels, which can have positive impacts on overall health. By limiting the intake of carbohydrates that rapidly raise blood sugar levels, the diet helps avoid spikes in insulin production and subsequent crashes. This controlled insulin response may reduce the risk of developing certain chronic conditions such as diabetes and metabolic syndrome.
In addition, the Atkins Diet has been found to effectively suppress appetite and curb cravings for sugary and starchy foods. The high protein and fat content of the diet contribute to increased satiety and a decreased desire for snacking, which can aid in weight management.
Another key aspect of the Atkins Diet’s mechanism is the regulation of hormones and their impact on metabolism. By restricting carbohydrate intake, the diet improves the body’s sensitivity to insulin and affects the balance of hormones involved in hunger, satiety, and fat storage. These hormonal changes can further support weight loss and the maintenance of a healthy body composition.
Overall, the mechanism of the Atkins Diet involves altering the body’s metabolism, regulating blood sugar and insulin levels, suppressing appetite, and influencing hormonal activity. These elements work together to promote weight loss and potentially improve various aspects of health.
Ketosis and Fat Burning
In this section, we will delve into the fascinating process of ketosis and how it relates to the burning of fat in the body. Understanding the concept of ketosis is crucial in comprehending the mechanism behind the Atkins diet and its potential health benefits. Here, we will explore the intricate workings of our body’s metabolism and the role ketones play in fueling fat burning.
Ketosis refers to a metabolic state in which our body utilizes fat as its primary source of energy instead of carbohydrates. Normally, our body relies on glucose derived from carbohydrates to meet its energy demands. However, in situations where carbohydrate intake is limited, such as during a low-carb diet like Atkins, our body switches to burning stored fat for energy.
As we restrict our carbohydrate intake, our liver begins to produce ketones through a process called ketogenesis. These ketones, namely acetone, acetoacetate, and beta-hydroxybutyrate, act as alternative fuel sources for our body and are transported to various tissues, including the brain, where they can be converted back into energy.
The key advantage of ketosis is its ability to enhance fat burning. A body in ketosis becomes highly efficient in breaking down fat reserves and converting them into usable energy. This metabolic state promotes the utilization of stored fat, leading to weight loss and a reduction in body fat percentage.
Additionally, ketosis has shown potential benefits in controlling appetite and regulating blood sugar levels. The consumption of low-carb, high-fat foods triggers hormonal changes that promote satiety and help stabilize blood glucose levels. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with conditions such as diabetes or insulin resistance.
While there are potential benefits to ketosis and fat burning, it’s important to note that this metabolic state may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions or dietary requirements. Before embarking on any diet or lifestyle change, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure it aligns with one’s individual needs and goals.
In the following sections, we will explore the science behind ketosis further, examining the effect of carbohydrate restriction on insulin levels, the production of ketones, and the potential risks and side effects of a ketogenic diet.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as medical advice. Please consult with a healthcare professional before making any changes to your diet or exercise routine.
Carbohydrate Restriction and Insulin Regulation
A fundamental aspect of the Atkins diet revolves around the reduction of carbohydrate intake, which has a significant impact on the regulation of insulin levels in the body. By limiting the consumption of carbohydrates, the diet aims to optimize insulin function and promote various health benefits.
Carbohydrates, commonly found in foods such as grains, sugars, and starchy vegetables, are the main sources of glucose in the body. When consumed, carbohydrates are broken down into glucose, leading to an increase in blood sugar levels. In response, the pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps transport glucose from the bloodstream into cells for energy production.
However, consistently high levels of carbohydrates in the diet can result in frequent and excessive insulin release, leading to insulin resistance. This condition occurs when cells become less responsive to the effects of insulin, causing elevated blood sugar levels and potentially contributing to the development of diabetes and weight gain.
The Atkins diet, through its emphasis on carbohydrate restriction, aims to address this issue by promoting insulin regulation. By reducing carbohydrate intake, the body relies on alternative sources of fuel, such as fat, which stimulates a metabolic state called ketosis. During ketosis, the liver converts fat into ketones, which can be used by the body and the brain as an efficient energy source.
Furthermore, carbohydrate restriction may lead to a reduction in insulin levels, as there is a decreased need for the hormone to manage the influx of glucose. This can potentially enhance insulin sensitivity and improve the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, thus reducing the risk of insulin resistance and related health conditions.
In addition to its impact on insulin regulation, carbohydrate restriction in the Atkins diet has been associated with numerous health benefits. These may include weight loss, improved lipid profiles, increased satiety, and better blood sugar control. However, it is crucial to approach any dietary changes, including carbohydrate restriction, with caution and under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
- Reduced carbohydrate intake promotes optimal insulin function.
- Excessive carbohydrate consumption can lead to insulin resistance.
- The Atkins diet aims to address insulin regulation through carbohydrate restriction.
- Carbohydrate restriction promotes ketosis, where fat is used as an alternative energy source.
- By lowering carbohydrate intake, insulin levels may decrease, improving insulin sensitivity.
- Carbohydrate restriction in the Atkins diet has been associated with weight loss and other health benefits.
Protein Intake and Muscle Preservation

When it comes to the Atkins diet, one important aspect to consider is the role of protein intake in preserving muscle mass. By understanding how protein consumption affects our bodies, we can better appreciate the significance of incorporating adequate amounts into our dietary choices.
Protein, often referred to as the building blocks of life, is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in maintaining and repairing tissues, including muscles. In the context of the Atkins diet, protein intake becomes even more significant as it becomes the primary source of calories while limiting carbohydrates.
- Adequate protein intake during the Atkins diet helps to support muscle preservation and growth. As the body enters a state of ketosis, where it primarily relies on fat for fuel, consuming enough protein becomes imperative to prevent muscle breakdown.
- Protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, fish, eggs, and dairy products, provide the necessary amino acids needed for muscle protein synthesis. This process is essential for rebuilding and maintaining skeletal muscle mass.
- More specifically, certain amino acids, such as leucine, have been shown to have a significant impact on muscle synthesis. The Atkins diet encourages the consumption of protein sources rich in leucine to optimize muscle preservation.
- In addition to its muscle-preserving properties, protein also promotes satiety, helping individuals feel full and satisfied for longer periods. This can be beneficial for adhering to the Atkins diet and maintaining overall caloric intake.
- It’s important to note that the exact amount of protein required may vary depending on individual factors such as age, gender, activity level, and overall health. Consulting with a healthcare professional or nutritionist can help determine the optimal protein intake for each person.
Overall, understanding the relationship between protein intake and muscle preservation is crucial when following the Atkins diet. By ensuring an adequate supply of protein, individuals can support their muscle mass while reaping the many health benefits associated with this low-carb approach to eating.
Questions and answers
What is the Atkins Diet?
The Atkins Diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet that aims to induce weight loss by forcing the body into a state of ketosis.
How does the Atkins Diet work?
The Atkins Diet works by restricting carbohydrate intake, which causes the body to burn fat for fuel instead of carbohydrates, leading to weight loss.
What are the health benefits of the Atkins Diet?
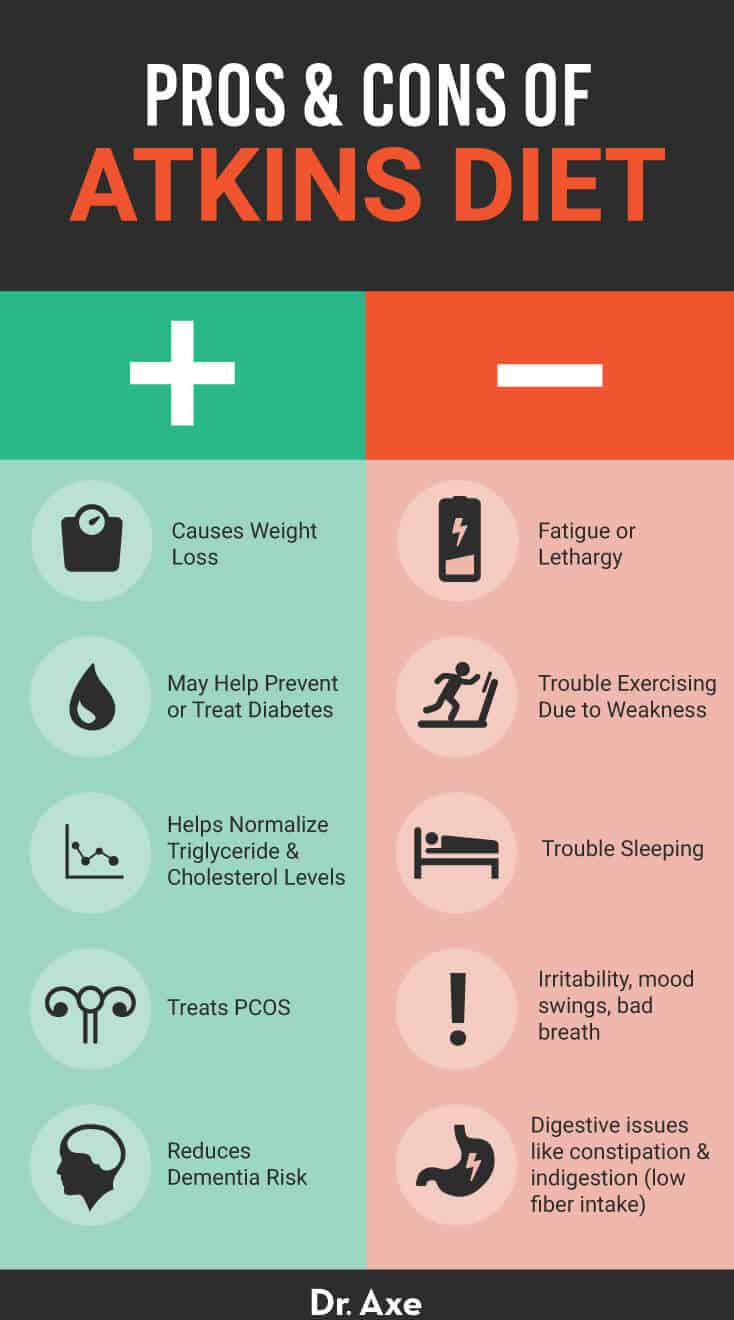
The Atkins Diet has been shown to promote weight loss, improve blood sugar control, and lower triglyceride levels. It may also decrease the risk of heart disease and improve mental health.
Is the Atkins Diet safe?
The Atkins Diet is generally considered safe for most healthy individuals. However, it may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions. It is always recommended to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any diet plan.
What are some foods allowed on the Atkins Diet?
Foods allowed on the Atkins Diet include meat, fish, eggs, non-starchy vegetables, full-fat dairy products, nuts, and seeds. Foods high in carbohydrates, such as grains, legumes, and sugary snacks, should be avoided or limited.

I’m Jake Morgan, a 23-year-old Keto diet and fitness expert from sunny California. Passionate about helping you achieve your dream body with the right nutrition and workout. Connect or consult via Telegram.