- The Unavoidable Influence of Unwholesome Nourishment on One’s Well-being: Comprehending the Detrimental Consequences
- The Adverse Effects of Unhealthy Food on Physical Well-being
- Dietary Habits and their Impact on Overall Health
- Understanding the Relationship between Food Choices and Well-being
- The Role of Unhealthy Food in the Development of Chronic Diseases
- Effects of Poor Nutrition on the Body’s Immune System
- Obesity Epidemic: Unhealthy Food as a Major Contributor
- The Link between Processed Food Consumption and Weight Gain
- The Influence of High-Fat and Sugar-Rich Diets on Obesity Rates
- How Unhealthy Food Marketing Contributes to the Growing Obesity Problem
- Cardiovascular Health: The Hidden Danger of Unhealthy Food
- Questions and answers
The Unavoidable Influence of Unwholesome Nourishment on One’s Well-being: Comprehending the Detrimental Consequences
In today’s fast-paced and modern society, the impact of unhealthy sustenance on an individual’s physical well-being is an indisputable reality. The choices we make when it comes to the nourishment we consume have far-reaching implications for our overall health. The profound effects of inadequate nutrition extend beyond mere dietary preferences and exert a powerful sway over our bodies, influencing our vitality, strength, and resilience.
It is imperative to acknowledge the significance of comprehending the harmful repercussions of consuming unsound food. This knowledge is instrumental in empowering individuals to make informed decisions and embrace a healthier lifestyle. By understanding the profound implications of unwholesome nutrition, individuals can be motivated to take charge of their well-being and seek a balanced diet that nurtures their bodies and enhances their physical capabilities.
The consequences of consuming nutrition devoid of essential nutrients and laden with harmful additives are manifold and alarming. The detrimental effects encompass not only physical well-being but also impact mental agility and emotional stability. Regular intake of unhealthful fare can lead to a host of chronic illnesses such as diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and obesity, which can severely diminish one’s quality of life.
Moreover, a closer examination reveals that the consequences extend beyond personal well-being to encompass socio-economic factors. The burden on healthcare systems and economies due to the health issues arising from unhealthy sustenance is substantial. The need for preventive measures and awareness campaigns to combat the adverse effects of unwholesome nourishment is growing urgent, requiring concerted efforts from individuals, communities, and institutions.
The Adverse Effects of Unhealthy Food on Physical Well-being
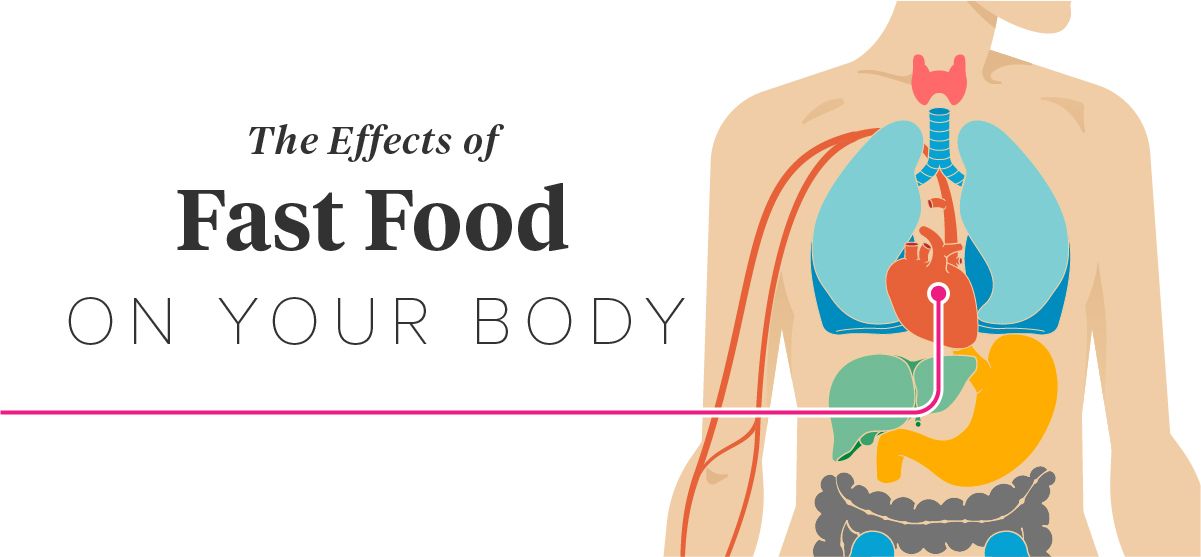
Poor dietary choices and inadequate nutrition can have detrimental consequences on an individual’s overall physical well-being.
When individuals consume food that lacks essential nutrients, their bodies may experience negative effects that can impact their overall health. Consuming an imbalanced diet can result in an array of health issues, including weight gain or obesity, increased risk of chronic diseases, and compromised immune function. Moreover, unhealthy food choices may lead to a higher chance of developing cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and other related health conditions. It is therefore crucial to understand the detrimental effects that unhealthy food can have on one’s physical well-being.
Weight gain or obesity is a common consequence of regularly consuming unhealthy food. Processed and high-calorie foods often contain excessive amounts of sugar, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives, contributing to weight gain. A sedentary lifestyle combined with a poor diet further exacerbates this issue. Obesity can lead to various health complications, such as heart disease, diabetes, arthritis, and even certain types of cancer, significantly affecting an individual’s physical well-being.
The consumption of unhealthy food increases the risk of chronic diseases. Foods that are high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium can raise blood pressure, leading to hypertension and increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Additionally, a diet lacking in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains reduces the intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, which are crucial for maintaining a healthy body and preventing chronic diseases.
Unhealthy food choices can compromise immune function. A diet lacking in essential nutrients weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and illnesses. Consuming processed foods, sugary snacks, and beverages can suppress immune responses, hindering the body’s ability to fight off diseases effectively. This compromises an individual’s physical well-being and may lead to a higher risk of contracting various illnesses.
By understanding the adverse effects of unhealthy food on physical well-being, individuals can make informed choices to support their overall health. Prioritizing a balanced diet, rich in nutrients, and avoiding the consumption of processed and unhealthy foods can significantly improve physical well-being and reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases. It is important that individuals take responsibility for their dietary choices and prioritize their health by opting for nutritious and wholesome foods.
Dietary Habits and their Impact on Overall Health
In the realm of physical well-being, our eating choices possess a substantial influence on our overall health. The manner in which we consume sustenance and the dietary patterns we develop have far-reaching consequences that cannot be undermined or denied. An individual’s nutritional habits have the potential to profoundly affect their various bodily systems, vitality, and general wellness.
Indeed, the dietary practices we adopt can either fortify or undermine our overall health. Our eating habits encompass not only the types and quantities of food we consume but also the frequency and manner in which we partake of them. The decisions we make regarding our diet have the potential to shape the functioning of our organs, tissues, and cells, ultimately dictating our energy levels, immunity, and susceptibility to various ailments.
A conscious effort to establish and maintain a healthful nutrient intake can yield significant benefits. Selecting and consuming a wide variety of nutrient-dense foods allows us to obtain the essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants necessary for optimal physiological functioning. Conversely, an overreliance on nutritionally deficient options high in unhealthy fats, refined sugars, and processed ingredients can lead to a plethora of health issues, ranging from obesity and cardiovascular problems to weakened immune systems and digestive disorders.
Furthermore, our dietary habits can contribute to the development of chronic conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension, and certain types of cancer. The excessive consumption of sugary beverages, fast food, and highly processed snacks not only provides an abundance of empty calories but also disrupts critical metabolic processes, exacerbating the risk of various illnesses.
It is imperative to recognize that our dietary choices are not isolated occurrences but rather cumulative actions that mold our overall health and well-being. By cultivating mindful and conscious eating habits, we can optimize our physical vitality, enhance our immune function, and reduce the likelihood of developing chronic diseases. Embracing a balanced and nutrient-rich diet is an investment in our long-term health, empowering us to lead vibrant and fulfilling lives.
Understanding the Relationship between Food Choices and Well-being

Exploring the intricate connection between the selections we make regarding our nourishment and our overall state of well-being reveals a compelling narrative. The decisions we make in relation to our daily sustenance possess a profound influence on our physical and mental health, actively shaping our bodies and minds in ways that are both subtle and substantial.
Profound influence
The choices we make regarding the foods we consume each day wield a deep-seated impact on our well-being. These choices, ranging from the types of nutrients we prioritize to the way we approach our meals, hold the power to shape the trajectory of our physical and mental health. As we consciously select or unconsciously succumb to certain food choices, we actively mold our bodies and minds, thereby influencing our overall state of being.
Subtle and substantial
The effects of our food choices extend beyond the bounds of the physical body, infiltrating the realms of cognition and emotional stability. While the consequences of unhealthy food on physical health are clearly evident, the impact on mental well-being is equally undeniable. Nutritional deficiencies and imbalances can disrupt brain function, leading to mood swings, reduced cognitive abilities, and even mental disorders. In contrast, a diet rich in essential nutrients can foster optimal brain health, promoting clarity, focus, and emotional equilibrium.
A delicate balance
Understanding the relationship between food choices and well-being necessitates an examination of the delicate equilibrium that exists within our bodies. It is crucial to recognize that an excess or deficiency of certain nutrients can tip this balance, leading to detrimental consequences for both our physical and mental health. Striving for a diverse and balanced diet that encompasses a range of essential nutrients can ultimately foster a harmonious relationship between our food choices and our overall well-being.
An empowering journey
Embarking on the quest to comprehend and optimize the relationship between food choices and well-being is an empowering journey. By cultivating an awareness of the ways in which our nourishment impacts our physical and mental health, we are equipped with the knowledge and agency to make informed decisions. This newfound understanding enables us to nourish our bodies and minds with intention, fostering a state of well-being that resonates deeply from within.
The Role of Unhealthy Food in the Development of Chronic Diseases
In the context of our discussion on the detrimental effects of unhealthy dietary choices, it is crucial to delve into the significant role that such food plays in the onset and progression of chronic diseases. By exploring the intricate relationship between unhealthy food consumption and the development of these long-term health conditions, we can gain a better understanding of the grave consequences that stem from poor dietary habits.
Diminishing the quality of one’s diet by frequently consuming food that lacks essential nutrients and is abundant in harmful substances poses a grave risk to long-term health. The consistent intake of unhealthy food, characterized by excessive levels of saturated fats, added sugars, and refined carbohydrates, contributes to the development of chronic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular ailments, and certain forms of cancer. These diseases are pervasive and prevalent in our society today, presenting a significant challenge to the overall well-being and longevity of individuals.
It is important to recognize that the root cause of chronic diseases often lies in dietary patterns that prioritize convenience and indulgence over nutrition and balance. The modern lifestyles and food environments that thrive on processed, fast food options have fostered a culture where cheap, easily accessible, and calorie-dense meals have become the norm. This dietary shift has led to a surge in chronic diseases, warranting urgent attention and a proactive approach in addressing the critical connection between diet and health.
Unhealthy food not only contributes to the development of chronic diseases but also exacerbates their progression and complicates their management. The detrimental effects of a poor diet extend beyond initial disease onset, as they can worsen symptoms, hinder treatment efficacy, and increase the risk of complications. For instance, individuals diagnosed with diabetes who consistently consume high-sugar, high-fat foods face greater challenges in controlling their blood sugar levels, leading to a heightened risk of long-term complications such as kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems.
In conclusion, a strong correlation exists between the consumption of unhealthy food and the development of chronic diseases. By acknowledging the pivotal role of nutrition in disease prevention and management, we can empower individuals, healthcare professionals, and policymakers to prioritize healthier dietary choices, implement effective interventions, and strive for widespread change in order to curb the burden of chronic diseases on society.
Effects of Poor Nutrition on the Body’s Immune System
Impact of inadequate nourishment on the body’s defensive mechanism
Poor nutrition and unhealthy dietary choices can have a detrimental effect on the body’s immune system. When an individual lacks essential nutrients and consumes an imbalanced diet, the body’s ability to defend against pathogens and prevent infections is compromised. This compromises the immune system’s ability to function optimally, leaving the body more susceptible to illnesses and diseases.
| Decreased production of immune cells | Increased susceptibility to infections |
|---|---|
| Insufficient intake of vital nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can lead to a decrease in the production of immune cells, including white blood cells. | The compromised immune system is unable to effectively fight off invading pathogens, making individuals more prone to developing infections and illnesses. |
| Reduced function of immune cells | Delayed wound healing |
| Poor nutrition negatively affects the functionality of immune cells, impairing their ability to recognize and destroy harmful substances. | Inadequate nutrition can impact the body’s ability to heal wounds efficiently, as the immune system’s response and tissue regeneration are compromised. |
| Increased inflammation | Higher risk of chronic diseases |
| A diet lacking in essential nutrients can trigger chronic low-grade inflammation, which can lead to various health problems. | Poor nutrition contributes to the development of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and certain types of cancer. |
In conclusion, the effects of poor nutrition on the body’s immune system are undeniable. A balanced and nutritious diet is crucial to support a strong and functional immune system, preventing the onset of diseases and maintaining overall health.
Obesity Epidemic: Unhealthy Food as a Major Contributor
In recent years, the prevalence of obesity has reached unprecedented levels, leading health experts to declare it a global epidemic. Although many factors contribute to obesity, a critical element is the excessive intake of unhealthy food options. The abundance of high-calorie, low-nutrient foods has become easily accessible and appealing to individuals of all ages, leading to the adoption of poor dietary habits.
Unhealthy food plays a prominent role in fueling weight gain and the development of obesity. It is evident that the consumption of foods high in saturated fats, added sugars, and sodium not only impairs physical health but also contributes to the accumulation of excess body fat. Furthermore, the lack of essential nutrients found in unhealthy food options can lead to various health issues, such as cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
Moreover, the addictive nature of many unhealthy food products exacerbates the obesity problem. Highly processed foods often contain additives and preservatives that can alter brain chemistry and trigger an addictive response, leading individuals to consume these foods in excessive quantities. The cycle of craving and indulgence further perpetuates poor eating habits and increases the likelihood of weight gain.
Addressing the obesity epidemic requires a comprehensive approach, with an emphasis on reducing the consumption of unhealthy foods. Educating individuals about the harmful effects of these food choices and promoting healthier alternatives is crucial in combating this growing health crisis. By empowering individuals to make informed choices and adopting well-balanced, nutritious diets, we can begin to reverse the devastating impact of unhealthy food on physical health and promote a healthier future for generations to come.
The Link between Processed Food Consumption and Weight Gain
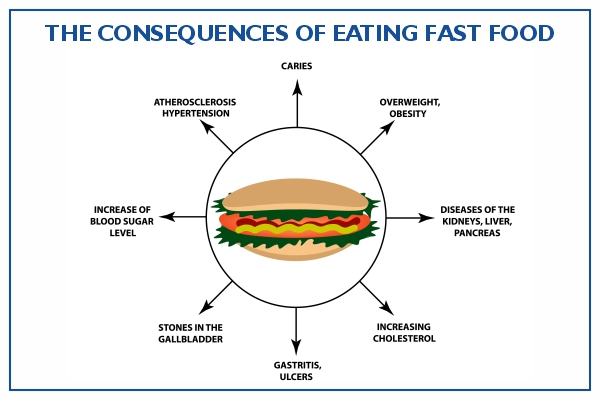
Processed food consumption has long been associated with an increase in body weight. The excessive intake of processed foods has been linked to weight gain and obesity, as these foods are typically high in calories, unhealthy fats, sugar, and sodium. The consumption of processed foods can lead to an imbalance in nutrient intake and disrupt the body’s natural ability to regulate weight.
One of the main factors contributing to weight gain from processed food consumption is the high calorie content. Processed foods are often highly processed and contain added sugars, which can significantly increase the calorie content of a meal or snack. Additionally, these foods are often low in fiber and protein, which are essential for promoting feelings of satiety and regulating hunger. This lack of satiety can lead to overeating and ultimately result in weight gain over time.
Furthermore, processed foods are usually high in unhealthy fats, such as trans fats and saturated fats. These fats have been linked to an increased risk of obesity, cardiovascular disease, and other health problems. The excessive consumption of unhealthy fats can also lead to the accumulation of visceral fat, which is stored around the organs and has been associated with a higher risk of various health conditions, including diabetes and certain types of cancer.
In addition to their calorie and fat content, processed foods are often loaded with added sugars and high amounts of sodium. Sugar-sweetened beverages and sugary snacks, which are commonly consumed as part of a processed food diet, can contribute significantly to weight gain. Excessive sugar intake can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels, followed by crashes that can trigger cravings for more sugary foods. Similarly, a high sodium intake can contribute to water retention and bloating, further exacerbating weight gain.
To mitigate the risks associated with processed food consumption and weight gain, it is essential to prioritize a diet consisting mainly of whole, unprocessed foods. Choosing fresh fruits and vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats can provide the body with the necessary nutrients while promoting satiety and aiding weight management. Limiting the intake of processed foods and being mindful of portion sizes can also contribute to maintaining a healthy weight and overall well-being.
- Processed food consumption has been linked to weight gain and obesity.
- The high calorie content of processed foods can contribute to weight gain.
- Unhealthy fats found in processed foods can lead to an increased risk of obesity and other health problems.
- Added sugars and sodium in processed foods contribute to weight gain.
- Eating a diet consisting mainly of whole, unprocessed foods can help prevent weight gain.
The Influence of High-Fat and Sugar-Rich Diets on Obesity Rates
Understanding the impact of diets high in fat and sugar on obesity rates is a crucial aspect of comprehending the detrimental effects of unhealthy food choices on physical well-being. Consumption of diets rich in high levels of fat and sugar has an undeniable association with the rise in obesity rates observed globally. This section aims to delve into the influence of such dietary patterns on the prevalence of obesity and shed light on the alarming consequences that ensue.
How Unhealthy Food Marketing Contributes to the Growing Obesity Problem
Marketing practices employed by the food industry play a significant role in the alarming rise of obesity rates. Through strategic advertising techniques and persuasive messages, the promotion of unhealthy food products has become pervasive in our society. This section will delve into the detrimental effects of such marketing tactics and how they contribute to the escalating obesity problem.
- 1. Misleading Claims: Food advertisements often make use of exaggerated claims and misleading information to convince consumers that their products are healthier than they actually are. This misrepresentation leads individuals to believe that consuming these foods will not negatively impact their health, ultimately contributing to their overconsumption and weight gain.
- 2. Targeting Vulnerable Populations: Unhealthy food marketing is particularly effective at targeting vulnerable populations, such as children and low-income individuals. Companies utilize appealing advertisements, characters, and promotions to entice these demographics into consuming unhealthy foods regularly, further exacerbating the obesity problem among these groups.
- 3. Availability and Accessibility: The widespread marketing and promotion of unhealthy food products make them easily accessible to consumers. Their presence in supermarkets, convenience stores, and fast-food chains ensures that individuals are constantly exposed to these options, leading to increased consumption and subsequent weight gain.
- 4. Emotional Manipulation: Advertisements often manipulate consumers’ emotions, linking the consumption of unhealthy foods to feelings of happiness, comfort, and fulfillment. This psychological association compels individuals to seek these foods as a means of emotional gratification, regardless of their detrimental impact on their physical health.
- 5. Influence on Consumption Patterns: Continuous exposure to unhealthy food marketing significantly influences individuals’ consumption patterns. It normalizes the consumption of these foods, making them seem like the default choice, while healthier options take a backseat. This shift in consumption patterns directly contributes to the growing obesity problem.
In conclusion, the rampant promotion of unhealthy food through various marketing tactics has substantial implications for the rising obesity rates. Misleading claims, targeting vulnerable populations, ease of accessibility, emotional manipulation, and altered consumption patterns all work together to perpetuate this growing public health concern. Recognizing and addressing the harmful effects of unhealthy food marketing is crucial in combatting the obesity problem and promoting overall well-being.
Cardiovascular Health: The Hidden Danger of Unhealthy Food
Food choices can have an insidious impact on our well-being, often imperceptible yet incredibly damaging. One area that is particularly affected by poor dietary decisions is cardiovascular health. The hidden danger of indulging in unhealthy food can manifest itself in various detrimental effects on the heart and blood vessels.
|
One of the primary concerns when it comes to cardiovascular well-being is the heightened risk of developing arterial plaque. This condition occurs as a result of an unhealthy diet rich in saturated fats, refined sugars, and high cholesterol content. These harmful substances infiltrate our bloodstream and gradually accumulate within our arteries, forming a thick, sticky buildup that obstructs blood flow. Such blockages can lead to heart attacks, stroke, and other life-threatening cardiovascular conditions. |
|
Furthermore, consuming excessive amounts of unhealthy food can contribute to high blood pressure. Salty and processed foods are notorious for their sodium content, which disrupts the delicate balance of our body’s fluids. This disruption causes our blood vessels to narrow, putting additional strain on the heart as it tries to pump blood through the constricted pathways. Over time, this constant stress on the cardiovascular system can lead to hypertension and increase the likelihood of heart disease. |
|
Additionally, unhealthy food choices can negatively impact cholesterol levels. Diets high in trans fats, found in fried and processed foods, can raise low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as bad cholesterol. Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol can contribute to the formation of plaques in the arteries, further obstructing blood flow and increasing the risk of developing cardiovascular issues. |
|
In conclusion, it is critical to understand the hidden dangers that unhealthy food poses to cardiovascular health. The consequences of indulging in such food choices can be severe, leading to arterial plaque, high blood pressure, and unfavorable cholesterol levels. By making conscious dietary decisions and opting for nutritious alternatives, individuals can safeguard their cardiovascular well-being and reduce the risk of experiencing serious health complications. |
Questions and answers
How does unhealthy food affect our physical health?
Unhealthy food has several detrimental effects on our physical health. It can lead to weight gain and obesity, increase the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease, weaken the immune system, and negatively impact our energy levels and overall vitality.
What are the specific harmful effects of consuming excessive sugar?
Consuming excessive sugar through unhealthy food can have numerous harmful effects. It can cause weight gain, increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, contribute to tooth decay, raise the risk of heart disease, and negatively impact liver health.
What are some long-term consequences of regularly consuming fast food?
Regularly consuming fast food can have severe long-term consequences on physical health. It increases the risk of obesity, leads to higher cholesterol levels, raises blood pressure, contributes to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, and increases the likelihood of developing heart disease or stroke.
Can eating unhealthy food affect mental health as well?
Yes, the impact of unhealthy food is not limited to physical health alone. Eating unhealthy food has been linked to an increased risk of mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and decreased cognitive function. The lack of essential nutrients in unhealthy food can negatively affect brain health and overall mental well-being.
What steps can be taken to reduce the consumption of unhealthy food and improve physical health?
To reduce the consumption of unhealthy food and improve physical health, several steps can be taken. These include incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into the diet, avoiding processed and sugary foods, cooking at home more often, reading food labels, practicing portion control, and engaging in regular physical exercise.
What are some examples of unhealthy foods?
Examples of unhealthy foods include fast food, processed snacks, sugary drinks, fried foods, and desserts high in fat and sugar.
How does unhealthy food affect our physical health?
Unhealthy food can negatively impact physical health in various ways. Consuming excessive unhealthy food can lead to weight gain, increase the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. It can also result in nutrient deficiencies and weaken the immune system.
What are the harmful effects of consuming too much sugar?
Consuming excessive amounts of sugar can have several harmful effects on the body. It can contribute to weight gain and obesity, increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, lead to tooth decay, cause inflammation in the body, and elevate the risk of heart diseases.
Is it possible to have a balanced diet while occasionally consuming unhealthy food?
While occasional consumption of unhealthy food is not detrimental, it is important to maintain a balanced diet to ensure proper nutrition. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in the diet can help offset the negative effects of occasional unhealthy food consumption.
Can unhealthy food consumption have an impact on mental health as well?
Yes, unhealthy food consumption can have an impact on mental health. Research suggests that diets high in processed and sugary foods can increase the risk of developing mental health disorders such as depression and anxiety. Unhealthy food consumption may also affect mood, cognitive function, and overall well-being.